Large Intestine: Appendectomy
Trocar Placement
Normal Placement
- Access: Hasson or Veress Needle
- 10 mm Port: Infraumbilical or Supraumbilical
- 5 mm Ports (x2): LLQ & Suprapubic
- *Some Elect for Two Left Sided Ports Instead to Avoid Bladder Injury
Placement In Pregnancy
- *Need to Avoid Gravid Uterus in Second & Third Trimesters
- First Trimester
- Normal Placement
- Second Trimester
- Access: Hasson (May Consider Veress at Subxiphoid or Left Costal Margin)
- 10 mm Port: Supraumbilical
- 5 mm Ports (x2): LLQ & RLQ
- Third Trimester
- Access: Hasson (Consider Veress Subxiphoid or Left Costal Margin)
- 10 mm Port: Supraumbilical
- 5 mm Ports (x2): Two Along Right Side
- RLQ, Right Mid-Abdomen, RUQ or Subxiphoid
- Also Consider Positioning in Full or Partial Left Lateral Decubitus During the Second/Third Trimesters
Basic Procedure
Laparoscopic Appendectomy
- Position Supine, Left-Arm Tucked, Left-Side Down & Trendelenburg
- Identify & Expose the Appendix Along its Length from Base to Tip
- Bluntly Create a Tunnel Through the Mesoappendix at the Base
- Staple Across the Mesoappendix Near the Appendix
- Grey Staple Load (2.0 mm) Preferred – White Staple Load (2.5 mm) Has Significantly Higher Risk of Postoperative Bleeding
- Staple Across the Base of the Appendix
- Remove Appendix Through an Endoscopic Bag
- Aspirate Overt Fluid but Avoid Peritoneal Irrigation (May Increase Risk of Abscess)
- Close the Port Sites
Open Appendectomy
- Incision Options:
- McBurney’s Incision – Oblique Following Skin Lines
- Center Incision at Site of Most Pain on Exam or at McBurney’s Point
- Rockey-Davis Incision – Transverse Incision
- If Converting from Laparoscopic: Low Midline Laparotomy (Connecting Periumbilical & Suprapubic Incisions
- McBurney’s Incision – Oblique Following Skin Lines
- Using a Muscle Splitting Technique Dissect Through the Abdominal Wall
- Locate the Ascending Colon/Cecum & Then Identify the Appendix
- Mobilize Appendix into the Opening
- Divide the Mesoappendix
- Divide the Appendix at its Base
- Close the Abdominal Wall & Incision
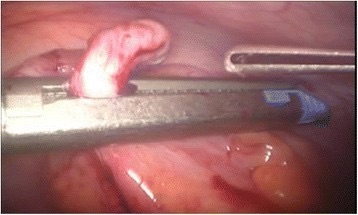
Laparoscopic Appendectomy 1
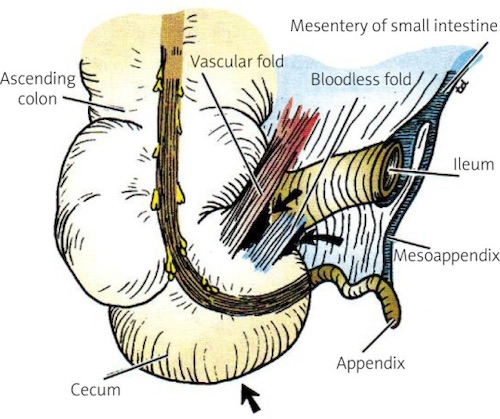
Appendix Anatomy 2
Complications
Surgical Site Infection
- Most Common Complication
- Laparoscopic Risk: 1.9-3.7%
- Open Risk: 4.3-7.0%
Intraabdominal Abscess
- Risk:
- Overall: 2-4%
- If Perforated: 6-10%
- Higher Rates in Laparoscopic Than Open Surgery
- Tx: Percutaneous Drainage
Stump Appendicitis
- Recurrent Appendicitis Due to Incomplete Appendectomy Leaving an Excessively Long Stump
- More Common After Perforation
- Tx: Stump Resection
- May Require Partial Cecectomy or Bowel Resection
Other Complications
- Bleeding/Hematoma (1%)
- Bowel Injury
- Incisional Hernia
References
- Strzałka M, Matyja M, Rembiasz K. Comparison of the results of laparoscopic appendectomies with application of different techniques for closure of the appendicular stump. World J Emerg Surg. 2016 Jan 6;11:4. (License: CC BY-4.0)
- Bakar SM, Shamim M, Alam GM, Sarwar M. Negative correlation between age of subjects and length of the appendix in Bangladeshi males. Arch Med Sci. 2013 Feb 21;9(1):55-67.(License: CC BY-NC-ND-3.0)