Skin & Soft Tissue: Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
Basics
- Tumor from Epidermal Basal Epithelial Cells
- Most Common Skin Cancer (Over 4x Incidence of SCC)
- Most Common Malignancy in US
Risk Factors
- Cumulative Sun Exposure
- Fair Skinned
- Elderly
- Norther European Ancestry
- Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome (Gorlin Syndrome)
- PTCH1 Mutation
- Develops Dozens-Hundreds of BCC’s
- Also Associated with Bony Cysts, Medulloblastoma & Craniofacial Abnormalities
Presentation
- Appearance: Pearly & Rolled Borders
- Most Common Site: H&N
- Path: Peripheral Palisading Nuclei & Stromal Retraction
Types
- Nodular (80%)
- Most Common Type
- Most Common on Face
- Produces Pigment
- Superficial (15%)
- Most Common on Trunk
- Produces Pigment
- Morpheaform (5-10%)
- Flesh-Colored – Does Not Produce Pigment
- Produces Collagenase
- Most Aggressive
- Other Subtypes:
- Nonaggressive
- Keratotic
- Infundibulocystic
- Aggressive
- Micronodular
- Infiltrative
- Sclerosing
- Desmoplastic
- Basosquamous
- Nonaggressive
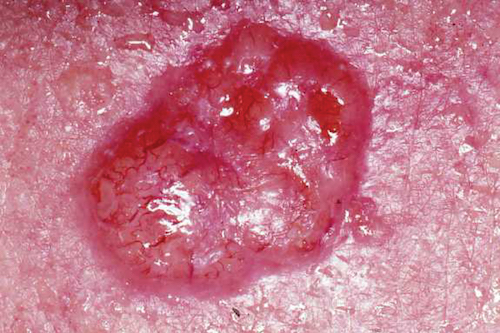
Basal Cell Carcinoma 1
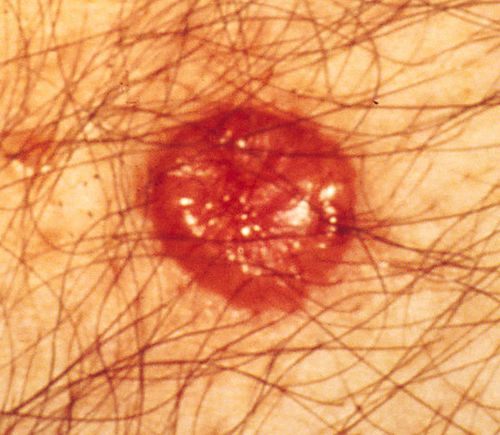
Basal Cell Carcinoma 2
Prognosis
- Generally Slow Growing
- Metastases are Rare
High-Risk Factors for Local Recurrence
- ≥ 2 cm on Trunk or Extremities
- ≥ 1 cm on Cheeks, Forehead, Scalp, Neck or Pretibial
- Any Size on Face, Genitalia, Hands or Feet
- Poorly Defined Borders
- Recurrence
- Immunosuppressed
- Site of Prior XRT
- Pathology:
- Aggressive Growth Pattern (Not Nodular or Superficial)
- Perineural Invasion
Treatment
- Tx: Excision (0.4 cm Margins)
- Consider Mohs Micrographic Surgery if High-Risk
- Positive Margins: Repeat Excision (With Wider Margins) or Mohs Micrographic Surgery
- Nodal or Distant Mets:
- Resection if Able
- Consider XRT
- Consider Hedgehog Pathway Inhibitors (Vismodegib or Sonidegib)
References
- Hendrix J. Wikimedia Commons. (License: Public Domain)
- National Cancer Institute. Wikimedia Commons. (License: Public Domain)