Esophagus: Foreign Body
Foreign Body Ingestion
Foreign Body Ingestion
- Most Common in Young Children (6 Months – 3 Years)
- Most Common Site of Impaction: Esophagus
- Occurs at Sites of Physiologic Narrowing:
- Upper Esophageal Sphincter (UES)
- Crossover of the Aortic Arch
- Diaphragmatic Hiatus/Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES)
- Most Common Site Overall: Thoracic Inlet (Below Cricopharyngeus)
- Occurs at Sites of Physiologic Narrowing:
- Risk of Perforation Increases with Length of Time
Common Objects
- Food Impaction – Most Common Esophageal Foreign Body in Adults
- Coins – Most Common Foreign Body in Peds
- Magnets – Bowel Trapped Between Magnets Can Cause Pressure Necrosis & Perforation
- Button (Disc) Batteries
- Sharp Objects – Can Perforate
- Superabsorbent Polymer – Can Expand in Size When Hydrated Up to 30-60 Times
- Long Object > 5-6 cm – Generally Cannot Pass
Urgency of Endoscopic Management
Emergent Indications
- Esophagus:
- Sharps
- Button Batteries
- Complete Obstruction (Drooling/Cannot Handle Secretions)
- Causing Airway Compromise
- Stomach/Duodenum:
- None
Urgent Indications
- Esophagus:
- Blunt Objects
- Food Impaction
- Stomach/Duodenum:
- Sharps
- Either:
- Magnets – Some Recommend Observation if Only a Single Magnet
- Long Object > 5-6 cm
- Superabsorbent Polymer
- Lead-Containing Products
Non-Urgent Indications
- Esophagus:
- Coins (Can Observe 12-24 Hours)
- Stomach/Duodenum:
- Button Batteries (Can Observe for 48 Hours – Remove if Not Passed)
- Blunt Objects with Diameter > 2.5 cm
Battery Ingestion
Button Battery Ingestion
- Can Cause Necrosis & Ulceration/Perforation from Electrical Current When in Esophagus or Retained in Stomach
- Initial Management:
- Indications for Radiographic Localization:
- Age ≤ 12 Years
- Battery Size ≥ 12 mm or Unknown
- Single Small Battery: Observe at Home without Imaging
- Indications for Radiographic Localization:
- Treatment:
- Esophageal Impaction: Emergency Endoscopic Removal
- Stomach Location:
- Symptomatic: Endoscopic Removal
- Asymptomatic:
- *Asymptomatic Indications Debated
- Age < 5 Years & Battery Size ≥ 20 mm
- Remains in Stomach After 4 Days & Age < 6 Years or Battery Size ≥ 15 mm
- *Asymptomatic Indications Debated
- Intestinal Location:
- Asymptomatic: Observe
- Symptomatic: Surgical Removal
Cylindrical Battery Ingestion
- Initial Management: Radiographic Localization for All
- Treatment: Generally Observe
- Stomach Location:
- Some Recommend Removal Depending on Type of Battery & Age
- Endoscopic Removal if Remains in Stomach After 48 Hours
- Intestinal Location:
- Surgical Removal if Concerned for Perforation/Peritonitis
- Stomach Location:
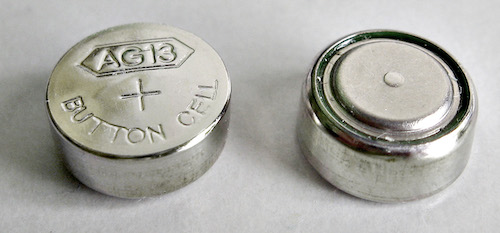
Button Battery 1
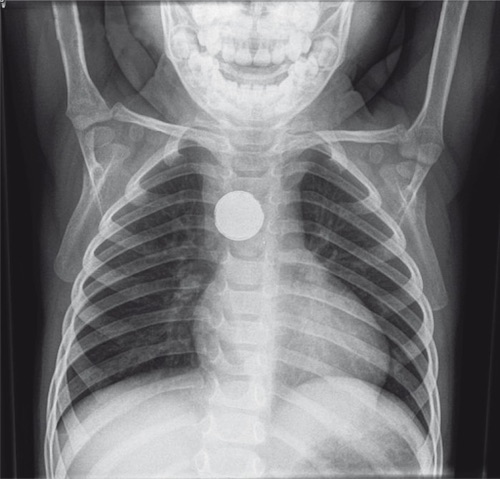
Button Battery Impaction in Esophagus 1
References
- Wikimedia Commons. Public Domain
- Szaflarska-Popławska A, Popławski C, Romańczuk B, Parzęcka M. Endoscopic removal of a battery that was lodged in the oesophagus of a two-year-old boy for an extremely long time. Prz Gastroenterol. 2015;10(2):122-6. (License: CC BY-NC-ND-3.0)