Large Intestine: Anatomy & Physiology
Anatomy
Layers
- Mucosa (Columnar Epithelium, Lamina Propria, Muscularis Mucosa)
- Submucosa
- Muscularis Propria (Inner Circular, Outer Longitudinal)
- Serosa
Structure
- Portions
- Ascending Colon (Retroperitoneal)
- Appendix
- Cecum – Most Common Site of Non-Iatrogenic Perforation
- Due to Law of LaPlace: ΔP = γ/r
- Change in Pressure = Surface Tension / Radius
- *Largest Radius will Have Highest Surface Tension
- Due to Law of LaPlace: ΔP = γ/r
- Transverse Colon
- Descending Colon (Retroperitoneal)
- Sigmoid Colon
- Ascending Colon (Retroperitoneal)
- Structures
- Crypts of Lieberkühn (Paneth Cells): Mucin Secreting Goblet Cells of the Small Intestine & Colon
- Plicae Semiluminares: Transverse Bands/Folds Between Haustra
- Haustra: Small Pouches Formed by Plicae Semiluminares
- Taenia Coli: 3 Bands That Run Along the Colon
- Broaden at Rectosigmoid Junction to Completely Encircle
- Taenia Libera (Free Taenia Coli)
- Anterior in Cecum, Ascending, Descending & Sigmoid Colon
- Inferior in the Transverse Colon
- Taenia Mesocolica (Mesocolic Taenia Coli)
- Posteromedial in Cecum, Ascending, Descending & Sigmoid Colon
- Posterior in Transverse Colon
- Taenia Omentalis (Omental Taenia Coli)
- Posterolateral in Cecum, Ascending, Descending & Sigmoid Colon
- Anterosuperior in Transverse Colon
- Ileocecal Fold/Veil (Bloodless Fold of Treves) – Peritoneal Fold Between the Ileum & Cecum
- Mesoappendix – Mesentery of the Appendix
Vascular Supply
- Arterial Supply
- 80% of Flow is Supplied to the Mucosa & Submucosa
- Colon is More Sensitive to Ischemia than Small Bowel (Less Collaterals)
- *See Vascular Surgery: Abdominal Vasculature
- Venous Flow
- IMV into Splenic Vein
- Splenic Vein & SMV Become the Portal Vein (Behind the Pancreas)
- Lymphatics
- Follows Arterial Flow
- Superior & Inferior Mesenteric Lymph Nodes Drain to the Pre-Aortic Lymph Nodes
- Pre-Aortic Lymph Nodes Drain to the Cisterna Chyli
Nerves
- Meissner’s/Submucosal Plexus: Inner Submucosa
- Auerbach’s/Myenteric Plexus: Outer Muscularis Propria
- Pelvic Splanchnic Nerves: Parasympathetic Innervation
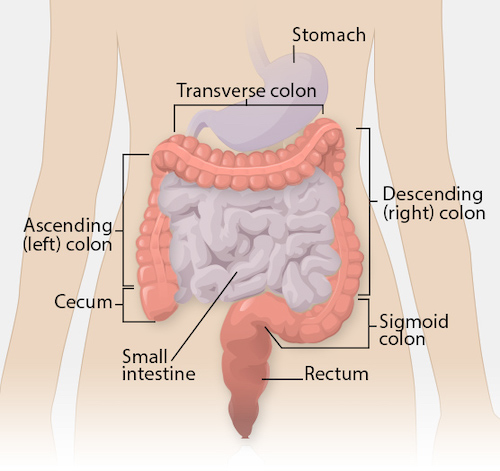
Colon Anatomy 1
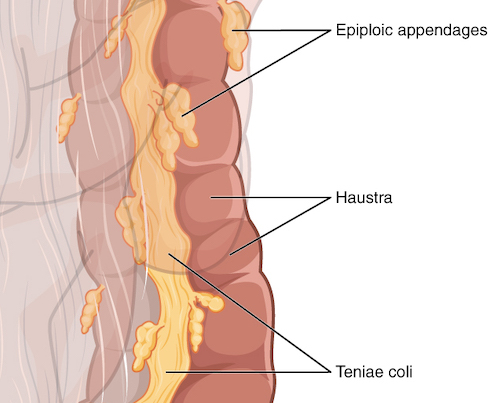
Taenia Coli & Haustra 2
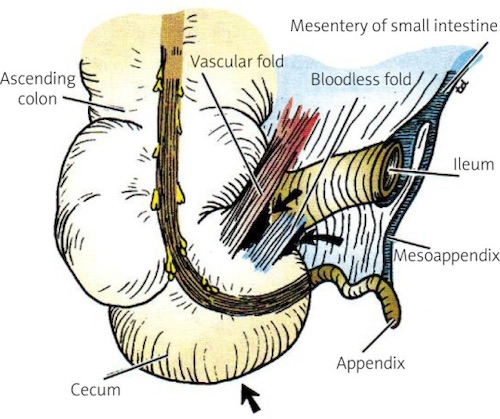
Anatomy of the Cecum & Appendix 3
Physiology
Physiology
- Colon Secretes K; Reabsorbs NaCl/H2O
- Active Na/K-ATPase
- Passive H2O Absorption (Jejunum Absorbs Majority of H2O)
- Mostly Right Colon
- Colonocyte Main Nutrient: Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFA)
- Produced by Bacterial Fermentation in the Colon
- Acetate, Butyrate & Propionate
- Ascending Colon Has the Greatest Absorptive Capacity of Fluid in the Colon
GI Microflora
References
- CDC. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-SA-4.0)
- OpenStax College. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-3.0)
- Bakar SM, Shamim M, Alam GM, Sarwar M. Negative correlation between age of subjects and length of the appendix in Bangladeshi males. Arch Med Sci. 2013 Feb 21;9(1):55-67.(License: CC BY-NC-ND-3.0)