Liver: Abscess
Pyogenic Abscess
Basics
- Most Common Visceral Abscess
- Source:
- From Biliary Tract (Most Common)
- From Portal Vein After Bowel Perforation & Peritonitis
- From Arteries with Bacteremia
- Most Common in Right Lobe
Organisms
- Most Polymicrobial
- Organisms:
- E. coli (Most Common)
- Klebsiella (Most Common in Asia)
- Streptococci
- Staphylococcus
Presentation
- Fever
- Abdominal Pain
- Leukocytosis
- Elevated LFT’s
CT Findings
- *See Liver: Mass CT Characteristics
- Well-Defined
- Central Hypoattenuation
- Rim Enhancement with Peripheral Edema
Treatment
- Tx: ABX & Drainage
- Single & Unilocular: Percutaneous Drainage
- If Fails: Upsize Drain
- Recurrence Most Likely from Clogged or Migrated Drain
- Multiple or Multilocular: Surgical Drainage
- Multiple Small Abscesses: Consider Long-Term ABX (4-6 Weeks)
- *Although Surgical Drainage is the Traditional Approach Some Now Consider Percutaneous Drainage First & Surgical Drainage Only if Fails
- Single & Unilocular: Percutaneous Drainage
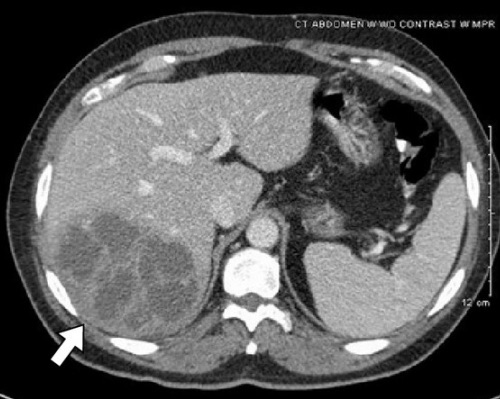
Pyogenic Liver Abscess 1
Amebic Abscess
Basics
- Parasite: Entamoeba histolytica
- Amebic Colitis (Primary Infection) Transmits Through Portal Vein to Liver
- Generally Migrants/Travelers From Endemic Areas
- Endemic Areas: Mexico, Central/South America, Africa & India Mn
- Most Common in Posterior Right Lobe
Risk Factors
- Adult Men (Most Common)
- HIV/Immunosuppressed
- Alcoholism
- Pregnancy
- Malnutrition
Presentation
- Abdominal Pain
- Fever
- Weight Loss
- History of Dysentery
Diagnosis
- Dx: CT/US & Serology
- Stool Cx Usually Negative (Simultaneous Liver Abscess & Colitis is Uncommon)
- Aspirate Cx Can be Negative (Parasite Only in Peripheral Rim)
- Anchovy Past Fluid
CT Findings
- *See Liver: Mass CT Characteristics
- In Peripheral Liver
- No Rim Enhancement
- Peripheral Edema
Treatment
- Primary Tx: Metronidazole Mn
- If > 10 cm, Risk of Rupture or ABX Failure: Percutaneous Drainage
- If Ruptures: Surgery
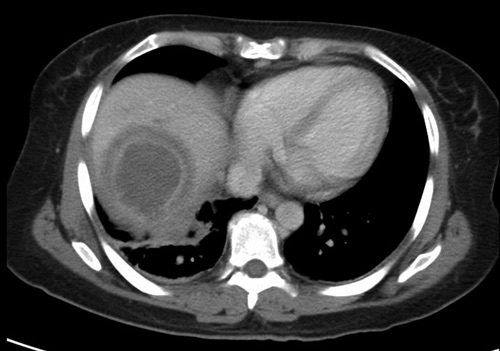
Amebic Abscess 2
Hydatid Cyst
Basics
- Parasite: Echinococcus
- Source: Dogs; Sheep are Carriers
- Rupture Will Cause Anaphylactic Shock
Diagnosis
- Dx: Serology & US
- Double Wall – Inner Cyst Wall/Hydatid Sand Separate from Hydatid Membrane
CT Findings
- *See Liver: Mass CT Characteristics
- Inner Wall Infoldings
- Double-Walled with Calcified Rim
- May See Septa/Daughter Cysts
Treatment
- Primary Treatment: Albendazole Mn
- Definitive Treatment:
- Unilocular < 5 cm: Albendazole Alone
- Multilocular, > 10 cm or High Rupture Risk: Surgical Excision (Need Entire Wall)
- *May Consider PAIR (Puncture, Aspiration, Injection, Reaspiration) if Unilocular 5-10 cm
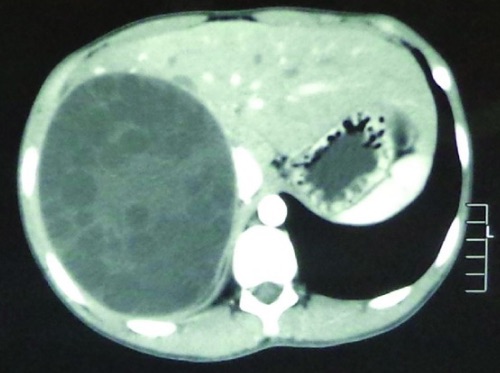
Hydatid Cyst of the Liver 3
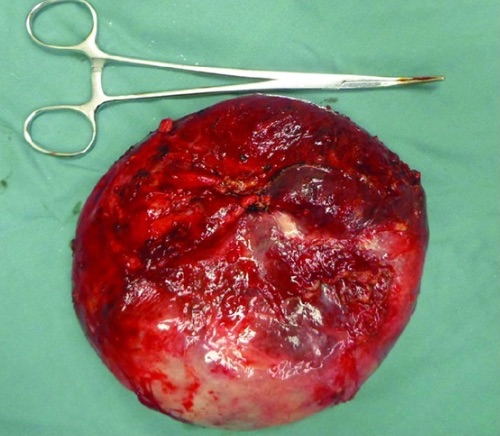
Hydatid Cyst of the Liver 3
Fungal Abscess
Basics
- Most Common in Immunocompromised (Often Following Chemotherapy for Hematologic Malignancy)
- Most Common Fungi:
- Candida – Most Common
- Aspergillus
- Cryptococcus
- Often Mixed Fungi & Bacteria
- Presentation:
- Fever
- Jaundice
- RUQ Pain
Treatment
- Primary Tx: Percutaneous Drainage & Antifungals
- First-Line Antifungals: Micafungin or Caspofungin
Mnemonics
Entamoeba vs Echinococcus Abscesses
- “Mexican Fire Ants & Bent Rhino Horns”
- Amebic/Entamoeba:
- Mexican: “Mexico Connection”
- Fire: (F-F) Flagyl Treatment
- Ants: (A-A) Amebic & (Ant:Ent) Entamoeba
- Hydatid/Echinococcus:
- Bent: Al-BEND-azole
- R-HINO: Ec-HINO-coccus
- Horns: (H-H) Hydatid
References
- Livingston LV, Perez-Colon E. Streptococcus intermedius Bacteremia and Liver Abscess following a Routine Dental Cleaning. Case Rep Infect Dis. 2014;2014:954046. (License: CC BY-3.0)
- Garvin KW, Willig JH. Amebic liver abscess. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2010 Nov;83(5):961. (License: CC BY-2.5)
- Ma Z, Yang W, Yao Y, Liu Q. The adventitia resection in treatment of liver hydatid cyst: a case report of a 15-year-old boy. Case Rep Surg. 2014;2014:123149. (License: CC BY-3.0)