Liver: Anatomy & Physiology
Structure
Couinaud Segments Mn
- Anatomical Divisions – Each Has Own Vascular Inflow, Outflow & Biliary Drainage
- Caudate Lobe
- I – Entire Caudate
- Left Lobe
- II – Superior Left Lateral
- III – Inferior Left Lateral
- IVa – Superior Left Medial
- IVb – Inferior Left Medial (Quadrate)
- Right Lobe
- V – Inferior Right Anteromedial
- VI – Inferior Right Posterolateral
- VII – Superior Right Posterolateral
- VIII – Superior Right Anteromedial
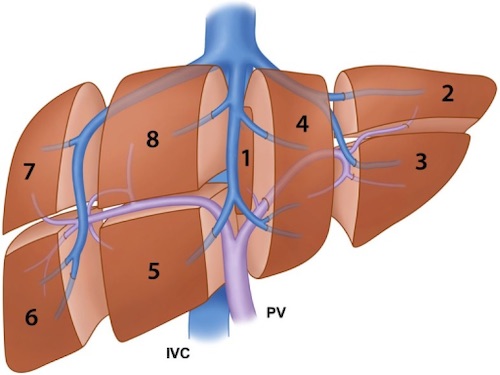
Couinaud Segments 1
Structure
- Porta Hepatis/Portal Fissure
- Transverse Fissure Between Caudate (I) & Quadrate Lobes (IVb)
- On Visceral Surface
- Cantlie’s Line
- Imaginary Division Separating Left & Right Lobes
- From Gallbladder Fossa to Middle Hepatic Vein/IVC
- Ligaments
- Falciform Ligament
- Separates Medial & Lateral Left Lobe
- Attaches to Anterior Abdominal Wall & Extends to Umbilicus
- Contains Ligamentum Teres
- Ligamentum Teres (Round Ligament)
- Contained in Free Edge of Falciform Ligament
- Carries Remnant Umbilical Vein
- Ligamentum Venosum
- Remnant Ductus Venosus
- From Ligamentum Teres to IVC
- Falciform Ligament
- Portal Triad
- Contained within Hepatoduodenal Ligament
- Enters Porta Hepatis
- Contents: Mn
- Lateral: Bile Ducts
- Medial: Proper Hepatic Artery
- Posterior: Portal Vein
- *A Pulse Felt Posterior-Lateral May Be from a Replaced Right Hepatic Artery from the SMA
- Epiploic Foramen (Foramen of Winslow)
- Entrance of Lesser Sac
- Borders:
- Anterior: Hepatoduodenal Ligament
- Posterior: IVC
- Superior: Caudate Lobe of Liver
- Inferior: Duodenum
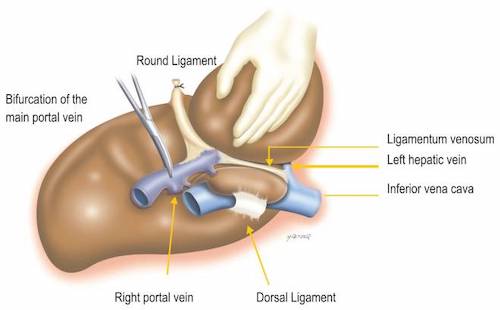
Ligamentum Venosum & Teres 2
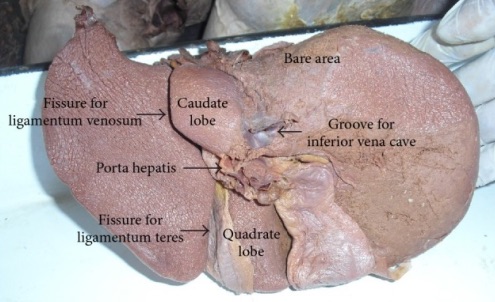
Underside of the Liver Showing Fissures of the Ligamentum Teres & Venosum 3
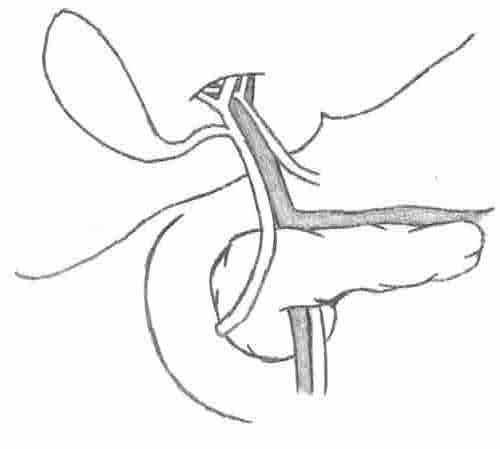
Portal Triad
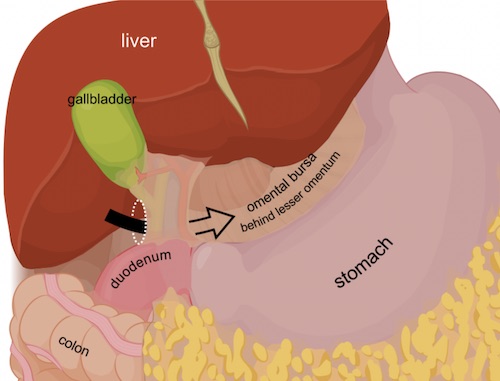
Foramen of Winslow 4
Blood Supply
Arterial Supply (Supplies 25%)
- General Structure
- Proper Hepatic Artery Branches to Left & Right Hepatic Arteries
- Middle Hepatic Artery Branches off Left
- *See Vascular Surgery: Abdominal Vasculature
- Most Common Variants:
- Replaced Right Hepatic: From SMA
- Overall Most Common Hepatic Artery Anomaly
- May Be Seen Posterior-Lateral at the Porta Hepatis
- Replaced Left Hepatic: From Left Gastric Artery (In Gastrohepatic Ligament)
- Replaced Right Hepatic: From SMA
- Biliary System Depends On: Hepatic Artery
Portal Supply (Supplies 75%)
- General Structure
- IMV Enters Splenic Vein
- Splenic Vein & SMV Combine to Form Portal Vein
- Portal Vein Branches into Left & Right Portal Veins
- Coronary Veins (From Left Gastric Vein)
- Shunt from Portal Vein to Lower Esophagus & Azygous System
- Cause of Esophageal Varices
- Portal Vein Has No Valves
Venous Drainage
- Segment I
- Drains Directly into IVC
- Left Hepatic Vein
- Drains: Segments II & III
- Drains into: IVC
- Middle Hepatic Vein
- Drains: Segments VIA, VIB, V & VIII
- Drains into: Left Hepatic Vein
- Right Hepatic Vein
- Drains: Segments V, VI, VII & VIII
- Drains into: IVC
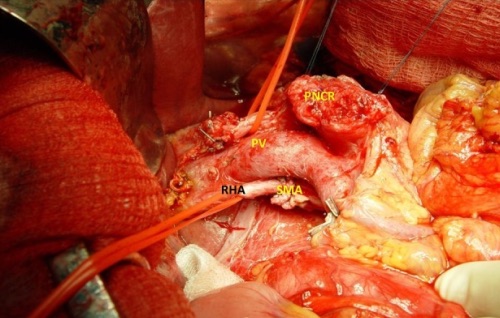
Replaced Right Hepatic Artery (Off SMA) 5
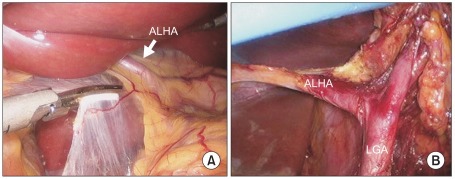
Replaced Left Hepatic Artery (Off Left Gastric) 6
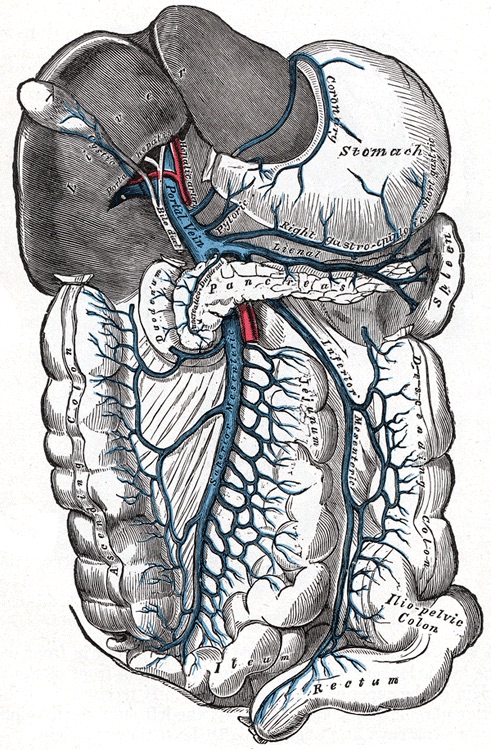
Portal Venous System 7
Lobules
Lobules
- Hexagonal Structures Forming Liver Parenchyma
- Hepatic Vein at Center & Portal Triad at Corners
- Acinar Zones I (Corners), II (Middle) & III (Center)
- Follows Blood Flow
- Middle Most Sensitive to Ischemia
Tracts
- Sinusoid
- Inflow Tract
- Contains Blood from Portal & Arterial System
- Space of Disse
- Perisinusoidal Space
- Facilitates Absorption
- Bile Canaliculus
- Outflow Tract
- Contains Bile
- Site of Alkaline Phosphatase
- Periportal Space of Mall
- Space Between the Portal Canal Stroma & Outermost Hepatocytes
- One of the Sites That Generates Lymph
Specific Cells
- Hepatocytes
- The Primary Functional Cell
- Conjugate Bilirubin
- Remove Metabolic Wastes
- Store Glycogen
- Main Energy Source: Ketones
- Kupffer Cells
- Macrophages within the Sinusoids
- Ito/Stellate Cells
- Normally Quiescent (Store Vitamin A)
- Mediates Fibrosis
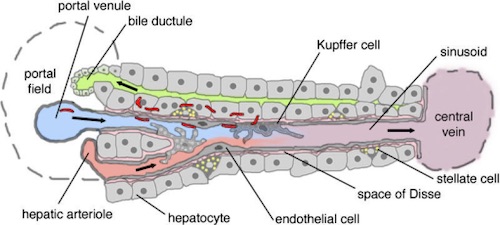
Hepatic Lobule 8
Mnemonics
Liver Segments
- “Handy” Mnemonic Using Fist & Fingers
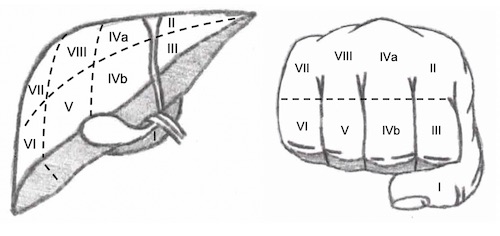
Portal Triad Orientation
- *P-P: Portal is Posterior
- Bile Ducts are Lateral (From the Gallbladder which is Lateral)
- Proper Hepatic Artery is Medial (From the Aorta which is Medial)
References
- Orcutt ST, Kobayashi K, Sultenfuss M, Hailey BS, Sparks A, Satpathy B, Anaya DA. Portal Vein Embolization as an Oncosurgical Strategy Prior to Major Hepatic Resection: Anatomic, Surgical, and Technical Considerations. Front Surg. 2016 Mar 11;3:14. (License: CC BY-4.0)
- Chaib E, Ribeiro MA Jr, Souza YE, D’Albuquerque LA. Anterior hepatic transection for caudate lobectomy. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2009;64(11):1121-1125. (License: CC BY-4.0)
- Vinnakota S, Jayasree N. A new insight into the morphology of the human liver: a cadaveric study. ISRN Anat. 2013;2013:689564. (License: CC BY-4.0)
- Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-SA-3.0)
- Noussios G, Dimitriou I, Chatzis I, Katsourakis A. The Main Anatomic Variations of the Hepatic Artery and Their Importance in Surgical Practice: Review of the Literature. J Clin Med Res. 2017 Apr;9(4):248-252. (License: CC BY-NC-4.0)
- Kim J, Kim SM, Seo JE, Ha MH, An JY, Choi MG, Lee JH, Bae JM, Kim S, Jeong WK, Sohn TS. Should an Aberrant Left Hepatic Artery Arising from the Left Gastric Artery Be Preserved during Laparoscopic Gastrectomy for Early Gastric Cancer Treatment? J Gastric Cancer. 2016 Jun;16(2):72-7. (License: CC BY-NC-4.0)
- Gray H. Anatomy of the Human Body (1918). Public Domain.
- Frevert U, Engelmann S, Zougbédé S, Stange J, Ng B, Matuschewski K, Liebes L, Yee H. Intravital observation of Plasmodium berghei sporozoite infection of the liver. PLoS Biol. 2005 Jun;3(6):e192. (License: CC BY-4.0)