Femoral Hernia
Richard Davis Winters, MD
The Operative Review of Surgery. 2023; 1:310-313.
Table of Contents
Definitions and Descriptors
Basics
- Definition: Hernia Through the Femoral Canal
- 4x More Common in Women 1
- Inguinal Hernias are Still the Most Common in Females Overall
- Highest Risk of Strangulation 2
- 22% Risk at 3 Months
- 45% Risk at 21 Months
- 40% Present Emergently as Incarceration or Strangulation 3
Additional Descriptors
- Reduction en Masse: Hernia Sac is Reduced but the Bowel is Still Incarcerated within the Reduced Sac 4
- Causes a Risk of Progression to Ischemia and Necrosis Despite Reduction
- “Classically” Describing an Inguinal Hernia 4
- Richter Hernia: Only the Antimesenteric Border of the Bowel Wall is Herniated 5
- Also Described as a “Partial Enterocele” 5
- May Not Cause Obstruction as Bowel Contents Can Pass Through the Intraperitoneal Portion of the Bowel
- High Risk of Incarceration and Strangulation of the Herniated Portion
- Littre Hernia: Hernia Contains a Meckel Diverticulum 6
- De Garengeot Hernia: Femoral Hernia Containing the Appendix 7
- May Be Confused with an Amyand Hernia (Inguinal Hernia Containing the Appendix) 8
- Sliding Hernia: A Retroperitoneal Organ is Included as Part of the Hernia Sac 9
- Most Common Organs:
- Males: Sigmoid Colon and Cecum
- Females: Ovary and Fallopian Tube (Ligate the Round Ligament and Return the Ovary at Surgery)
- Most Common Organs:
Other Groin Hernias
- Inguinal Hernia
- Obturator Hernia
- Athletic Pubalgia (Sports Hernia)
- *See Athletic Pubalgia (Sports Hernia)
- Not a True Hernia
- *96% of Groin Hernias are Inguinal, 4% are Femoral 10,11
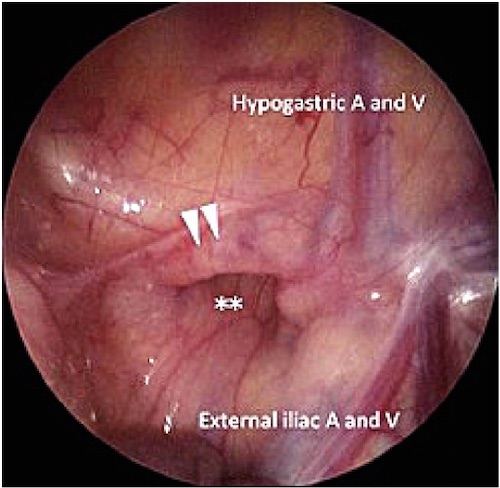
Femoral Hernia Seen on Laparoscopy 12
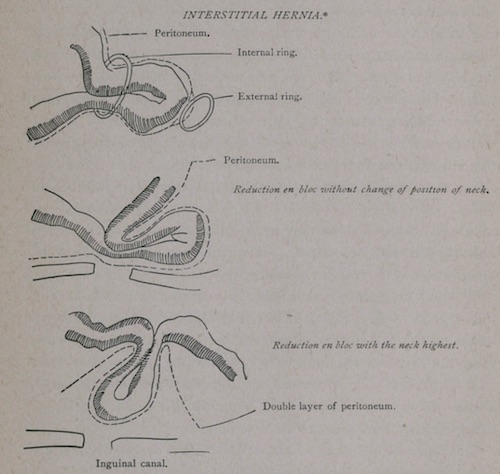
Reduction en Masse 4
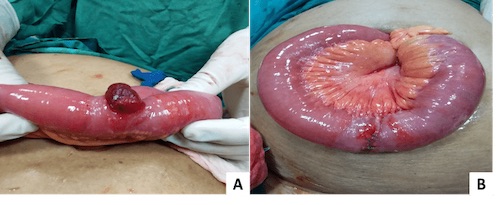
Richter Hernia 13
Presentation and Diagnosis
Presentation
- Groin Bulge
- Groin Pain and Discomfort
- May be Worsened by Coughing or Straining
- Symptoms of Bowel Obstruction
- Nausea and Vomiting
- Constipation
- Risk for Bowel Incarceration, Strangulation, and Necrosis
- Overlying Skin Can Develop Erythema, Ischemia, or Ulceration Due to Excessive Pressure
Diagnosis
- Generally a Clinical Diagnosis
- Often Difficult to Differentiate from an Inguinal Hernia on Physical Exam
- Hernia Found Inferior to the Inguinal Ligament and Medial to the Femoral Vessels
- Small Hernias May Be Difficult to Palpate
- More Difficult to Diagnose in Females and Obese
- Imaging May Be Required if Uncertain
- US – More Cost Effective and Allows Dynamic Assessment with Valsalva (Operator Dependent)
- CT – Allows Better Evaluation of Large and Complex Defects
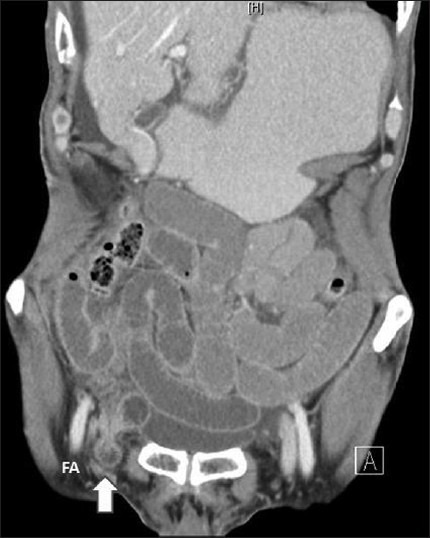
Femoral Hernia Seen on CT Medial to the Femoral Vessels 14
Treatment
Treatment
- All Should Undergo Early Surgical Repair Regardless of Symptoms
- Higher Risk of Incarceration and Strangulation Preclude Watchful Waiting
- Higher Risk for Recurrence Than After Inguinal Hernia Repairs 15,16
- Due Partially to Increased Rates of Emergency Surgery and Overall Complications
Surgical Technique
- Open Hernia Repair
- Open Hernia Repairs are Traditionally Done by a McVay Repair
- May Require Division of the Inguinal Ligament to Reduce Bowel
- Bassini and Lichtenstein Repairs Do Not Close the Femoral Canal
- Other Open Options:
- Trans-Inguinal Preperitoneal (TIPP/Kugel) Repair
- Anterior Mesh Plug
- *See Open Inguinal Hernia Repair
- Open Hernia Repairs are Traditionally Done by a McVay Repair
- Minimally Invasive (Laparoscopic/Robotic) Hernia Repair
- Generally Preferred Over Open Repairs for Elective Cases if Possible 17,18
- Lower Recurrence Rates
- Better to Identify Occult Hernias
- *See Minimally Invasive Inguinal Hernia Repair
- Generally Preferred Over Open Repairs for Elective Cases if Possible 17,18
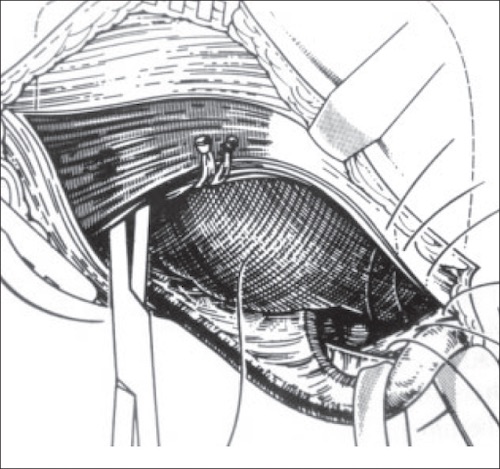
McVay Repair with Placement of a Preperitoneal Mesh 19
References
- Nilsson E, Kald A, Anderberg B, Bragmark M, Fordell R, Haapaniemi S, Heuman R, Lindhagen J, Stubberöd A, Wickbom J. Hernia surgery in a defined population: a prospective three year audit. Eur J Surg. 1997 Nov;163(11):823-9.
- Gallegos NC, Dawson J, Jarvis M, Hobsley M. Risk of strangulation in groin hernias. Br J Surg. 1991 Oct;78(10):1171-3.
- McIntosh A, Hutchinson A, Roberts A, Withers H. Evidence-based management of groin hernia in primary care–a systematic review. Fam Pract. 2000 Oct;17(5):442-7.
- Mynter H. Reduction En Masse. Buffalo Med Surg J. 1888 Dec;28(5):245-250.
- Treves F. Richter’s Hernia or Partial Enterocele. Med Chir Trans. 1887;70:149-67.
- Pinto J, Viana CM, Pereira A, Falcão J. Littré’s hernia. BMJ Case Rep. 2019 Feb 28;12(2):e228784.
- Kalles V, Mekras A, Mekras D, Papapanagiotou I, Al-Harethee W, Sotiropoulos G, Liakou P, Kastania A, Piperos T, Mariolis-Sapsakos T. De Garengeot’s hernia: a comprehensive review. Hernia. 2013 Apr;17(2):177-82.
- Lee CH, Chien LJ, Shen CY, Su YJ. Amyand’s hernia. Am J Med Sci. 2022 Oct;364(4):e8-e9.
- Komorowski AL, Moran-Rodriguez J, Kazi R, Wysocki WM. Sliding inguinal hernias. Int J Surg. 2012;10(4):206-8.
- Rutkow IM, Robbins AW. Demographic, classificatory, and socioeconomic aspects of hernia repair in the United States. Surg Clin North Am. 1993 Jun;73(3):413-26.
- Lockhart K, Dunn D, Teo S, Ng JY, Dhillon M, Teo E, van Driel ML. Mesh versus non-mesh for inguinal and femoral hernia repair. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Sep 13;9(9):CD011517.
- Tainaka T, Uchida H, Ono Y, Tanano A, Shirota C, Yokota K, Murase N, Makita S, Shirotsuki R. A new modification of laparoscopic percutaneous extraperitoneal closure procedure for repairing pediatric femoral hernias involving a special needle and a wire loop. Nagoya J Med Sci. 2015 Aug;77(3):531-5. (License: CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
- Abo-elmagd A, Ahmed K. Richter Paraumbilical Hernia Managed by Invagination: A Case Report and Review of Literature. Am J Surg Case Reports. 2019. (License: CC Unspecified)
- Sucandy I, Kolff JW. Incarcerated femoral hernia in men: incidence, diagnosis, and surgical management. N Am J Med Sci. 2012 Nov;4(11):617-8. (License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0)
- Dahlstrand U, Wollert S, Nordin P, Sandblom G, Gunnarsson U. Emergency femoral hernia repair: a study based on a national register. Ann Surg. 2009 Apr;249(4):672-6.
- Glassow F. Femoral hernia. Review of 2,105 repairs in a 17 year period. Am J Surg. 1985 Sep;150(3):353-6.
- Bay-Nielsen M, Kehlet H, Strand L, Malmstrøm J, Andersen FH, Wara P, Juul P, Callesen T; Danish Hernia Database Collaboration. Quality assessment of 26,304 herniorrhaphies in Denmark: a prospective nationwide study. Lancet. 2001 Oct 6;358(9288):1124-8.
- Andresen K, Bisgaard T, Kehlet H, Wara P, Rosenberg J. Reoperation rates for laparoscopic vs open repair of femoral hernias in Denmark: a nationwide analysis. JAMA Surg. 2014 Aug;149(8):853-7.
- Alexandre JH, Bouillot JL, Dupin P, Aouad K, Bethoux JP. Cure of inguinal hernias with large preperitoneal prosthesis: Experience of 2,312 cases. J Minim Access Surg. 2006 Sep;2(3):134-8. (License: CC BY 2.0)