Large Intestine: Colovesicular Fistula
Colovesicular Fistula
General Enteric Fistulas
Basics
- A Fistula from the Colon to the Urinary Bladder
- Most Common in Males (2-3:1) – Female Protected by Uterus
Causes
- Diverticulitis – Most Common (65-79%)
- Malignancy
- Crohn’s Disease
- Surgery
- Colonic Stents
- Radiation
- Trauma
Symptoms
- Pneumaturia (50-95%) – Most Often at the End of Urination
- Fecaluria (40-70%)
- Suprapubic Pain (30-90%)
- Recurrent UTI – Dysuria, Urgency & Frequency
Diagnosis
- Dx: CT with Oral/Rectal Contrast (No IV Contrast – Renal Excretion will Obscure)
- Colonoscopy to Rule Out Malignancy
- Cystoscopy if Needed to Evaluate Malignant Invasion of Bladder
- Other Tests:
- Poppy Seed Test – Oral Ingestion of Poppy Seeds See Seeds Passed in the Urine within 48 Hours
- High Sensitivity (Nearly 100%) but No Localization Detail
- Barium Enema – Low Sensitivity (30%)
- Poppy Seed Test – Oral Ingestion of Poppy Seeds See Seeds Passed in the Urine within 48 Hours
Treatment
- Tx: ABX & Surgical Repair
- Surgical Repair:
- Segmental Bowel Resection (Sigmoidectomy)
- Primary Closure of Bladder
- If Unable to Find – Instill Methylene Blue Retrograde Through Foley Catheter
- Place Omentum Interposition Between Colon & Bladder
- Other Considerations:
- Low Rectum: Rectal Advancement Flap
- Consider Two-Stage Procedure with Temporary Ostomy if High-Risk for Leak or Unable to Tolerate a Prolonged Operation
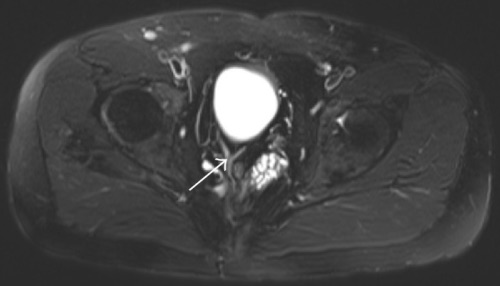
Colovesicular Fistula 1
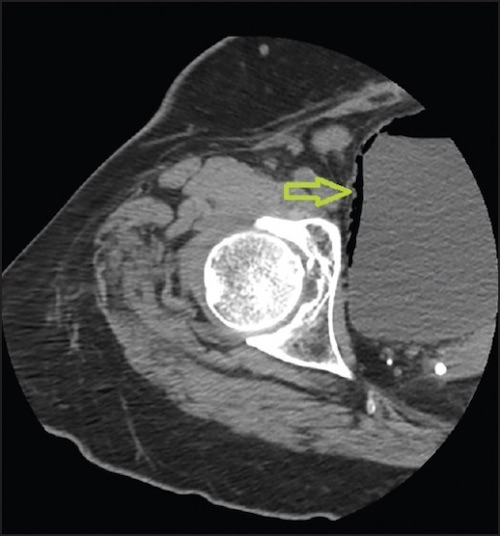
Pneumaturia 2
References
- Weyant GW, Karamchandani DM, Rassaei N. Colorectal microcarcinoids in association with long-term exposure to urinary content: a case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Pathol. 2015;2015:806310. (License: CC BY-3.0)
- Singh S, Jehangir W, Littlefield J 2nd, Hanna G, Bowling G, Yousif A, Middleton JR. Emphysematous Cystitis: A Rare Disease of Genito-Urinary System. N Am J Med Sci. 2015 Jul;7(7):332-3. (License: CC BY-NC-SA-3.0)