Pancreas: Acute Pancreatitis
Acute Pancreatitis
Pathogenesis
- Acute Inflammation of the Pancreas
Causes Mn
- Gallstones (Most Common) – 40-70%
- Alcohol (Second Most Common) – 25-35%
- Post-ERCP
- Hypertriglyceridemia & Hypercalcemia
- Genetic or Autoimmune
- Trauma
- Medications
- Infection
- Idiopathic
Presentation
- Symptoms:
- Epigastric Pain Radiating to the Back
- Nausea/Vomiting
- Fever
- Complications:
- Acute Pancreatic Fluid Collection
- Pancreatic Pseudocyst
- Necrosis
- Infection
- Organ Failure
- Pseudoaneurysm
- Portosplenomesenteric Venous Thrombosis (PSMVT) If Necrotizing
- Most Common Causes of Death:
- Early (< 2 Weeks): SIRS & Organ Failure
- Late (> 2 Weeks): Sepsis
Revised Atlanta Classification
- CT Criteria of Fluid Collections Seen After Acute Pancreatitis
| Timing | Fluid Density | Wall | |
| Acute Pancreatic Fluid Collection | ≤ 4 Weeks | Homogenous | No Defined |
| Pancreatic Pseudocyst | > 4 Weeks | Homogenous | Well Defined |
| Acute Necrotic Collection | ≤ 4 Weeks | Heterogenous | No Defined |
| Walled-Off Pancreatic Necrosis | > 4 Weeks | Heterogenous | Well Defined |
- Term “Pancreatic Abscess” No Longer Used
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis Requires ≥ 2 Of:
- Acute Persistent Severe Epigastric Pain
- Elevated Lipase/Amylase ≥ 3x Normal
- CT Characteristic
Severity Classification
- Mild: No Local/Systemic Complications or Organ Failure
- Moderate: Local/Systemic Complications or Organ Failure < 48 Hours
- Severe: Persistent Organ Failure > 48 Hours
Treatment
- Initial Treatment: Medical (Aggressive IV Fluids & NPO)
- Considerations:
- Early Refeeding (≤ 48 Hours) if Stable & Tolerating Diet
- If Not Tolerating Oral Diet: Give Enteral Nutrition Through Jejunal Feeding Tube
- *Old Dogma to Give TPN and Avoid Enteral Nutrition Disproven – Increased Mortality
- Give ABX Only if There is Concern for Infection
- *Prophylactic ABX Are Not Recommended Regardless of Severity or Necrosis
- Early Refeeding (≤ 48 Hours) if Stable & Tolerating Diet
- Gallstone Pancreatitis:
- 25-30% Risk of Recurrence within 6-18 Weeks
- All Should Undergo Elective Cholecystectomy During the Same Admission
- Mild-Moderate Pancreatitis: Early (< 48 Hours) OK
- Severe Pancreatitis: Wait Until Resolved
- Cholangitis or Signs of Clear Obstruction: ERCP & Sphincterotomy
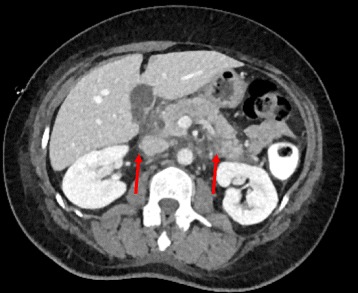
Acute Pancreatitis 1
Acute Pancreatitis – Prognostic Criteria
BISAP (Bedside Index for Severity in Acute Pancreatitis)
- BUN > 25
- Impaired Mentation
- SIRS ≥ 2
- Age > 65
- Pleural Effusion
Ranson Criteria Mn
- Admission:
- Glucose > 200
- Age > 55
- LDH > 250
- AST > 250
- WBC > 16,000
- Within 48 Hours:
- Ca < 8
- Hct Drop > 10%
- O2 < 60 Arterial
- BUN > 5 Increase
- Base Deficit > 4
- Sequestration of Fluids > 6 L Needed
Mnemonics
Causes of Acute Pancreatitis
- “I GET SMASHED”
- Idiopathic
- Gallstones
- Ethanol
- Trauma
- Steroids
- Mumps
- Autoimmune
- Scorpion Stings
- High Ca/TG
- ERCP
- Drugs
Ranson Criteria
- Admission Criteria: “GA LAW”
- Glucose > 200
- Age > 55
- LDH > 250
- AST > 250
- WBC > 16,000
- 48 Hour Criteria: “Calvin & HOBBS”
- Ca < 8
- Hct Drop > 10%
- O2 < 60 Arterial
- BUN > 5 Increase
- Base Deficit > 4
- Sequestration of Fluids > 6 L Needed
References
- Bédat B, Scarpa CR, Sadowski SM, Triponez F, Karenovics W. Acute pancreatitis after thoracic duct ligation for iatrogenic chylothorax. A case report. BMC Surg. 2017 Jan 23;17(1):9. (License: CC BY-4.0)