Endocrine: Goiter
Goiter
Definition
- Definition: Any Enlargement of the Thyroid Gland
- Types:
- Toxic: Functional
- Nontoxic: Not Functional
Causes
- Toxic Causes:
- Nontoxic Causes:
- Iodine Deficiency – Most Common Identified Cause
- Physiologic (Puberty or Pregnancy)
- Goitrogens (Bamboo Sheets, Cabbage, Maize & Sweet Potatoes)
- Dysmorphogenesis
- Radiation Exposure
- Low Grade TSH Stimulation
Substernal Goiter Origins
- Primary (Rare)
- Originates in Mediastinum
- Vessels from Innominate Artery
- Secondary (More Common)
- Migrates to Mediastinum
- Vessels from Thyroid Arteries
Presentation
- Toxic Symptoms:
- Nontoxic Symptoms: Mostly Due of Mass Effect/Compression
- Neck Pain
- Dysphagia
- Dyspnea
- Hoarseness
Diagnosis
- Initial Evaluation: US & Labs (TSH & Free T4/T3)
- Suspicious or Nonfunctioning Nodules Require FNA
Treatment
- If Small & Asymptomatic: Nothing
- Primary Treatment: Surgery
- Indications:
- Large > 4 cm
- Dysphagia
- Airway Compromise
- Local Discomfort
- Substernal Location (Risk of Hidden Malignancy & Further Extension Can Require More Extensive Surgery in the Future)
- Approach:
- Unilateral Enlargement: Lobectomy
- Bilateral Enlargement: Total/Near-Total Thyroidectomy
- Substernal Goiters Can Mostly Be Removed Through a Cervical Incision & Rarely Require Sternotomy
- Indications:
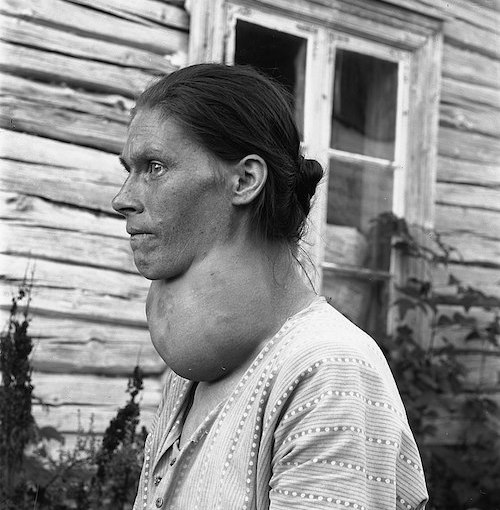
Goiter 1
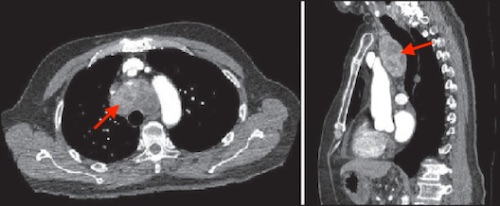
Substernal Goiter (Arrow) on CT 2
References
- Wikimedia Commons. (License: Public Domain)
- Suut S, Al-Ani Z, Allen C, Rajiah P, Durr-E-Sabih, Al-Harbi A, Al-Jahdali H, Khan AN. Pictorial essay of radiological features of benign intrathoracic masses. Ann Thorac Med. 2015 Oct-Dec;10(4):231-42. (License: CC BY-NC-SA-3.0)