Cardiothoracic Surgery: Bronchial Adenoma
Bronchial Adenoma
Types
- Bronchopulmonary Carcinoid Tumor (90% – Most Common)
- Salivary Gland Tumors (10%):
- Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma (ACC)
- Invades Nerve Roots & Can Spread by Perineural Lymphatics
- Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
- Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma (ACC)
Bronchopulmonary Carcinoid Tumor
- *See Small Intestine: Carcinoid Tumor
- Presentation:
- Dyspnea
- Wheezing
- Cough
- Hemoptysis
- Carcinoid Syndrome (Diarrhea, Flushing, etc.)
- May Secrete Ectopic ACTH (Cushing Syndrome)
- Diagnosis:
- Initial Imaging: CT
- May Consider Somatostatin Receptor Scintigraphy (SRS) to Localize or Identify Metastatic Lesions
- Diagnosis: Bronchoscopy with Biopsy
- Initial Imaging: CT
- Treatment:
- Primary Treatment: Surgical Resection
Salivary Gland Tumors
- Arise from the Submucosal Glands of the Tracheobronchial Tree
- Presentation:
- Dyspnea
- Wheezing
- Cough
- Hemoptysis
- Diagnosis:
- Initial Imaging: CT
- Diagnosis: Bronchoscopy with Biopsy
- Treatment:
- Primary Treatment: Surgical Resection
- Adjuvant Radiation Therapy for Adenoid Cystic Adenoma (Very Radiosensitive)
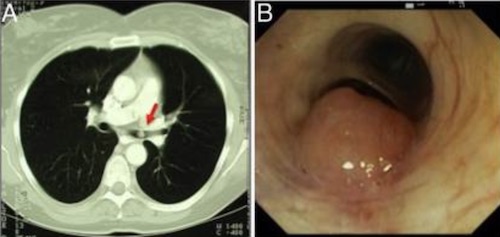
Bronchopulmonary Carcinoid Tumor on CT (A) and Bronchoscopy (B) 1
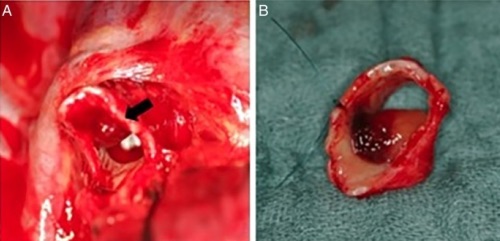
Bronchopulmonary Carcinoid Tumor on Resection 1
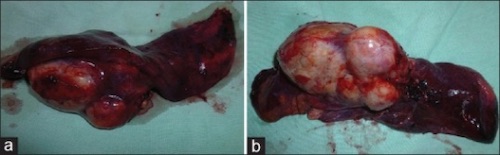
Bronchial Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma After Lobectomy 2
References
- Neuberger M, Hapfelmeier A, Schmidt M, Gesierich W, Reichenberger F, Morresi-Hauf A, Hatz RA, Lindner M. Carcinoid tumours of the lung and the ‘PEPPS’ approach: evaluation of preoperative bronchoscopic tumour debulking as preparation for subsequent parenchyma-sparing surgery. BMJ Open Respir Res. 2015 Jul 15;2(1):e000090. (License: CC BY-NC-4.0)
- Krishnamurthy A, Ramshankar V, Majhi U. Role of fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography-computed tomography in management of pulmonary mucoepidermoid carcinomas and review of literature. Indian J Nucl Med. 2016 Apr-Jun;31(2):128-30. (License: CC BY-NC-SA-3.0)