Endocrine: Adrenal Anatomy & Physiology
Adrenal Anatomy
Structure
- Adrenal Cortex
- Embryologic Origin: Mesoderm
- No Innervation
- Adrenal Medulla
- Embryologic Origin: Ectoderm
- Innervated by Sympathetic Splanchnic Nerves
- Secretes: Catecholamines (Epinephrine, Norepinephrine & Dopamine)
- Extraadrenal Sites:
- Usually in Retroperitoneum
- Most Common Site: Organ of Zuckerkandl
- At Aortic Bifurcation
- Gerota’s Fascia
- Encapsulates Kidney & Adrenal Glands

Adrenal Gland 1
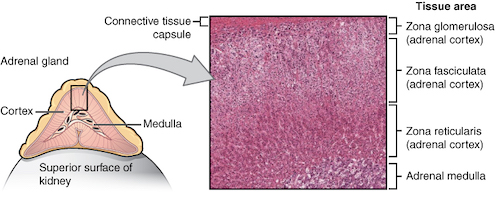
Adrenal Cortex Layers Mn
- Zona Glomerulosa
- Outer Layer
- Secretes Aldosterone
- Zona Fasciculata
- Middle Layer (Widest Zone)
- Secretes Glucocorticoids (Cortisol)
- Zona Reticularis
- Inner Layer
- Secretes Androgens/Estrogens
Adrenal Gland Layers 2
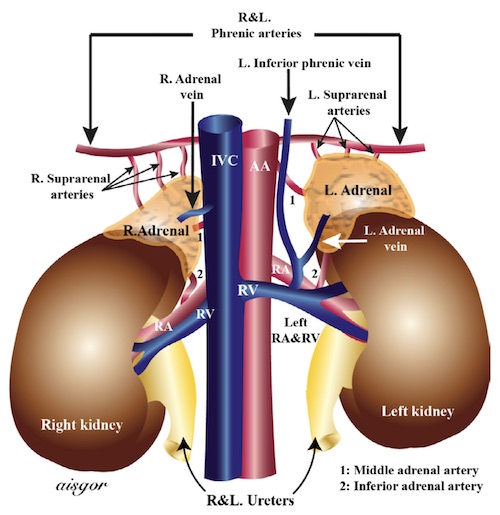
Vascular Supply
- Arterial Supply – More Variable
- Superior Adrenal Artery – From the Inferior Phrenic Artery
- Middle Adrenal Artery – From the Aorta
- Inferior Adrenal Artery – From the Renal Artery
- Venous Drainage – Generally Constant
- Left Adrenal Vein – Drains into the Left Renal Vein
- Right Adrenal Vein – Drains into the IVC
Lymphatic Drainage
- Subdiaphragmatic & Renal Lymph Nodes
Adrenal Vasculature 3
Adrenal Hormones
Aldosterone
- Mineralocorticoid Hormone
- Secreted by Adrenal Cortex – Zona Glomerulosa
- Stimulated By: Hyperkalemia (Strongest), Angiotensin II & ACTH (Minimally)
- RAAS (Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System)
- Function: Increased BP, Hypernatremia, Hypokalemia & Metabolic Alkalosis
- Directly Upregulates Na/K-ATPase in Kidney (Distal Tubule & Collecting Duct)
- Increases Sodium Reabsorption & Potassium Secretion
- Increases Water Reabsorption
- Indirectly Causes Loss of Hydrogen Ions
- Increased Potassium Secretion Effects Alpha Intercalated Cells of Late Distal Tubule & Collecting Duct
- Potassium Ions Are Exchanged for Hydrogen Ions
- Directly Upregulates Na/K-ATPase in Kidney (Distal Tubule & Collecting Duct)
Glucocorticoids (Cortisol)
- Secreted by Adrenal Cortex – Zona Fasciculata
- Stimulated by: ACTH
- Steroidogenesis Derived from Cholesterol
- Functions:
- Increases Gluconeogenesis & Glycogenolysis
- Increases Inotropy & Chronotropy
- Increases Peripheral Vascular Resistance
- Immune Suppression
Catecholamines
- Secreted by Adrenal Medulla
- Stimulated by: Sympathetic Stimulation
- Hormone Synthesis:
- Amino Acid Conversion: Mn
- Tyrosine > L-DOPA > Dopamine > Norepinephrine > Epinephrine
- Enzymes: Mn
- Tyrosine Hydroxylase: Tyrosine > DOPA (Rate Limiting Step)
- DOPA-Decarboxylase: DOPA > Dopamine
- Dopamine-β-Hydroxylase: Dopamine > Norepinephrine
- Phenylethanolamine N-Methyltransferase (PNMT): Norepinephrine > Epinephrine
- Amino Acid Conversion: Mn
- Hormones:
- Epinephrine (85%)
- Norepinephrine (15%)
- Extraadrenal Sites of Synthesis Can Only Produce Norepinephrine, Not Epinephrine Because PNMT is Only Present in the Adrenal Medulla
- Break Down:
- Half-Life Only 2-3 Minutes
- Primary Enzymes of Degradation:
- Monoamine Oxidase (MAO)
- Catechol-O-Methyltransferase (COMT)
- Degradation Metabolites:
- Vanillylmandelic Acid (VMA)
- Homovanillic Acid (HVA)
- Metanephrine
- Metabolites are Secreted in the Urine
Sex Hormones
- Adrenal Cortex Produces a Small Amount of Testosterone & Estrogen
- Production is Usually Overshadowed by the Amount Produced in Testes & Ovaries

Adrenal Hormone Synthesis 4
Mnemonics
Layers of the Adrenal Cortex
- G.F.R.
- Zona Glomerulosa
- Zona Fasciculata
- Zona Reticularis
Hormone Production of the Adrenal Cortex
- “Salt, Sugar, Sex – The Deeper You Go the Sweeter it Gets”
- Zona Glomerulosa – Secretes Aldosterone
- Zona Fasciculata – Secretes Glucocorticoids (Cortisol)
- Zona Reticularis – Secretes Androgens/Estrogens
Catecholamine Amino Acid Conversion
- With the Fight-or-Flight Excitement “True Love Does Not Exist”
- T>L>D>N>E
- Tyrosine > L-DOPA > Dopamine > Norepinephrine > Epinephrine
Catecholamine Amino Acid Conversion – Enzymes
- Enzymes are Generally “-oxylase” of the Enzyme They Degrade
- Exception: PNMT
- Enzymes:
- Tyrosine Hydroxylase: Tyrosine > DOPA (Rate Limiting Step)
- DOPA-Decarboxylase: DOPA > Dopamine
- Dopamine-β-Hydroxylase: Dopamine > Norepinephrine
- Phenylethanolamine N-Methyltransferase (PNMT): Norepinephrine > Epinephrine
References
- Gray H. Anatomy of the Human Body (1918). Public Domain.
- OpenStax College. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-SA-3.0)
- Uludağ M, Aygün N, İşgör A. Surgical Indications and Techniques for Adrenalectomy. Sisli Etfal Hastan Tip Bul. 2020 Mar 24;54(1):8-22. (License: CC BY-NC-4.0)
- Colo M. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-SA-3.0)