Trauma: Bladder Trauma
Bladder Trauma
General
- Most Common in Blunt Trauma
- 90% Associated with Pelvic Fractures
- Most Common Associated Fracture: Obturator Ring
AAST Bladder Injury Scale
- *See AAST
- Injury Scale is Under Copyright
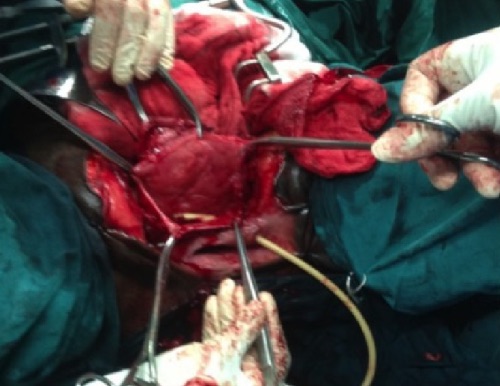
Bladder Trauma 1
Diagnosis
- Sx: Gross Hematuria (Very Reliable, 95-100%), Pain & Low Urine Output
- Dx: CT Cystography (Inject ≥ 300 cc Contrast Through Foley)
- Intraperitoneal Leak: Outlines Loops of Bowel or Fills Cul-De-Sac
- Extraperitoneal Leak: Flame or Starbursts
- If Conventional Cystography (XR Fluoroscopy) Must Obtain Post-Drainage Films
Treatment
- Extraperitoneal Rupture:
- Uncomplicated: Foley (7-14 Weeks)
- Complicated: Surgical Repair
- Indications:
- Open Pelvic Fracture with Bone Exposed in Bladder Lumen
- Concurrent Vaginal/Rectal Injury (Risk for Fistula)
- Bladder Neck Injury
- Persistent Hematuria/Clots (Will Obstruct Foley)
- Indications:
- Intraperitoneal Rupture: Surgical Repair & Foley
- Use Absorbable Sutures in 2 Layers (Permanent Irritate Mucosa & Are Lithogenic)
- Cystogram Every 7-10 Days to Evaluate for Foley Removal
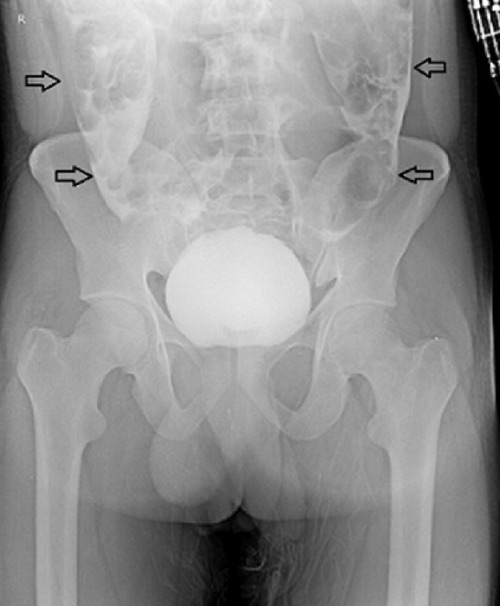
Intraperitoneal Bladder Injury 2
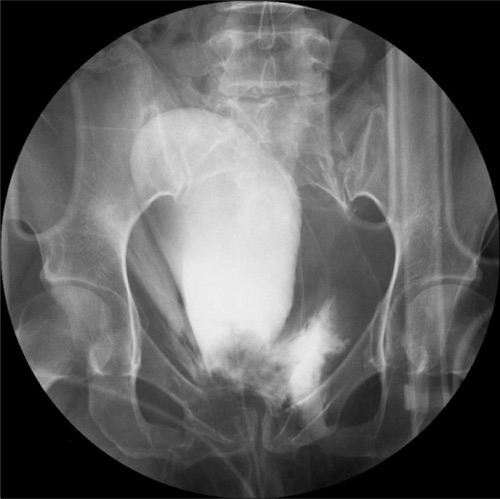
Extraperitoneal Bladder Injury 3
References
- Ojewola RW, Tijani KH, Badmus OO, Oliyide AE, Osegbe CE. Extraperitoneally Ruptured, Everted, and Prolapsed Bladder: A Very Rare Complication of Pelvic Injury. Case Rep Urol. 2015;2015:476043. (License: CC BY-3.0)
- Vagholkar K, Vagholkar S. Posttraumatic Haematuria with Pseudorenal Failure: A Diagnostic Lead for Intraperitoneal Bladder Rupture. Case Rep Emerg Med. 2016;2016:4521827. (License: CC BY-4.0)
- Kim JH, Ha YC, Kim TH, Myung SC, Moon YT, Kim KD, Chang IH. Delayed presentation of intravesical bone penetration after pelvic ring fracture. Korean J Urol. 2012 Dec;53(12):887-9. (License: CC BY-NC-3.0)

