Small Intestine: Medical Abdominal Pain
Acute Viral Gastroenteritis
Most Common Organisms
- Norovirus #1 – From Contaminated Food/Water or Person-to-Person Spread
- Rotavirus
- Enteric Adenovirus
- Astrovirus
Presentation
- Diarrhea (89%)
- Nausea (93%)
- Vomiting (81%)
- Abdominal Pain (76%)
- Fever (50%)
- Weight Loss
- Fatigue
- Dehydration
Diagnosis
- Clinical – Characteristic History of Diarrheal Disease (≥ 3 Times Per Day with Rapid Onset for < 1-2 Weeks) Accompanied by Other GI Symptoms
Treatment
- Supportive Care (Fluid Rehydration & Unrestricted Nutrition)
- ABX Generally Not Recommended
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Basics
- Definition: Chronic Abdominal Pain & Altered Bowel Habits without any Organic Cause
- The Most Commonly Diagnosed GI Condition
- Pathophysiology Multifactorial & Uncertain
Subtypes
- IBS-C (Constipation): > 25% of Stools Hard (Bristol Type 1 or 2)
- IBS-D (Diarrhea): > 25% of Stools Loose (Bristol Type 6 or 7)
- IBS-M (Mixed): Both C & D
- IBS-U (Unsubtyped): Neither C, D or M
- IBS-A (Alternating): Alternates Between C & D
Diagnosis (Rome IV Criteria)
- Recurrent Abdominal Pain ≥ 1 Day/Week
- *Not Abdominal “Discomfort” as Was in Rome III Criteria
- Lasting for ≥ 3 Months
- At Least 2 Of:
- Pain Related to Defecation
- Change in Stool Frequency
- Change in Stool Form
Treatment
- Initial Tx: Lifestyle & Dietary Modifications
- Diet – Avoid Gas-Producing Foods & Low FODMAPs (Fermentable Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides & Polyols)
- May Have Concurrent Celiac Disease or Lactose Intolerance Requiring Gluten/Dairy Avoidance
- Psychological Therapy May Benefit Some Patients
- If Fails or Moderate-Severe Sx: Add Pharmacologic Tx (Laxatives or Antidiarrheals)
Celiac Disease (Celiac Sprue/Gluten-Sensitive Enteropathy)
Basics
- Definition: Small Bowel Disorder Upon Exposure to Dietary Gluten with Relief After Withdrawal of Gluten from Diet
- Primarily Occurs in Whites of Northern European Ancestry
- Classically a Disease of Infants After Introduction of Gluten into the Diet
- Now Presenting Later, Often in Adults
Presentation
- Primary Sx:
- Abdominal Pain
- Diarrhea
- Steatorrhea
- Flatulence
- Other Sx:
- Nutrient & Vitamin Deficiencies
- Iron Deficiency Anemia
- Neuropsychiatric Disorders
- Arthritis
- Associated Conditions:
- Dermatitis Herpetiformis
- Type 1 Diabetes
- Autoimmune Thyroiditis
- Down Syndrome
- GERD
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Selective IgA Deficiency
Diagnosis
- Serology: Anti-Tissue Transglutaminase IgA Antibody (Best)
- Other Antibodies: Anti-Endomysial Ab or Anti-Gliadin Ab
- Indicative but Need Bx for Diagnosis
- Endoscopic Small Bowel Bx: Atrophic/Flattened Villi, Crypt Cell Hyperplasia & Mucosal Inflammation
Treatment
- Gluten-Free Diet (Wheat, Rye & Barley)
- May Have Concurrent Lactose Intolerance Requiring Dairy Avoidance
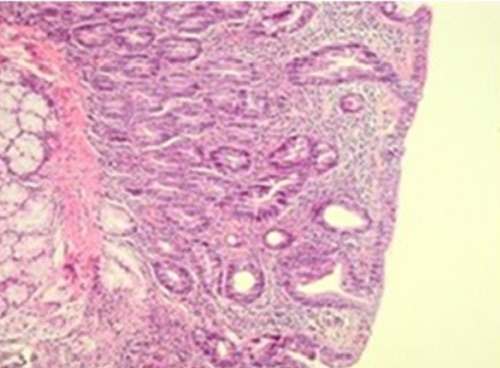
Celiac Disease Histology – Flattened Villi & Crypt Cell Hyperplasia 1
Lactose Intolerance
Definitions
- Lactase Deficiency – Deficiency of Lactase (Brush Border Enzyme to Allow Absorption of Lactose)
- Excess Lactose in Colon Causes Fermentation by Bacteria with Production of Hydrogen Gas
- Lactose Intolerance – Clinical Syndrome Where Lactose Ingestion Cases Symptoms
- May or May Not Be Associated with Lactase Deficiency
Presentation
- Symptoms Develop After Lactose Ingestion
- Symptoms:
- Abdominal Pain
- Bloating
- Flatulence
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
Diagnosis
- Lactose-Tolerance Test
- Provocative Oral Lactose Load Given & Monitoring of Symptoms
- Diagnoses Lactose Intolerance
- Lactose Hydrogen Breath Test
- Diagnoses Lactose Malabsorption
Treatment
- Restrict Lactose in Diet (Dairy)
- May Consider Lactase Enzyme Replacement
References
- Sayar I, Demirtas L, Gurbuzel M, Isik A, Peker K, Gulhan B. Familial multiple lipomas coexisting with celiac disease: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2014 Sep 16;8:309. (License: CC BY-4.0)