Vascular: Carotid Artery Aneurysm
Extracranial Carotid Artery Aneurysm (ECAA)
Basics
- Aneurysmal Dilation of the Carotid Artery Outside the Skull
- Most Common Sites: Bifurcation & Proximal ICA
Causes
- Atherosclerotic Degeneration – Most Common Cause
- Trauma
- Dissection
- Infection
- Radiation
- Fibromuscular Dysplasia
- Complication After Carotid Endarterectomy
Presentation
- Painless Pulsatile Mass – Most Common
- Pain & Erythema if Infected
- Amaurosis Fugax
- TIA/CVA
- Horner’s Syndrome – Compression of Sympathetic Chain
- Hoarseness – Vagus Compression
- Rupture (Rare)
Types
- Type I: Isolated to the ICA
- Type II: Complete ICA, Involving the Bifurcation
- Type III: Bifurcation
- Type IV: ICA & CCA
- Type V: Isolated to the CCA
Diagnosis
- Dx: US or CTA/MRA
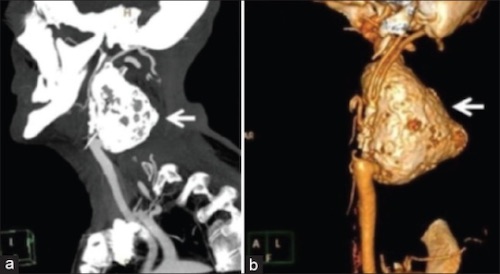
Carotid Artery Aneurysm on CTA 1
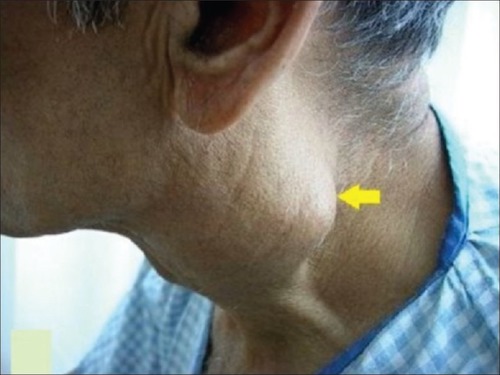
Cervical Swelling from Carotid Aneurysm 1
Treatment
- Small & Asymptomatic: Observation
- Surgical/Endovascular Interventions:
- General Indications:
- Large (> 2 cm) or Enlarging
- Symptomatic
- Mycotic Aneurysm
- Thrombosis within Aneurysm
- Possible Interventions:
- Surgical Excision with End-to-End Anastomosis or Interposition Graft
- Endovascular Stents or Coiling
- Often Preferred if in Distal ICA without Unstable Thrombosis
- General Indications:
References
- Panda A, Mahajan M. Unusual cause of asymptomatic neck swelling. Ann Med Health Sci Res. 2014 Mar;4(Suppl 1):S67. (License: CC BY-NC-SA-3.0)