Breast: Breast Cysts
Breast Cysts
Basics
- Definition: Benign Fluid-Filled Round Mass from the Terminal Duct Lobular Unit (TDLU)
- About 25% of Benign Breast Lesions
- Risk of Malignancy:
- Simple/Complicated: < 1%
- Complex: 1-23%
Classification
- Simple: Well Circumscribed Anechoic Lesions
- BI-RADS 2
- Complicated: Homogenous with Low-Level Internal Echoes without Solid Components, Thick Walls, Thick Septa or Vascular Flow
- BI-RADS 2-3
- Complex: Solid Components, Thick Walls, Thick Septa or Vascular Flow
- BI-RADS 4-5
Presentation
- Palpable Mass
- Pain/Discomfort
Diagnosis
- Primary Diagnostic Evaluation: US
- Mammogram or MRI Showing Cyst Should Be Followed Up with US
- Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA) May Be Considered for Simple/Complicated Cysts
- Shows Varying Color (Not Blood)
- Collapses with Aspiration
- Core Needle Biopsy is Required for Complex Cysts (BI-RADS 4-5)
Treatment
- Simple/Complicated Cysts: No Intervention Required
- Consider Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA) if Symptomatic, Inflamed or Infected
- Follow BI-RADS Recommendations as Appropriate
- Complex Cysts: Core Needle Biopsy to Evaluate for Malignancy
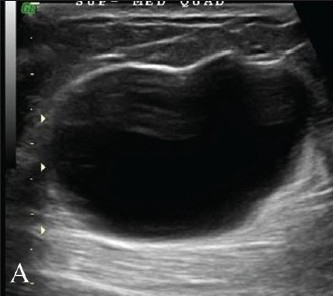
Simple Breast Cyst 1
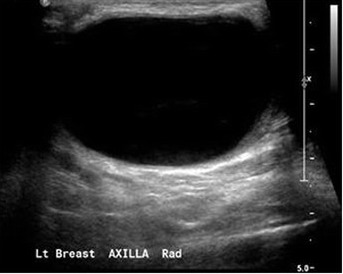
Complicated Breast Cyst 2
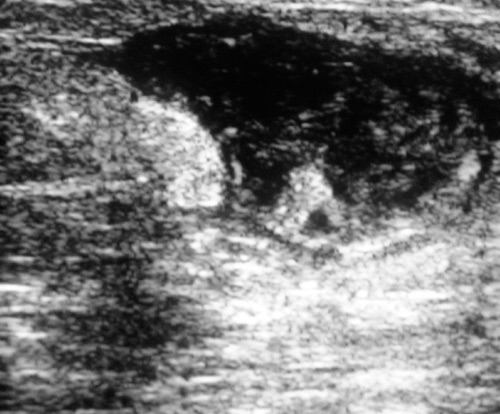
Complex Breast Cyst 3
References
- Shah G, Jankharia B. Pictorial essay: Breast USG. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2010 May;20(2):98-104. (License: CC BY-2.0)
- Dialani V, James DF, Slanetz PJ. A practical approach to imaging the axilla. Insights Imaging. 2015 Apr;6(2):217-29. (License: CC Not Specified)
- Siddiqui B, Faridi SH, Arif SH, Aslam M. Primary hydatid disease of the breast clinically masquerading as a galactocele: A case report. J Transl Int Med. 2015 Apr-Jun;3(2):82-84.(License: CC BY-NC-ND-3.0)