Vascular: Carotid Artery Dissection
Carotid Artery Dissection
Basics
- Intimal Disruption Allows Blood Extravasation Between the Layers of the Wall
- Causes:
- Spontaneous
- Trauma
- Iatrogenic
- Most Common Site: 2-3 cm Past Bifurcation (More Distal Than Atherosclerotic Lesions)
Presentation
- Classic Triad:
- Ipsilateral Headache & Neck Pain
- Ipsilateral Partial Horner’s Syndrome (Oculosympathetic Palsy)
- Miosis & Ptosis Only, No Anhidrosis
- Cerebral or Retinal Ischemia
- Complications:
- Acute Stenosis
- Sudden Occlusion
- Aneurysm & Thromboembolism
Diagnosis
- Typical Tests: US, CTA or MRA
- Gold Standard: Four-Vessel Selective Cerebral Angiography
- Occlusions Tapered & “Flame-Shaped”
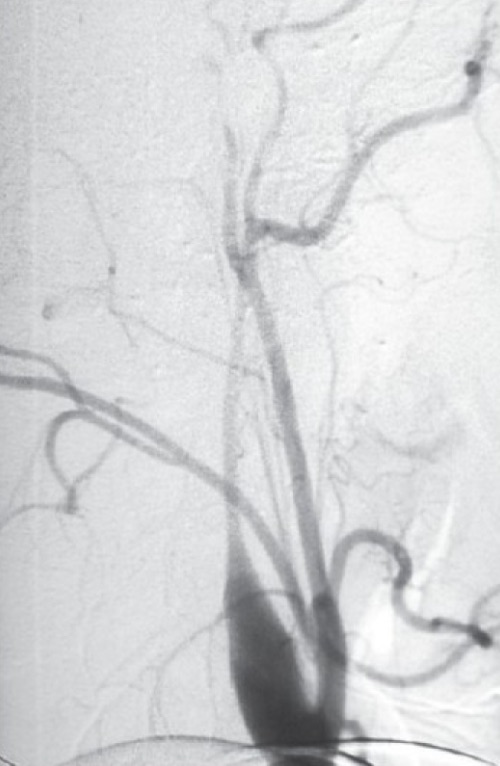
Carotid Dissection on Angio, “Flame-Shaped” 1
Treatment
- Primary Tx: Heparin
- Follow with Coumadin for 3-6 Months
- Surgical/Endovascular Interventions:
- General Indications:
- Fluctuating or Deteriorating Neurologic Symptoms
- Compromised Cerebral Blood Flow
- Anticoagulant Contraindications
- Symptomatic or Expanding Aneurysm
- Possible Interventions:
- Patch Angioplasty
- Interposition Saphenous Vein Graft
- Carotid Ligation
- Endovascular Stent Placement
- Endovascular Coiling
- Endovascular Embolization
- Best Treatment Modality is Not Yet Defined
- General Indications:
References
- Gooneratne IK, Gamage R, Gunarathne KS. Internal carotid artery dissection: an unusual cause of occipital infarction. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2010 Apr;13(2):148-9. (License: CC BY-2.0)