Esophagus: Barrett’s Esophagus
Barrett’s Esophagus
Basics
- Definition: Normal Squamous Epithelium of Distal Esophagus Replaced by Metaplastic Columnar Epithelium with Goblet Cells
- Cause: Chronic Exposure to Gastric Acid from GERD
- Risk of Development in GERD: 6-15%
- 30-125x Increased Risk for Adenocarcinoma
Risk Factors
- Male
- Age > 50
- Caucasian
- Obese
- Tobacco
- Family History
Diagnosis
- Screening Indication: Male with Chronic (> 5 Years) or Frequent (≥ Weekly) GERD Symptoms with ≥ 2 Other Risk Factors
- Seattle Protocol for Endoscopic Evaluation: Need 4 Quadrant Bx Every 1-2 cm of Metaplasia
- Recommend Review by Two Separate Pathologists (High Variability Between Observers)
Prague Criteria
- Grading Criteria Used When Reporting Extent of Disease (i.e. C5M7)
- C Value: Circumferential Extent
- Endoscope Depth at GE Junction Minus Depth at the Proximal-Most Circumferential Extent
- M Value: Maximum Extent
- Endoscope Depth at GE Junction Minus Depth at the Proximal-Most Maximum Extent
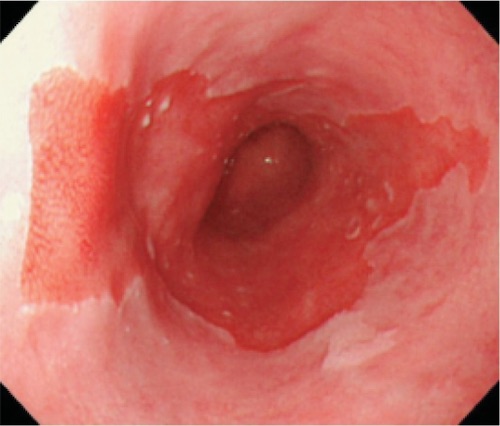
Barrett’s Esophagus 1
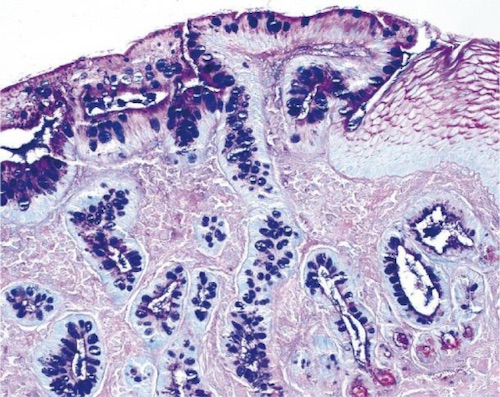
Columnar Metaplasia 2
Barrett’s Esophagus – Management
Surveillance Endoscopy Schedule
- No Dysplasia: Every 3-5 Years
- Indefinite for Dysplasia: Confirm At 3-6 Months, Then Every 12 Months
- Low-Grade Dysplasia: Every 6-12 Months
- High-Grade Dysplasia (If No Intervention): Every 3 Months
Indefinite for Dysplasia
- Primary Treatment: PPI & Surveillance Endoscopy
No Dysplasia
- Primary Treatment: PPI & Surveillance Endoscopy
- If Fails: Fundoplication
- Goal is to Prevent Symptoms & Further Metaplasia
- CA Risk Not Proven to Be Reversible
Low-Grade Dysplasia
- Primary Treatment: PPI & Surveillance Endoscopy
- If Persists: Fundoplication
- If Still Persists: Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)
High-Grade Dysplasia
- Primary Treatment: Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (Most Common) vs. Esophagectomy
- Indications for Esophagectomy:
- Patient Preference or Unable to Comply with Endoscopic Surveillance
- Large Lesion (> 2-3 cm)
- Multifocal
- Progression or Failed Ablation
- Impaired Esophageal Function
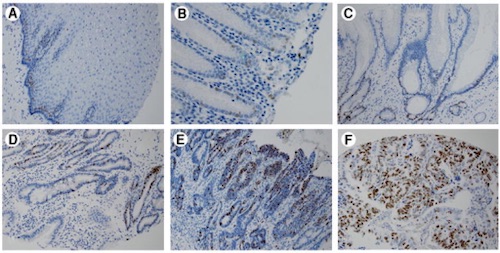
Immunohistochemical Analysis of Ki67 Expression: (A) Squamous Mucosa, (B) Columnar Metaplasia, (C) Barrett’s, (D) Low-Grade Dysplasia, (E) High-Grade Dysplasia, (F) Adenocarcinoma 3
References
- Japan Esophageal Society. Japanese Classification of Esophageal Cancer, 11th Edition: part I. Esophagus. 2017;14(1):1-36.(License: CC BY-4.0)
- Migaczewski M, Pędziwiatr M, Matłok M, Budzyński A. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication in the treatment of Barrett’s esophagus – 10 years of experience. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2013 Jun;8(2):139-45. (License: CC BY-NC-ND-3.0)
- Choy B, LaLonde A, Que J, Wu T, Zhou Z. MCM4 and MCM7, potential novel proliferation markers, significantly correlated with Ki-67, Bmi1, and cyclin E expression in esophageal adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and precancerous lesions. Hum Pathol. 2016 Nov;57:126-135.(License: CC BY-2.0)