Biliary Tract: Gallbladder Mass & Cancer
Gallbladder Nodules/Deposits
Cholesterolosis
- Scattered Cholesterol Deposits on Wall
- Physical Appearance of “Strawberry Gallbladder”
- Not Premalignant
- US: Multiple Hyperechoic & Pedunculated Masses with No Posterior Shadowing
- Tx: Cholecystectomy
Adenomyomatosis
- Thickened Nodule of Rokitansky-Aschoff Sinus
- Not Premalignant (Although Recent Reports Question Pre-Malignancy)
- Tx: Cholecystectomy
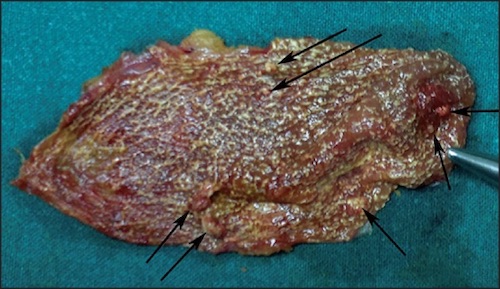
Cholesterolosis of the Gallbladder 1
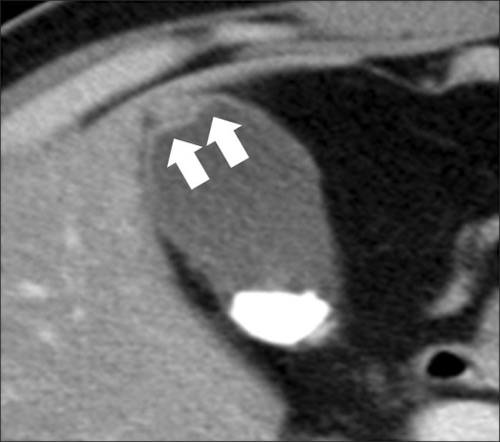
Adenomyomatosis of the Gallbladder 2
Gallbladder Polyps
Types
- Cholesterol Polyp (Most Common)
- Inflammatory
- Adenoma
Malignancy Risk Factors
- Size
- > 1 cm (43-77% Risk)
- > 2 cm (Nearly 100% Risk)
- Age > 50
- Associated Gallstones
- Solitary Polyp (vs Multiple)
Diagnosis
- Often Identified on US
- Should be Evaluated with CT or MRI
Treatment
- < 1 cm & ASx: Monitor with US
- Cholecystectomy if: PSC/UC
- > 1 cm or Sx: Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
- If > 2 cm: Consider Extended Cholecystectomy
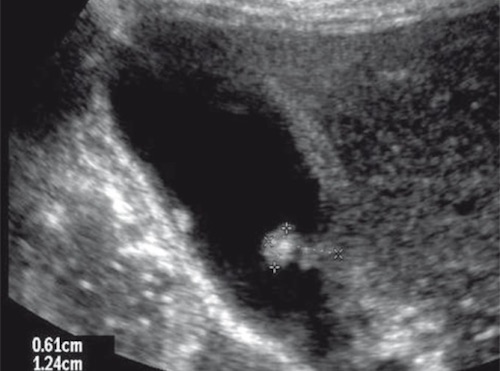
Gallbladder Polyp on US 3
Gallbladder Adenocarcinoma
Basics
- The Most Common Biliary CA
- Mets to Liver
- Often Diagnosed at Advanced Stage (Poor Prognosis)
- 5-Year Survival:
- Overall: 5-19%
- Early (Stage I/II): 50-64%
- Stage I: Almost 100%
- Stage II: 50%
- Late (Stage III/IV): 10-24%
Risk Factors
- Large Stones (> 3 cm) – Strongest Risk Factor
- Female Sex
- Polyps
- Anomalous Pancreaticobiliary Junction
- Chronic Infection
- Obesity
Presentation
- Majority (70%) Found Incidentally at Surgery for Gallstone Disease
- Frequency: 1-2% of Cases
- Sx: Nonspecific
- Courvoisier Sign – Painless Palpable Gallbladder with Jaundice
- Indicates Malignancy (Pancreas/Gallbladder)
- *Historical Sign with Limited Utility and Many Exception
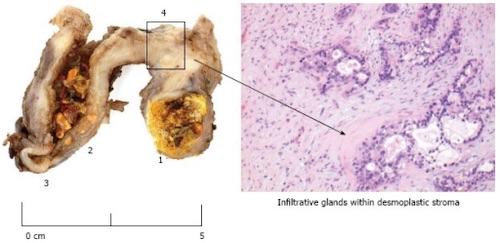
Gallbladder Carcinoma 4
TNM Staging – AJCC 8
- TNM
| T | N | M | |
| I | A – Lamina Propria Invasion
B – Muscularis Invasion |
1-3 LN | Distant Mets |
| II | A – Invades Perimuscular Connective Tissue on Peritoneal Side
B – Invades Perimuscular Connective Tissue on Hepatic Side |
≥ 4 LN | |
| III | Invades Liver/Organs | ||
| IV | Invades Portal Vein, Hepatic Artery or ≥ 2 Extrahepatic Organs |
- *Nodes Were Previously Based on Location (AJCC 7)
- N1 Was Previously: Cystic Duct, CBD or Portal Triad LN
- N2 Was Previously: Aortic, SMA or Celiac LN
- Stage
| T | N | M | ||
| I | T1 | N0 | M0 | |
| II | A | T2a | N0 | M0 |
| B | T2b | N0 | M0 | |
| III | A | T3 | N0 | M0 |
| B | T1-3 | N1 | M0 | |
| IV | A | T4 | N0-1 | M0 |
| B | Any T | N2 | M0 | |
| Any T | Any N | M1 | ||
Treatment
- If Discovered Intraoperatively: Abort Procedure & Complete Staging Prior to Return to OR
- T1a (Confined to Mucosa): Open Cholecystectomy
- *Some Preform Laparoscopically Although There is a Risk of Tumor Implants at Trocar Sites
- *If Done Laparoscopic – Do Not Resect Trocar Sites (No Improved Survival)
- ≥ T1b (Invades Muscle): Extended Cholecystectomy & Portal Lymphadenectomy
- Resection:
- Formal Segment IVb & V Anatomic Liver Resection – Historical Preference Now Fallen Out of Favor
- Extended Cholecystectomy – Nonanatomic Resection Extending into the Gallbladder Fossa
- Portal Lymphadenectomy Should Harvest ≥ 6 Lymph Nodes
- If Found on Postoperative Pathology: Return to OR & Complete Resection
- If Extends to CBD or Positive Cystic Duct Margin (Frozen Section): CBD Resection & Hepaticojejunostomy
- Resection:
- Unresectable or Mets: Chemotherapy
- Surgery Absolute Contraindications:
- Aortic, SMA or Celiac LN
- Distant Metastases
- Malignant Ascites
- Encasement of Major Vessels
- Surgery Absolute Contraindications:
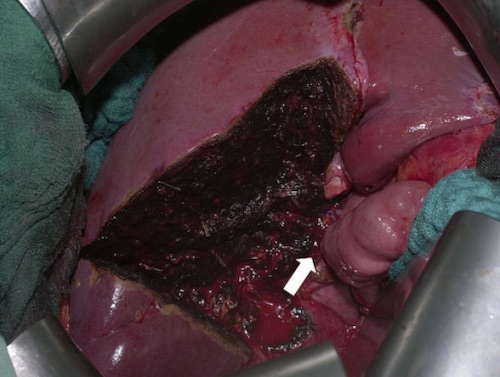
Formal Segment IVb & V Liver Resection 5
References
- Yadav S, Jategaonkar P, Bijlani M. Gallbladder polyps: an ambiguous cause of biliary colic. Ann Med Health Sci Res. 2014 Sep;4(Suppl 3):S332-3. (License: CC BY-NC-SA-3.0)
- Kim BS, Oh JY, Nam KJ, Cho JH, Kwon HJ, Yoon SK, Jeong JS, Noh MH. Focal thickening at the fundus of the gallbladder: computed tomography differentiation of fundal type adenomyomatosis and localized chronic cholecystitis. Gut Liver. 2014 Mar;8(2):219-23. (License: CC BY-NC-3.0)
- Walas MK, Skoczylas K, Gierbliński I. Standards of the Polish Ultrasound Society – update. The liver, gallbladder and bile ducts examinations. J Ultrason. 2012 Dec;12(51):428-45. (License: CC BY-NC-ND-3.0)
- Patel K, Dajani K, Iype S, Chatzizacharias NA, Vickramarajah S, Singh P, Davies S, Brais R, Liau SS, Harper S, Jah A, Praseedom RK, Huguet EL. Incidental non-benign gallbladder histopathology after cholecystectomy in an United Kingdom population: Need for routine histological analysis? World J Gastrointest Surg. 2016 Oct 27;8(10):685-692. (License: CC BY-NC-4.0)
- Scheingraber S, Justinger C, Stremovskaia T, Weinrich M, Igna D, Schilling MK. The standardized surgical approach improves outcome of gallbladder cancer. World J Surg Oncol. 2007 May 21;5:55. (License: CC BY-2.0)