Skin & Soft Tissue: Desmoid Tumor
Desmoid Tumor
General
- Fibroblastic Tumor of Fascial & Aponeurotic Connective Tissue
- Benign with No Mets
- Locally Aggressive with High Local Recurrence (30%)
Location
- Intraabdominal – Most are Unresectable at Time of Diagnosis
- Extraabdominal
- Most Common Site: Anterior Abdominal Wall (Often Following Pregnancy or Trauma)
Associations
- Most Are Sporadic
- Most Common Mutation: CTNNB1
- Repeated Trauma to an Area or Surgery (Seen Along a Scar)
- FAP/Gardner’s Syndrome (APC Mutation)
Diagnosis
- CT: Depends on Composition
- Can be Homogenous or Heterogenous
- Can by Hypointense or Hyperintense
- Core Needle Bx (Histology): Spindle Cells, Dense Fibrosis, High Cellularity & Low Mitotic Index
Treatment
- General Treatment: Surgical Resection
- Can Observe if Asymptomatic & Stable in Size
- If Unresectable: XRT or Chemo (Tamoxifen & Sulindac)
- Consider Colonoscopy to Evaluate FAP
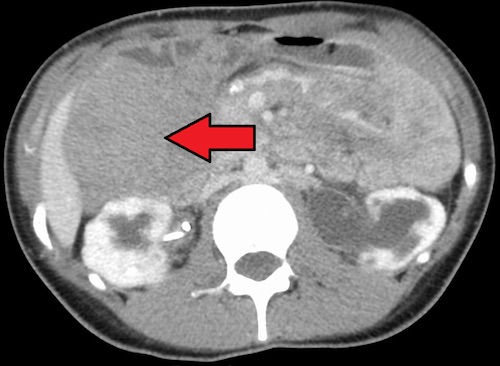
Retroperitoneal Desmoid Tumor 1

Desmoid Tumor Rectus Abdominis Postpartum 2
References
- Heilman J. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-SA-4.0)
- Choi SH, Lee JH, Seo BF, Kim SW, Rhie JW, Ahn ST. Desmoid tumor of the rectus abdominis muscle in a postpartum patient. Arch Plast Surg. 2012 Jul;39(4):439-41. (License: CC BY-NC-3.0)