General Abdomen: Retroperitoneal Fibrosis
Retroperitoneal Fibrosis (Ormond Disease)
Causes
- Primary/Idiopathic (Most Common)
- Secondary – Drugs, Malignancy, Infection, Radiation or Surgery
- Most Common Drug: Methysergide (Sansert) – Ergot Alkaloid Used for Migraines
Presentation
- Pain (Most Common Symptom)
- Trapped Ureters – Deviated Medially
- Lateral Deviation More Likely Related to Malignancy
- Renal Impairment/Hydronephrosis
- Lymph Obstruction
- Claudication or Mesenteric Ischemia
Diagnosis
- Dx: CT
- Require Bx if Atypical or Concern for Malignancy
- Rarely Used: IV Urography or Pyelography
Treatment
- Management of Fibrosis:
- Idiopathic Cause: Steroids/Immunosuppression
- Secondary Cause: Treat Underlying Etiology
- Management of Obstruction/Renal Impairment:
- Primary Treatment: Stent vs. Surgery (Ureterolysis & Wrap Ureter in Omentum)
- If Active Infection Present: Consider Percutaneous Nephrostomy with Delayed Definitive Surgery
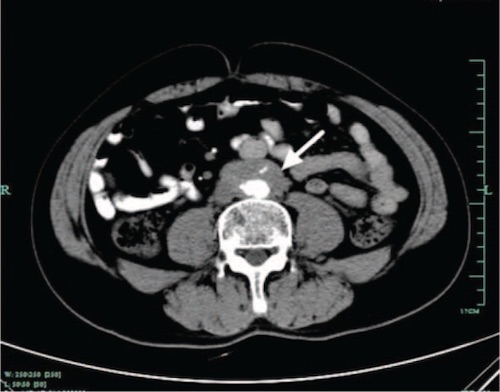
CT Showing Periaortic Soft Tissue Mass (Arrow) Consistent with Retroperitoneal Fibrosis 1
References
- Lei WH, Xin J, Shao CX, Mao MF, Zhu CY, Wu CF, Jin L. IgG4-related Kidney Disease Mimicking Malignant Ureter Tumor: Case Report and Literature Review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Jan;95(3):e2550. (License: CC BY-ND-4.0)