Breast: Breast Mass Evaluation
Breast Mass Evaluation
“Triple Test”
- Physical Exam
- Imaging
- Core Needle Biopsy
Physical (Bimanual) Exam
- Presentation:
- Most are Asymptomatic
- Pain
- Palpable Mass
- Suspicious Features:
- Single Dominant Lesion
- Hard
- Fixed/Immobile
- Irregular/Indistinct Borders
- Asymmetric Breasts
- Skin Retraction or Distortion
- Nipple Retraction or Discharge
Imaging Approach
- Young Women (Age < 30-35): Breast Ultrasound (US)
- Also Consider Bilateral Diagnostic Mammogram if Examination Indeterminate or Suspicious
- Older Women (Age > 30-35): Bilateral Diagnostic Mammogram
Breast Examination 1
Breast Mass Imaging
Mammogram
- Test: Bilateral Diagnostic Mammogram
- Allows Comparison Between the Two Sides
- Never Use a Unilateral or “Screening” Mammogram in Symptomatic Patients
- Preform Before Biopsy (Even if Palpable & Suspicious) – Goal to Identify Any Other Suspicious Areas & Biopsy May Alter Appearance
- Minimum Size Detected: > 5 mm
- Sensitivity/Specificity: 90%
- Less Sensitive in Younger Patients – Higher Breast Density
- Tomosynthesis – Three-Dimensional Mammography
- Suspicious Features:
- Most Specific Feature: Spiculated Soft Tissue Mass
- 90% Represent Invasive Cancer
- Grouped Microcalcifications
- Distortion
- Irregular Borders
- Asymmetric
- Multiple
- Small/Thin/Linear
- Most Specific Feature: Spiculated Soft Tissue Mass
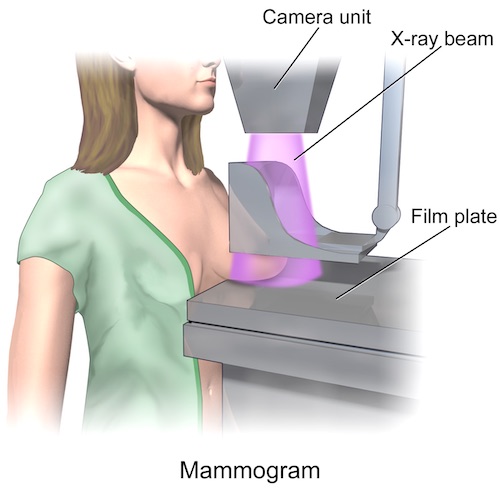
Mammogram 2
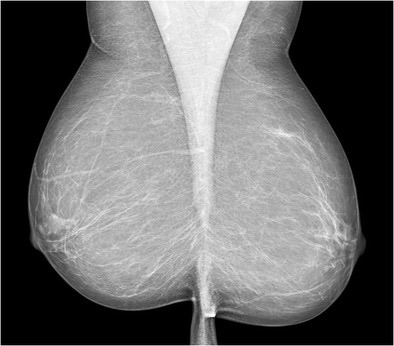
Normal Mammogram 3
Ultrasound
- Indications:
- Age < 30-35
- Identify a Cystic Mass
- Pregnant
- Palpable Mass but Negative Mammogram
- Suspicious Features:
- Taller-Than-Wide (Against Natural Parallel Lines of Chest Wall)
- Heterogenous
- Hypoechoic
- Internal Calcifications
- Shadowing
- Spiculated
- Indistinct Margins
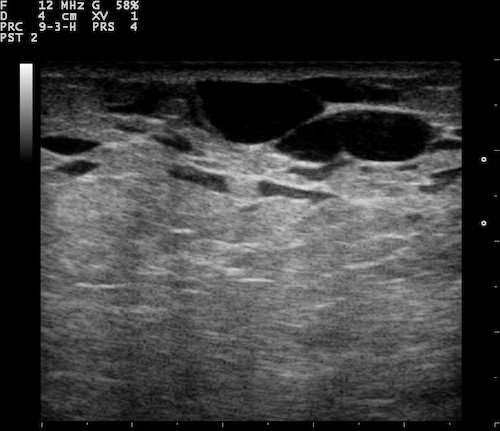
Normal Breast Ultrasound; Showing Ducts 4
MRI
- Few Absolute Indications
- Evaluate for Primary Cancer with Known Nodal Mets But No Obvious Breast Lesion
- Used in Screening: *See Breast: Breast Cancer Screening
- Better at Identifying Lesions in Dense Breast Tissue than Mammogram
- Suspicious Features:
- Irregular Margins
- Spiculated
- Heterogenous Enhancement
- Internal Septa
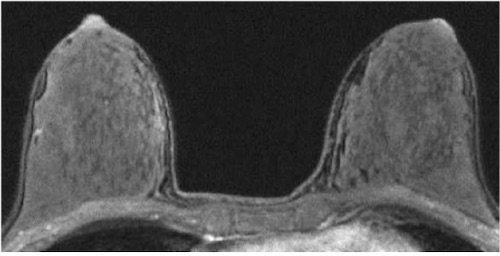
Breast MRI 5
Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS)
- Used for All Imaging Modalities
- Categories:
- BI-RADS 0: Incomplete (From Screening Mammogram)
- BI-RADS I: Negative
- BI-RADS II: Benign
- BI-RADS III: Probably Benign (< 2%)
- BI-RADS IV: Suspicious of Malignancy (> 2%)
- IVa: Low Suspicion (> 2%)
- IVb: Moderate Suspicion (> 10%)
- IVc: High Suspicion (> 50%)
- BI-RADS V: Highly Suggestive of Malignancy (> 95%)
- BI-RADS VI: Known Biopsy-Proven Malignancy
- Recommendations:
- BI-RADS 0: Further Imaging (Diagnostic Mammogram)
- BI-RADS I/II: Routine Screening
- BI-RADS III: Short Term (3-6 Month) Repeat Mammogram Mn
- BI-RADS IV/V: Core Needle Biopsy (CNB)
- BI-RADS VI: Treatment as Indicated
Breast Mass Biopsy
Core Needle Biopsy (CNB)
- Preferred Method of Initial Biopsy
- Evaluates: Architecture
- Benefits:
- Allows Appropriate Staging with SLNB
- Allows One-Step Surgery (Avoids Two Surgeries)
- Leaves a Marker Clip in the Sampled Region for Subsequent Management
- Allow Radiographic Confirmation of Correct Area Excision with Later Surgery
- Assists with Lesion Localization
- Methods:
- US-Guided – Preferred Method
- Stereotactic (X-Ray-Guided) – If Calcification Alone without Associated Mass or Not Well Seen on US
- Other Less Common Methods:
- Tomosynthesis-Guided
- MRI-Guided
- By Palpation
Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA)
- Evaluates: Cytology (Just Cells), Not Architecture
- Generally CNB is Preferred Over FNA
- Higher Rates of False Negative Results
- Cannot Distinguish in Situ & Invasive Cancer
- May Not Be Sufficient for Receptor Status Determination
- Variable Results
- Bloody: Cytology & CNB
- Not Bloody (Clear/Straw-Colored/Viscous): Observe
- If Fails to Resolve: CNB
Excisional Biopsy (EBx)
- Excision of the Entire Suspect Area
- Should Not Be Used as the Initial Biopsy Unless CNB is Not Feasible
- Indications After CNB:
- Non-Diagnostic (No Calcifications on Biopsy)
- Indeterminate
- Discordant/Non-Concordant (Benign But BI-RADS V)
- Atypia or Suspicious

Core Needle Biopsy 6
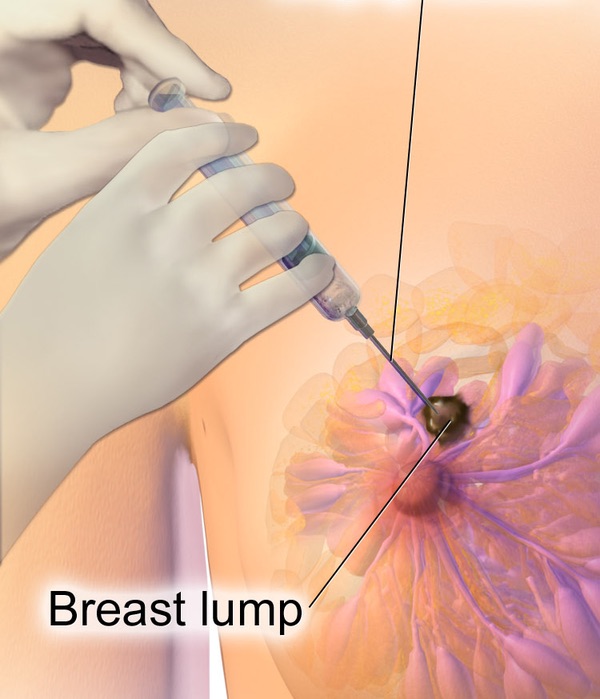
Breast FNA 7
Mnemonics
BI-RADS Management
- BI-RADS 3: 3-6 Months Repeat Mammogram
- Below – Routine Screening (Except 0)
- Above – Needs Biopsy/Surgery
References
- National Cancer Institute. Wikimedia Commons. (License: Public Domain)
- Blaus B. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-3.0)
- Sripathi S, Ayachit A, Kadavigere R, Kumar S, Eleti A, Sraj A. Spectrum of Imaging Findings in Paget’s Disease of the Breast-A Pictorial Review. Insights Imaging. 2015 Aug;6(4):419-29. doi: 10.1007/s13244-015-0415-z. Epub 2015 Jul 5. (License: CC BY-4.0)
- Dilmen N. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-SA-3.0)
- Kohara S, Ishigaki S, Satake H, Kawamura A, Kawai H, Kikumori T, Naganawa S. Background parenchymal enhancement in preoperative breast MRI. Nagoya J Med Sci. 2015 Aug;77(3):373-82. (License: CC BY-NC-ND-4.0)
- Dr Onco. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-SA-4.0)
- Blaus B. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-SA-4.0)