Vascular: Arterial Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS)
Definition
- Definition: Compression of Thoracic Outlet Neurovascular Bundle
Anatomy
Types
- Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
- Compression of the Brachial Plexus
- Most Common Type (95%)
- *See Cardiothoracic Surgery: Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
- Venous Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (Paget-von Schroetter Syndrome)
- Compression of the Subclavian Vein
- Accounts for 3% of TOS
- *See Vascular: Venous Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
- Arterial Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
- Compression of the Subclavian Artery
- Least Common Type (1%)
- Strongest Indication for Surgical Intervention
Arterial Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
Basics
- Cause: Compression of the Subclavian Artery
- Etiology: Almost All are Associated with Bone Abnormalities
- Cervical Rib (60% – Most Common)
- Anomalous First Rib (18%)
- Congenital Fibrocartilaginous Band (11-15%)
- Clavicle Fracture
- Most Common in Young Active Adults
Presentation
- Ischemic Hand Pain
- Arm Claudication
- Paresthesia
- Pallor
- Coldness
- Thrombosis
- Neck/Shoulder Symptoms Rare
Diagnosis
- Imaging:
- CT Angiography (CTA) – Generally Preferred
- Duplex Ultrasound
- Endovascular Arteriography – Gradually Being Replaced by CTA
- Compression Maneuvers for TOS: (Poor Accuracy)
- Adson’s Test: Decreased/Absent Radial Pulse with Ipsilateral Head Turn
- Costoclavicular Maneuver (Military Brace): Decreased/Absent Radial Pulse or Pain Reproduced by Passive Shoulder Depression & Retraction
- Wright Test (Halsted Maneuver/Hyperabduction Maneuver): Decreased Radial Pulse or Pain Reproduced by Shoulder Abduction > 90 Degrees
Scher Staging
- Stage 0: Asymptomatic Subclavian Artery Compression
- Stage 1: Stenosis of Subclavian Artery with Minor Post-Stenotic Dilation; No Intimal Disruption
- Stage 2: Subclavian Artery Aneurysm with Intimal Damage & Mural Thrombus
- Stage 3: Distal Embolization from Subclavian Artery Disease
Treatment
- Asymptomatic: Physical Therapy & Monitoring with Ultrasound
- Symptomatic: Surgical Decompression
- Indications:
- Symptomatic
- Asymptomatic with Arterial Disease (Aneurysmal Degeneration or Intimal Disruption)
- Surgery: First Rib Resection & Anterior Scalene Division
- May Require Cervical Rib Resection if Present
- May Require Artery Repair (Aneurysm Resection, Thromboembolectomy or Bypass Graft)
- Indications:
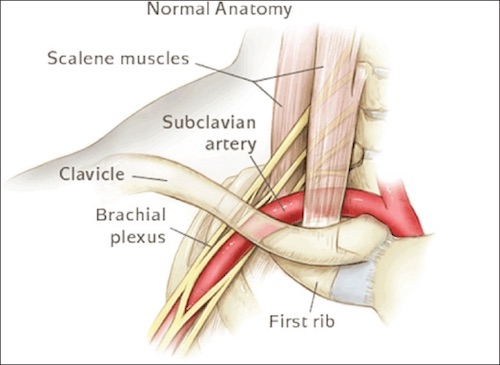
Thoracic Outlet – Arterial Anatomy 1
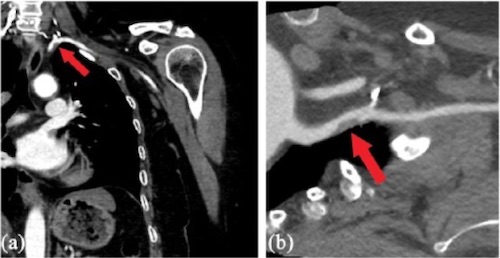
Arterial Thoracic Outlet Syndrome on CTA; Proximal Subclavian Artery Stenosis Due to a Prominent First Rib 2
References
- Khan A, Rattihalli RR, Hussain N, Sridhar A. Bilateral thoracic outlet syndrome: An uncommon presentation of a rare condition in children. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2012 Oct;15(4):323-5. (License: CC BY-NC-SA-3.0)
- Claus I, Van Bael K, Speybrouck S, Van Der Tempel G. Subclavian artery stenosis caused by a prominent first rib. SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2015 Apr 6;3:2050313X15578319. (License: CC BY-NC-3.0)