Vascular: Atherosclerosis (Arteriosclerosis)
Atherosclerosis (Arteriosclerosis)
Basics
- Plaque Formation in Arterial Walls
- Can Restrict Blood Flow Causing Ischemia
- Most Common Sites: Branch Points
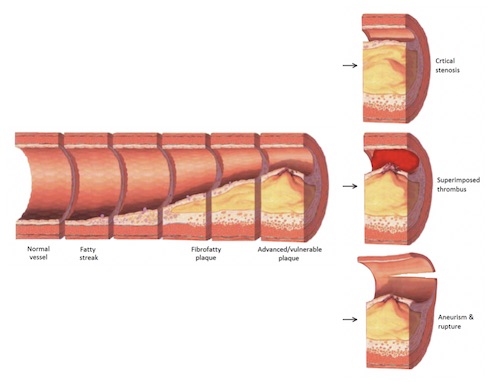
Stages of Atherogenesis
- Stage 1 (Initiation): Fatty Streak
- 1. Endothelial Dysfunction
- 2. Fatty Streak (Flat-Slightly Raised Yellow Discoloration) Formation within the Intima
- 3. Migration of Leukocytes & Smooth Muscle into the Vessel Wall
- 4. Foam Cell (Macrophages that Have Absorbed Lipids) Formation
- Primary Lipid: LDL
- Stage 2 (Adaptation): Plaque Progression
- Smooth Muscle Proliferation
- Extracellular Matrix Degradation with Wall Injury
- From Foam Cell Release of Growth Factors
- Stage 3 (Complication): Plaque/Intimal Disruption
- From Smooth Muscle Proliferation
- Exposed Collagen Leads to Thrombus
Atherosclerosis 1
Risk Factors
- Smoking
- Endothelial Dysfunction – Decreased Nitric Oxide & Increased Reactive-Oxygen Species
- Prothrombotic Environment – Promotes Platelet Aggregation & Increased Levels of vWF, Thrombin & Fibrin
- Promotes Inflammation – Increased Leukocytes, CRP, IL-6 & TNF-α
- Diabetes
- Hyperlipidemia
- Hypertension
- Familial Atherosclerosis
Complications
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
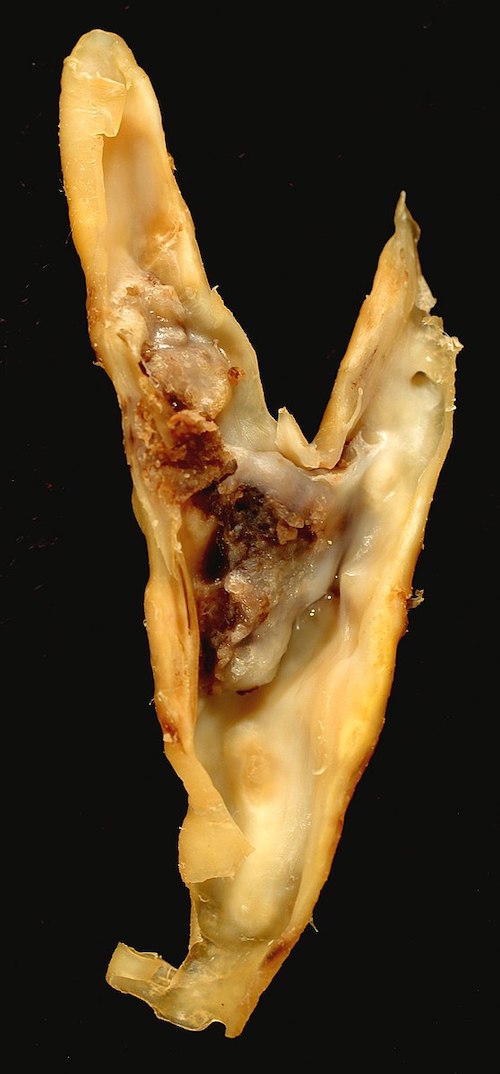
- Cerebral Vascular Disease/Carotid Stenosis
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
- Aneurysms
- Chronic Kidney Disease
Carotid Plaque 2
References
- Npatchett. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-SA-4.0)
- Uthman E. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-2.0)