Skin & Soft Tissue: Melanocytic Nevus (Mole)
Melanocytic Nevus (Mole)
Definitions
- Melanocytic Nevus: Benign Proliferation of Nevus Cells (Type of Melanocyte Clustered in Nests)
- Congenital Melanocytic Nevus: Present at Birth or First 6 Months of Age
- Extend Deeper than Acquired Melanocytic Nevi
- Acquired Melanocytic Nevus: Appear After 2 Years of Age
Congenital Melanocytic Nevus (CMN)
Presentation
- Pigmented Lesion
- Macules or Slightly Raised Papules
- Sharply Demarcated Borders
- Grow Proportionally with the Child – Cover the Same Relative Surface Area Throughout Growth
- Occur in Any Location
- Giant Lesions May Have a “Garment”/“Bathing Trunk”/“Coat Sleeve” Appearance Due to Large Surface Area Resembling Clothing
- Large-Giant Lesions Often Have Other Surrounding Satellite Lesions
Classification
- Size:
- Small: < 1.5 cm
- Medium: > 1.5 cm
- M1: 1.5-10 cm
- M2: 10-20 cm
- Large: > 20 cm
- L1: 20-30 cm
- L2: 30-40 cm
- Giant: > 40 cm
- G1: 40-60 cm
- G2: > 60 cm
- *Based on the Projected Largest Diameter Achieved by Adulthood
- Estimated Size Increase:
- Head: 1.7x
- Trunk/Arms: 2.8x
- Legs: 3.3x
- Estimated Size Increase:
- Satellite Lesions (Used to Further Classify Large-Giant Lesions):
- S1: 0
- S2: 1-19
- S3: 20-50
- S4: > 50
Melanoma Risk
- Small-Medium Sized: < 1%
- Large-Giant: 2-5%
- Half of the Risk is During the First Five Years of Life
Diagnosis
- Mostly Clinical (Based on History and Physical Exam)
- May Consider Skin Biopsy to Rule Out Malignancy
Treatment
- Small-Medium: Periodic Monitoring
- Excision Indications:
- Difficult Site to Monitor for Changes
- Parent Preference (Cosmesis or Anxiety)
- Excision Indications:
- Large-Giant: Surgical Excision
- May Be Difficult-Impossible to Completely Excise
- May Require Skin Grafting
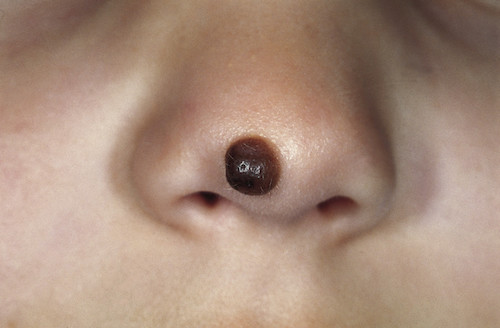
Congenital Melanocytic Nevus 1
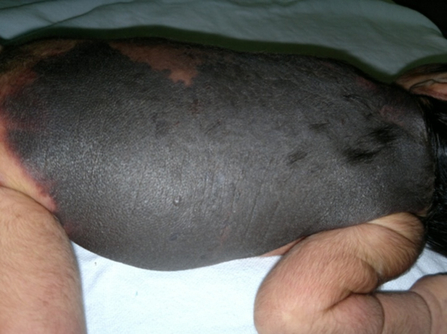
Giant Congenital Melanocytic Nevus 2
Acquired Melanocytic Nevus (AMN)
Presentation/Types
- Common (Banal)
- Pigmented Lesion
- Symmetric
- Homogenous Surface
- Round with Sharply Demarcated Borders
- Small (≤ 6 mm)
- Atypical
- Share Clinical Features of Melanoma (Asymmetric, Border Irregular, Color Variation or Diameter > 6 mm)
Diagnosis
- Mostly Clinical (Based on History and Physical Exam)
- May Consider Skin Biopsy to Rule Out Malignancy
- A Nevus with Different Features from Other Nevi (“Ugly Duckling”) Raises Concern for Melanoma
Treatment
- Common (Banal): Periodic Monitoring & Sun Protection
- Consider Excision for Patient Preference (Cosmesis)
- No Benefit to “Prophylactic” Removal – Most Melanomas Arise De Novo
- Atypical: Excisional Biopsy
- Re-Excision of Positive Margins is Debated
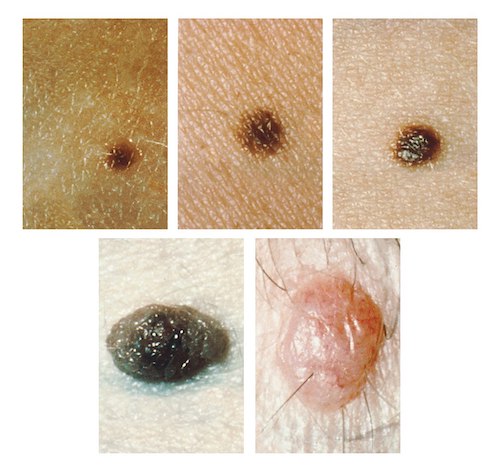
Acquired Melanocytic Nevus 3
References
- Sand M, et al. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-2.0)
- Sharma S, et al. Wikimedia Commons. (License: GNU FDL)
- National Cancer Institute. Wikimedia Commons. (License: Public Domain)