Vascular: Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT)
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Definitions
- Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) – Blood Clot within the Venous System
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) – Blood Clot within the Deep Venous System
- Provoked DVT – DVT Caused by a Known Event (Surgery, etc.)
- Unprovoked – DVT with No Known Provoking Event
- Proximal DVT – Iliac, Femoral or Popliteal Vessels
- Distal DVT – Below the Knee with No Proximal Component
- Pulmonary Embolism (PE) – Blood Clot Occlusion of the Pulmonary Arteries, Most Often Due to a DVT
Risk Factors
- Virchow’s Triad:
- Venous Stasis
- Hypercoagulability
- Endothelial Wall Injury
- Inherited Thrombophilia
- Acquired Hypercoagulability
- Prior Thrombotic Events
- Post-Thrombotic Syndrome – DVT Induced Injury to Valves Producing Chronic Venous Insufficiency
- Central Venous Catheter
- Highest Risk in Trauma: Spinal Cord Injury
Location
- Most Common Site: Calf
- Left Side 2x More Common Than Right
- May-Thurner Syndrome: Left Iliac Vein Thrombosis Due to Compression by Right Iliac Artery
Presentation
- Symptoms:
- Swelling
- Pain
- Warmth
- Erythema
- Homans Sign: Pain with Foot Dorsiflexion
- No Diagnostic Value – Poor Sensitivity & Specificity
- Phlegmasia Alba Dolens
- Early DVT Impairment of Arterial Supply
- Sx: White, Painful & Swollen
- Phlegmasia Cerulea Dolens
- Late DVT Impairment of Arterial Supply
- Sx: Blue, Painful & Swollen Mn
- Indicates Impending Gangrene
- Half Have Malignancy

Leg Swelling Due to DVT 1

Phlegmasia Alba Dolens 2

Phlegmasia Cerulea Dolens 3
Diagnosis
- Dx: Ultrasound
- US Findings:
- General DVT Findings:
- Intramural Thrombus
- Noncompressible Veins
- Venous Dilation
- No Flow
- Acute US Findings:
- Echolucent/Hypoechoic
- Homogenous
- Poorly Attached
- Smooth Borders
- Nonrigid
- Venous Dilation
- Small Collaterals
- Chronic US Findings:
- Brightly Echogenic
- Heterogenous
- Well Attached
- Irregular Borders
- Rigid
- Small/Contracted Veins
- Large Collaterals
- General DVT Findings:
- D-Dimer is Not Specific & Generally Not Useful in the Surgical Setting
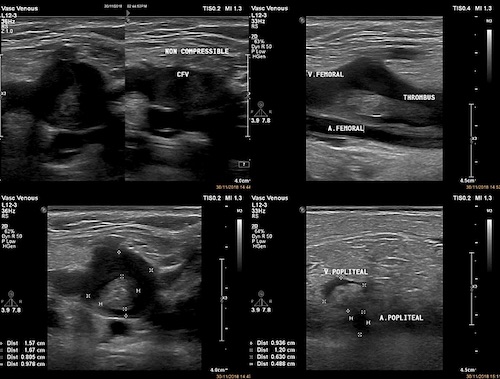
Femoral DVT on US 2
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) – Treatment
Prophylaxis
Treatment – First Episode
- Proximal DVT
- Provoked: 3-6 Months Anticoagulation
- Unprovoked: Long-Term (> 12 Months) Anticoagulation
- Consider Lifelong Anticoagulation if Hypercoagulable Disorder Present
- Distal DVT
- Symptomatic: Anticoagulation
- Asymptomatic: Serial US x2 Weeks
- Phlegmasia Cerulea Dolens
- Non-Threatened Extremity: Catheter-Directed Thrombolytics
- Threatened Extremity: Thrombectomy
- Choice of Agent:
- General Options:
- Unfractionated Heparin
- Low Molecular Weight Heparin (Lovenox)
- Fondaparinux
- Rivaroxaban
- Apixaban
- Warfarin/Coumadin – Cannot Be Sole Initial Treatment
- Malignancy: Low Molecular Weight Heparin (Lovenox)
- Pregnancy: Heparin or Low Molecular Weight Heparin (Lovenox)
- Warfarin is Teratogenic
- General Options:
- *May-Thurner Syndrome Managed with Venography, Thrombolysis/Thrombectomy & Left Iliac Stent
Treatment – Subsequent Episodes
- Second Episode: Long-Term (> 12 Months) Anticoagulation
- Third Episode: Life-Long Anticoagulation
IVC Filter
- Goal: PE Prophylaxis
- Indications:
- Acute Proximal DVT or PE with Anticoagulation Absolute Contraindication
- Includes:
- Active Bleeding
- Acute Intracranial Hemorrhage
- Major Trauma
- High Bleeding-Risk Surgery
- Includes:
- Recurrent VTE Despite Therapeutic Anticoagulation
- Acute Proximal DVT or PE with Anticoagulation Absolute Contraindication
- Placement:
- Access Through Right IJ – Most Direct Access
- Position:
- Infrarenal IVC (Generally Preferred)
- Minimize Risk of Filter Obstruction Occluding the Renal Veins
- Suprarenal IVC
- Used for a Renal Vein Thrombosis
- Used in Pregnancy – To Avoid Contact with a Gravid Uterus
- Infrarenal IVC (Generally Preferred)
- Removal:
- Filters Should Be Removed as Long as Protection is No Longer Needed
- Overall Retrieval Rate: 25-34%
- Best Predictor of Removal: Thrombosis Clinic Follow Up Appointment
- Highest Risk of Difficult Removal: Placement > 7 Months
- Complications:
- Increases DVT Risk
- IVC Thrombosis
- Filter Migration
- Filter Erosion
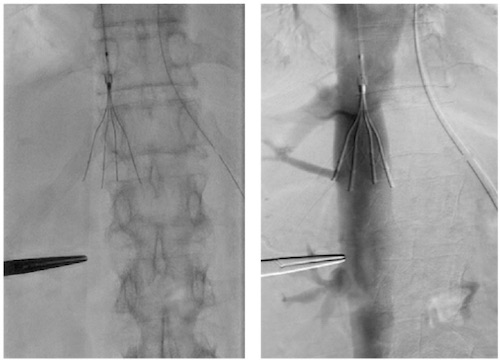
IVC Filter Placement 4
Mnemonics
DVT Color Changes by Severity
- USA!: Red, White & Blue
- Red – Swollen Red DVT
- White – Phlegmasia Alba Dolens
- Blue – Phlegmasia Cerulea Dolens
- Cerulea is “Cruel” & Worst
References
- Babu MR, Ramesh C, Thirumurugan K, Prasad GA. Deep vein thrombosis: A rare complication in oral and maxillofacial surgery: A review of two cases. Contemp Clin Dent. 2013 Apr;4(2):236-8. (License: CC BY-NC-SA-3.0)
- Suciadi L P, Aristo A N (March 24, 2021) Phlegmasia Alba Dolens Complicating Rhabdomyolysis. Cureus 13(3): e14080. (License: CC BY-4.0)
- Yang SS, Yun WS. Surgical Thrombectomy for Phlegmasia Cerulea Dolens. Vasc Specialist Int. 2016 Dec;32(4):201-204. (License: CC BY-NC-4.0)
- Kishima H, Fukunaga M, Nishian K, Saita T, Horimatsu T, Sugahara M, Mine T, Masuyama T. Aspiration thrombectomy in a patient with suprarenal inferior vena cava thrombosis. Case Rep Cardiol. 2015;2015:495065. (License: CC BY-3.0)