Esophagus: Motility Disorders
Chicago Classification – Version 3
Integrated Relaxation Pressure (IRP) Elevated
- Achalasia – Aperistalsis
- Type I: No Contractile Activity
- Type II: Pan-Esophageal Pressurization in ≥ 20% of Swallows
- Type III: Premature/Spastic Contractions in ≥ 20% of Swallows
- EGJOO – Peristalsis
Integrated Relaxation Pressure (IRP) Normal
- Major Disorders of Peristalsis
- DES – Premature Contractions ≥ 20% of Swallows
- Jackhammer Esophagus – DCI (Distal Contractile Integral) > 8,000 mmHg ≥ 20% of Swallows
- Absent Contractility – No Scorable Contraction
- Minor Disorders of Peristalsis
- Ineffective Esophageal Motility – ≥ 50% of Swallows Ineffective
- Fragmented Peristalsis – ≥ 50% of Swallows Fragmented
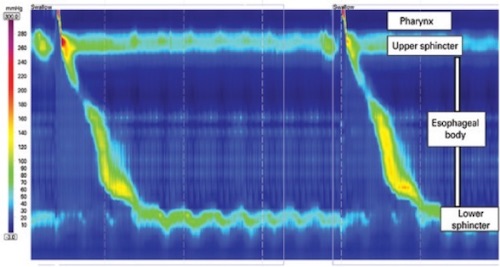
Normal Manometry 1
Achalasia
Basics
- Definition: Failure/Incomplete Relaxation of the LES with Esophageal Aperistalsis
- The Most Common Esophageal Motility Disorder
- Cause: Autoimmune Destruction of Neural Ganglion Cells in the Myenteric Plexus
- Risk Factors:
- Autoimmune Disorders
- Neurodegenerative Disorders
- Diabetes Type 1
- Increased Risk of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Symptoms
- Classic Triad:
- Dysphagia to Both Solids & Liquids (Most Common)
- Regurgitation
- Weight Loss
- Heartburn
- Chest Pain
- Difficulty with Belching
Diagnosis
- Manometry
- Required to Establish Diagnosis
- Findings: Incomplete LES Relaxation & Aperistalsis
- Barium Esophagram
- Preform if Manometric Findings are Equivocal
- Findings: Dilated Esophagus, Narrowed EG Junction & Delayed Emptying
- “Bird’s Beak” Appearance
- Upper Endoscopy
- Required to Rule Out Cancer Which Can Mimic
- Bx: T Cell & Eosinophil Infiltration of Myenteric Plexus
Chicago Classification – Version 3
- Type I (Classic Achalasia):
- High Integrated Relaxation Pressure (IRP)
- Aperistalsis
- No Contractile Activity
- Distal Contractile Integral (DCI/Strength of Distal Contraction) < 100 mmHg
- Type II:
- High Integrated Relaxation Pressure (IRP)
- Aperistalsis
- Pan-Esophageal Pressurization in ≥ 20% of Swallows
- Type III (Spastic Achalasia):
- High Integrated Relaxation Pressure (IRP)
- Aperistalsis
- Premature/Spastic Contractions in ≥ 20% of Swallows
- Distal Contractile Integral (DCI/Strength of Distal Contraction) < 450 mmHg
Treatment
- Heller Myotomy
- Historical Gold Standard (Still the “Safe Answer” on Testing)
- Dysphagia Relief
- Type I/II: 90%
- Type III: 50%
- Pneumatic/Balloon Dilation
- Graded Dilations are Superior to Single Dilation
- Emerging as the First-Line Initial Treatment
- Must Be Good Surgical Candidates as Perforation May Require Surgical Repair
- Compared to Heller Myotomy:
- Single Dilation is Inferior but Graded Dilations are Equivalent
- More Adverse Events
- Similar Quality of Life
- Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM)
- Must Be Good Surgical Candidates as Perforation May Require Surgical Repair
- Compared to Heller Myotomy:
- Similar Results
- Lower Complications
- Shorter Hospital Stay & Faster Recovery
- Highest Risk of GERD – Ablates LES, No Antireflux Procedure
- Options if Unable to Tolerate Surgery:
- Endoscopic Botulinum Toxin (Botox) Injections into LES
- Pharmacology: Nitrates, CCB or PDE-5 Inhibitors
- *Less Effective
Similar Findings
- Chagas Disease
- Parasite: Trypanosoma cruzi
- Predominantly in Central/South America
- Produces Similar Sx
- Pseudoachalasia
- Similar Imaging Findings but Due to CA
- Allgrove Syndrome:
- Autosomal Recessive Disorder
- Triad: Achalasia, Adrenal Insufficiency & Alacrima (Reduced Tear Production)
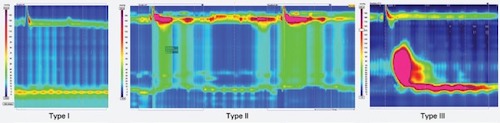
Achalasia Manometry; Type I – No Contractility with Incomplete LES Relaxation; Type II – Penesophageal Pressurization; Type III – Premature Spastic Contractions 1
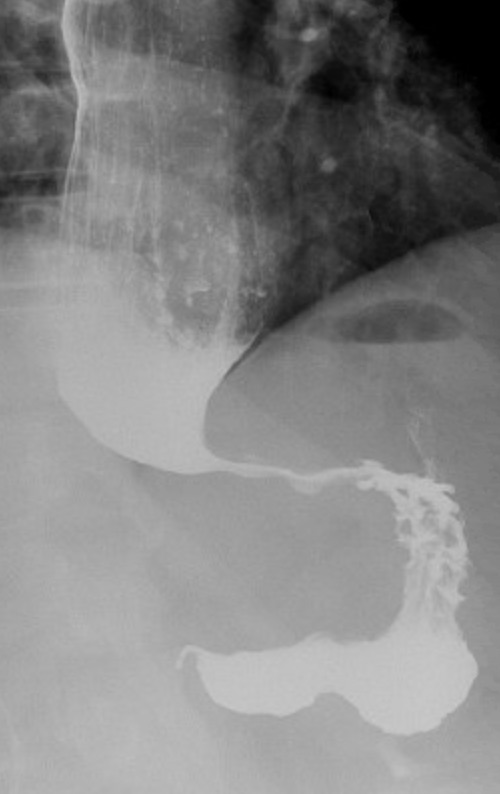
“Birds Beak” on Esophagram
Esophagogastric Junction Outflow Obstruction (EGJOO)
Basics
- Obstruction from Intrinsic or Extrinsic Compression
- May Be a Precursor to Achalasia
Causes
- Idiopathic
- Pseudoachalasia from Malignancy
- Hiatal Hernia
- Stricture
- Scarring
- Vascular Obstruction from Diseased Aortic Arch
Diagnosis
- Manometry
- Chicago Classification – Version 3:
- High Integrated Relaxation Pressure (IRP)
- Preserved Peristalsis
- Chicago Classification – Version 3:
- Barium Esophagram
- Upper Endoscopy
- Required to Rule Out Cancer or Other Structural Abnormality
Treatment
- Based on Symptoms
- Options: PPI, Botox Injection, Pneumatic Dilations, POEM or Myotomy
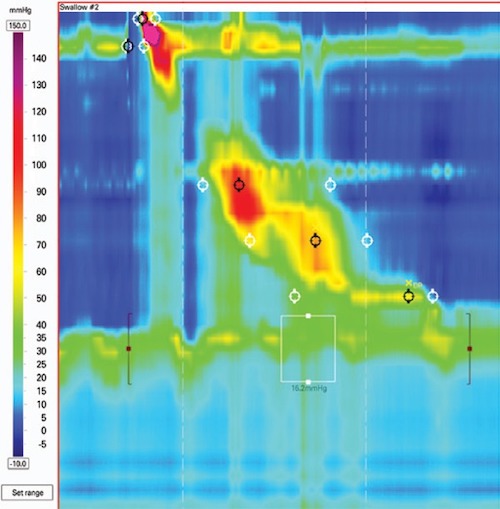
EGJOO Manometry 1
Diffuse Esophageal Spasm (DES)
Basics
- High-Amplitude Uncoordinated/Unorganized Contractions with No Peristalsis
- Premature Rapidly Propagated Contractions from Impaired Inhibitory Innervation
- Associated with Psychiatric Disorders
Symptoms
- Dysphagia to Both Solids & Liquids (Most Common)
- Regurgitation
- Heartburn
- Globus Sensation
- Chest Pain
Diagnosis
- Manometry
- Required to Establish Diagnosis
- Findings: High-Amplitude Uncoordinated/Unorganized Contractions with No Peristalsis
- Chicago Classification – Version 3:
- Normal Integrated Relaxation Pressure (IRP)
- Premature Contractions ≥ 20% of Swallows with Distal Latency < 4.5 Seconds
- Barium Esophagram
- Findings: “Corkscrew” Pattern
- Upper Endoscopy
- Required to Rule Out Cancer or Other Structural Abnormality
Treatment
- Primary Tx: Diltiazem (CCB) #1 or Imipramine (TCA)
- Other Meds: Trazodone, Venlafaxine or PDE-5 Inhibitors
- Other Options:
- Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM)
- Surgical Myotomy
- Endoscopic Botulinum Toxin (Botox) Injections
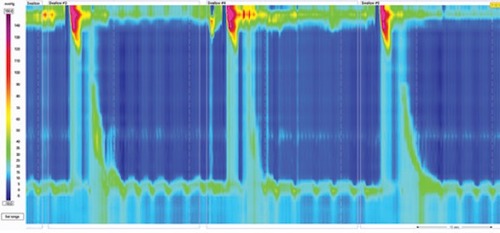
DES Manometry 1
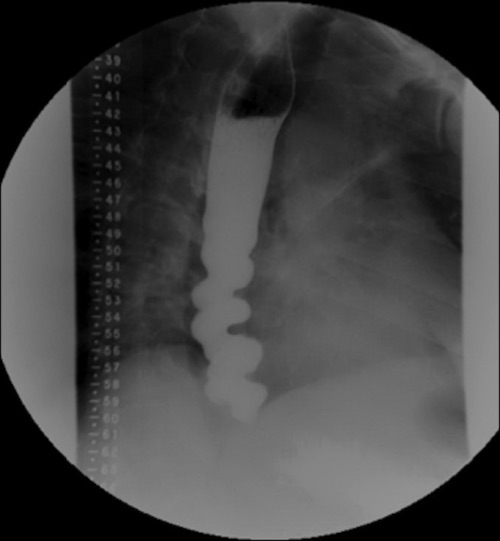
“Corkscrew” on Esophagram 2
Jackhammer (Nutcracker) Esophagus
Basics
- High-Amplitude Coordinated Contractions with Peristalsis
- Extreme Asynchronous Contractions from Excessive Cholinergic Drive
- Can Involve Esophageal Body or Be Limited to the GE Junction
Symptoms
- Dysphagia
- Chest Pain (More Prevalent Than in Other Motility Disorders)
- Regurgitation
- Heartburn
- Globus Sensation
Diagnosis
- Manometry
- Required to Establish Diagnosis
- Findings: High-Amplitude Coordinated Contractions with Peristalsis
- Chicago Classification – Version 3:
- Normal Integrated Relaxation Pressure (IRP)
- Distal Contractile Integral (DCI/Strength of Distal Contraction) > 8,000 mmHg
- ≥ 20% of Swallows
- Barium Esophagram
- Findings: Normal
- Upper Endoscopy
- Required to Rule Out Cancer or Other Structural Abnormality
Treatment
- Primary Tx: Diltiazem (CCB) #1 or Imipramine (TCA)
- Other Meds: Trazodone, Venlafaxine or PDE-5 Inhibitors
- Other Options:
- Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM)
- Surgical Myotomy
- Endoscopic Botulinum Toxin (Botox) Injections
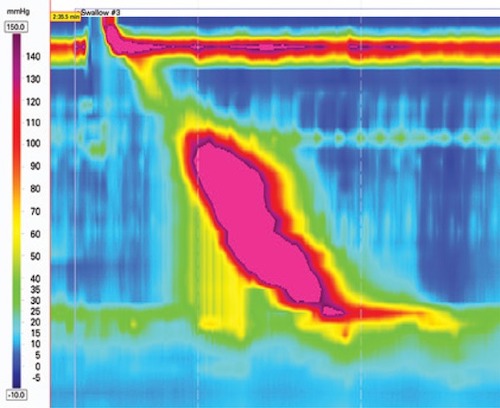
Hypercontractile Esophagus Manometry 1
Absent Contractility
Basics
- Most Often Associated with Connective Tissue Disorders (Scleroderma)
- Chicago Classification – Version 3
- Normal Integrated Relaxation Pressure (IRP)
- No Scorable Contraction
Scleroderma (Systemic Sclerosis)
- Massive Reflux & Dysphagia (Loss of LES Tone)
- Most Common Site: Esophagus (Fibrous Replacement of Smooth Muscle)
- Dx:
- Manometry: Low LES Pressure & No Peristalsis
- Tx:
- Primary Tx: PPI & Reglan
- Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass if Severe
- Avoid Fundoplication Alone (Scleroderma Can Also Affect Gastric Motility)
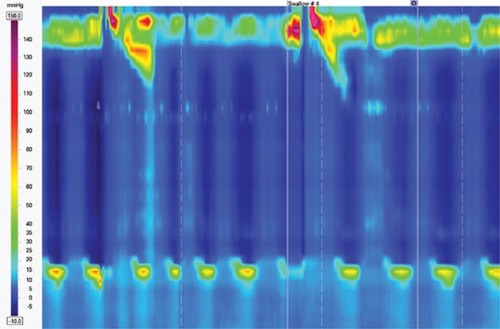
Absent Contractility Manometry 1
Minor Disorders of Peristalsis
Ineffective Esophageal Motility (IEM)
- ≥ 50% of Swallows Ineffective
- Most Often Caused by Distal Damage from Chronic GERD
- Often Have More Mild Symptoms & Require Less Intervention
- Manometry
- Chicago Classification – Version 3:
- Normal Integrated Relaxation Pressure (IRP)
- ≥ 50% of Swallows Ineffective
- Chicago Classification – Version 3:
- Tx: Control of GERD
Fragmented Peristalsis
- ≥ 50% of Swallows Fragmented
- Often Have More Mild Symptoms & Require Less Intervention
- Manometry
- Chicago Classification – Version 3:
- Normal Integrated Relaxation Pressure (IRP)
- ≥ 50% of Swallows Fragmented
- (DCI > 450 mmHg with > 5 cm Break)
- Chicago Classification – Version 3:
- Poorly Described in Literature
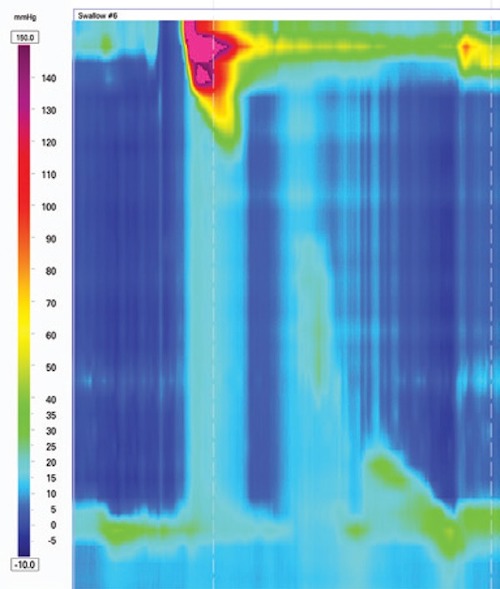
IEM Manometry 1
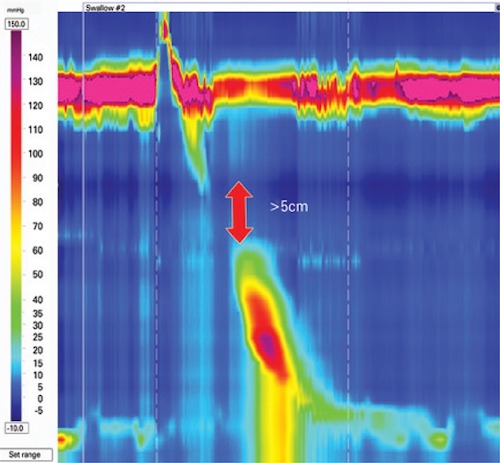
Fragmented Peristalsis Manometry 1
References
- Herbella FA, Armijo PR, Patti MG. A pictorial presentation of 3.0 Chicago Classification for esophageal motility disorders. Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2016 Jul-Sep;14(3):439-442. (License: CC BY-4.0)
- Samo S, Carlson DA, Kahrilas PJ, Pandolfino JE. Ineffective Esophageal Motility Progressing into Distal Esophageal Spasm and Then Type III Achalasia. ACG Case Rep J. 2016 Dec 21;3(4):e183. (License: CC BY-NC-ND-4.0)