Biliary Tract: Cholangiocarcinoma
Cholangiocarcinoma
Basics
- Cancer of the Bile Ducts
- Most Common in Elderly & Males
- Overall Poor Prognosis (5-Year Survival 10-50%)
Risk Factors
- Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
- Choledochal Cyst
- Recurrent Pyogenic Cholangitis
- Hepatitis
- Cirrhosis
- Thorotrast (Old Banned Contrast Agent)
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Parasitic Infections
Histology
- Type
- Adenocarcinoma (> 90%)
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Morphology
- Sclerosing (Most Common) – Early Invasion & Subepithelial Extension with Poor Prognosis
- Nodular – Highly Invasive & Poor Prognosis
- Papillary (Rarest) – Bulky Mass Causes Early Obstruction & Identification (Best Prognosis)
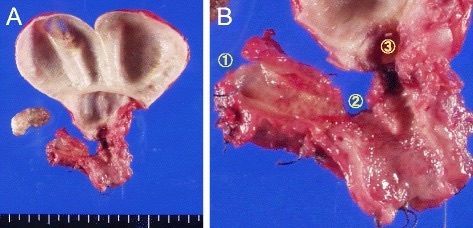
Cholangiocarcinoma 1
Bismuth-Corlette Classification Mn
- Type I – CBD or Common Hepatic Duct
- Type II – Bifurcation (Klatskin Tumor)
- Most Common (60-70%)
- Type III – Invades Unilateral Hepatic Duct
- IIIa – Right
- IIIb – Left
- Type IV – Bilateral Hepatic Ducts
Presentation
- Obstructive Jaundice
- Abdominal Pain
- Weight Loss & Fatigue
Diagnosis
- Generally Diagnosed on Imaging:
- Distal Extrahepatic: EUS/ERCP
- Perihilar: MRCP
- Intrahepatic: MRI vs MDCT (Multidetector-Row CT)
- Differentiate Hepatic vs Bile Duct Lesion
- If Imaging Indeterminate: Tissue Dx (FNA/Brush Cytology/IR Bx)
- Tumor Markers:
- CA 19-9 – Elevated
- CEA – Elevated
- AFP – Normal (Differentiate From HCC)
Treatment
- Unresectable Features:
- Extrahepatic Organ Invasion
- LN Beyond Hepatoduodenal Ligament (Periaortic or Celiac)
- Mets or Disseminated Disease
- Invades Main Portal Vein or Hepatic Artery (Some Centers May Reconstruct)
- Resectable Tx:
- Surgery:
- Distal CBD: Pancreaticoduodenectomy
- Compared to Whipple for Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
- Higher Survival
- Higher Incidence of Postoperative Pancreatic Fistula
- Compared to Whipple for Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
- Perihilar: En Bloc Resection (Extrahepatic Bile Ducts/Gallbladder) & Roux-en-Y Hepaticojejunostomy
- Type III/IV: Add Hepatic Lobectomy
- Intrahepatic: Hepatic Resection
- Distal CBD: Pancreaticoduodenectomy
- Consider Preoperative Biliary Drainage if Have Obstructive Jaundice (Controversial)
- Adjuvants:
- Neoadjuvant Chemo – Only for Highly-Selected Patients
- Adjuvant Chemo – Indicated for All Resectable Patients
- Also Consider XRT
- Liver TXP – Possibly in Setting of PSC or if Small but Unresectable
- Used for Hilar Tumors but Not if Intrahepatic
- Surgery:
- Unresectable Tx:
- Unresectable/Mets: Chemotherapy
- Obstruction Palliation: Stents
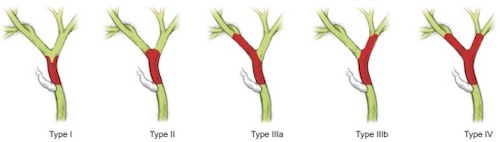
Bismuth-Corlette Classification of Cholangiocarcinoma 2

MRI of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma 3
Cholangiocarcinoma: TNM Staging – AJCC 8
Distal CBD Cholangiocarcinoma
- TNM
| T | N | M | |
| 1 | Depth < 5 mm | 1-3 | Mets |
| 2 | Depth 5-12 mm | ≥ 4 | |
| 3 | Depth > 12 mm | ||
| 4 | Invades Celiac Axis, SMA or Hepatic Artery |
- Stage
| T | N | M | ||
| I | T1 | N0 | M0 | |
| II | A | T1 | N1 | M0 |
| T2 | N0 | M0 | ||
| B | T2 | N1 | M0 | |
| T3 | N0-1 | M0 | ||
| III | A | T1-3 | N2 | M0 |
| B | T4 | Any N | M0 | |
| IV | Any T | Any N | M1 | |
Perihilar Cholangiocarcinoma
- TNM
| T | N | M | |
| 1 | Confined to Duct | 1-3 LN | Mets |
| 2 | A – Invades Adipose Tissue
B – Invades Liver |
≥ 4 LN | |
| 3 | Invades Branch of Portal Vein or Hepatic Artery | ||
| 4 | Invades Portal Vein or Hepatic Artery |
- Stage
| T | N | M | ||
| I | T1 | N0 | M0 | |
| II | T2 | N0 | M0 | |
| III | A | T3 | N0 | M0 |
| B | T4 | N0 | M0 | |
| C | Any T | N1 | M0 | |
| IV | A | Any T | N2 | M0 |
| B | Any T | Any N | M1 | |
Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma
- TNM
| T | N | M | |
| 1 | Solitary without Vascular Invasion
A – ≤ 5 cm B – > 5cm |
Any LN | Mets |
| 2 | Multiple or Invades Vasculature | ||
| 3 | Perforates Visceral Peritoneum | ||
| 4 | Invades Extrahepatic Structures |
- Stage
| T | N | M | ||
| I | A | T1a | N0 | M0 |
| B | T1b | N0 | M0 | |
| II | T2 | N0 | M0 | |
| III | A | T3 | N0 | M0 |
| B | T4 | N0 | M0 | |
| Any T | N1 | M0 | ||
| IV | Any T | Any N | M1 | |
Mnemonics
Bismuth-Corlette Classification of Cholangiocarcinoma
- Type I: “I” – Main Trunk (CBD or Common Hepatic Duct)
- Type II: “2 – Bi” – At the Bifurcation
- Type III: “I/I” – One or the Other Unilateral Hepatic Ducts
- Type IV: “Four Gets More” – Bilateral Hepatic Ducts
References
- Okabe H, Chikamoto A, Maruno M, Hashimoto D, Imai K, Taki K, Arima K, Ishiko T, Uchiyama H, Ikegami T, Harimoto N, Itoh S, Yoshizumi T, Beppu T, Baba H, Maehara Y. A long survivor with local relapse of hilar cholangiocarcinoma after R1 surgery treated with chemoradiotherapy: a case report and literature review. Surg Case Rep. 2016 Dec;2(1):69. (License: CC BY-4.0)
- Blechacz B. Cholangiocarcinoma: Current Knowledge and New Developments. Gut Liver. 2017 Jan 15;11(1):13-26. (License: CC BY-NC-4.0)
- Jeong WK, Kim YK, Song KD, Choi D, Lim HK. The MR imaging diagnosis of liver diseases using gadoxetic acid: emphasis on hepatobiliary phase. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2013 Dec;19(4):360-6. (License: CC BY-NC-3.0)