Hereditary Colorectal Cancer and Polyposis Syndromes
Jackson Phillip Bauer, MD, Johnathan W. Cain, DO, and Raphael Moore, MD
The Operative Review of Surgery. 2023; 1:138-141.
Table of Contents
Syndromes
Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP)
- Includes:
- Classical FAP
- Attenuated FAP (AFAP)
- Gastric Adenocarcinoma and Proximal Polyposis of the Stomach (GAPPS)
- Gardner’s Syndrome
- Turcot’s Syndrome
- *See Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP)
Lynch Syndrome
- Also Known as “Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colon Cancer (HNPCC)”
- *See Lynch Syndrome
Juvenile Polyposis Syndrome (JPS)
- Also Known as “Familial Juvenile Polyposis”
- *See Juvenile Polyposis Syndrome (JPS)
MUT Y Homolog (MUTYH)-Associated Polyposis (MAP)
Serrated Polyposis Syndrome (SPS)
- Historically Known as “Hyperplastic Polyposis Syndrome”
- *See Serrated Polyposis Syndrome (SPS)
Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome (PJS)
PTEN Hamartoma Tumor Syndrome (PHTS)
- Includes:
- Cowden Syndrome
- Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba Syndrome (BRRS)
- Proteus-Like Syndrome/SOLAMEN Syndrome
- *See PTEN Hamartoma Tumor Syndrome (PHTS)
Other Rare Polyposis Syndromes 2,3
- GREM1-Associated Polyposis (Hereditary Mixed Polyposis Syndrome/HMPS)
- Mutations: GREM1 (Autosomal Dominant)
- Associated with Multiple Polyps of Mixed Histology (Adenomas, Hyperplastic, Hematomas, and Juvenile)
- Increased Risk of Colorectal Cancer
- Associated with Desmoid Tumors, Prostate Cancer, and Duodenal Cancer
- Other Adenomatous Polyposis Syndromes (Autosomal Dominant):
- POLE-Associated Polyposis
- POLD1-Associated Polyposis
- AXIN2-Associated Polyposis (Oligodontia-Colorectal Cancer Syndrome)
- Other Adenomatous Polyposis Syndromes (Autosomal Recessive):
- NTHL1-Associated Polyposis
- MLH3-Associated Polyposis
- MSH3-Associated Polyposis
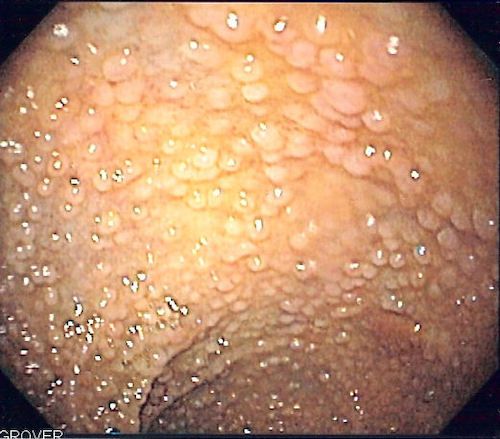
FAP on Colonoscopy 1
Comparisons
Genetic Mutations
- Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP): APC
- Lynch Syndrome: MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2, or EpCAM
- Juvenile Polyposis Syndrome (JPS): SMAD4 (MADH4) or BMPR1A
- MUTYH-Associated Polyposis (MAP): MUT Y Homolog (MUTYH) Gene
- Serrated Polyposis Syndrome (SPS): Genetic Basis is Mostly Unknown, RNF43 Most Closely Related
- Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome (PJS): STK11
- PTEN Hamartoma Tumor Syndrome (PHTS): PTEN
- Others: GREM1, POLE, POLD1, AXIN2, NTHL1, MLH3, or MSH3
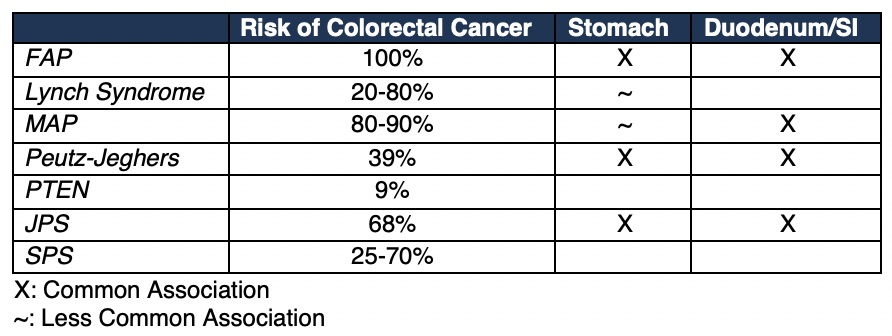
Malignancy of the GI Tract
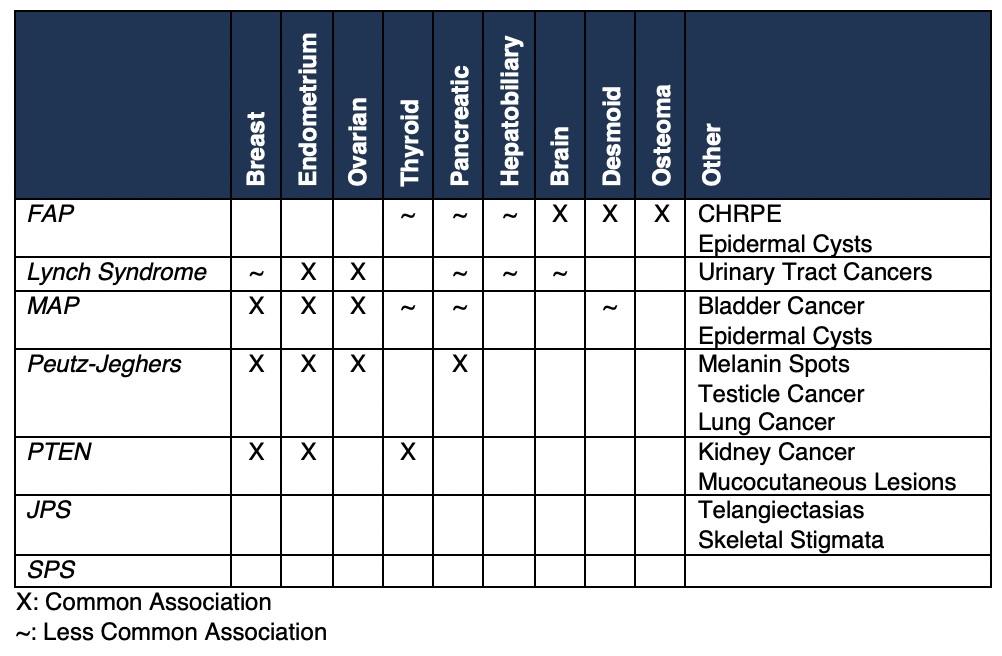
Extraintestinal Manifestations
References
- Makarewicz W, Bobowicz M, Sawicka W, Rzyman W. The treatment of chronic pleural empyema with laparoscopic omentoplasty. Initial Report. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2014 Dec;9(4):548-53. (License: CC BY-NC-ND 3.0)
- Jelsig AM, Karstensen JG, Jespersen N, Ketabi Z, Lautrup C, Rønlund K, Sunde L, Wadt K, Thorlacius-Ussing O, Qvist N. Danish guidelines for management of non-APC-associated hereditary polyposis syndromes. Hered Cancer Clin Pract. 2021 Oct 7;19(1):41.
- Lieberman S, Walsh T, Schechter M, Adar T, Goldin E, Beeri R, Sharon N, Baris H, Ben Avi L, Half E, Lerer I, Shirts BH, Pritchard CC, Tomlinson I, King MC, Levy-Lahad E, Peretz T, Goldberg Y. Features of Patients With Hereditary Mixed Polyposis Syndrome Caused by Duplication of GREM1 and Implications for Screening and Surveillance. Gastroenterology. 2017 Jun;152(8):1876-1880.e1.