Pancreas: Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
Invasive Ductal Adenocarcinoma
Basics
- Most Common Exocrine Pancreatic Neoplasia (85-90%)
- 4th Most Common CA-Related Death
- Most Common Location: Main Duct & Head
- Spreads Through Lymphatics
Associated Mutations
- K-Ras (Most Common)
- p16 (CDKN2A)
- p53
- BRCA1/2
- MLH1
- ATM
Risk Factors
- Tobacco #1
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Chronic Pancreatitis
- BRCA2
- FAP
- Cystic Fibrosis
- History of Cholecystectomy
Subtypes
- Adenosquamous
- Colloid (Best Prognosis)
- Hepatoid
- Medullary
- Anaplastic, Colloid, etc.
Presentation
- Symptoms:
- Jaundice – Most Common Presenting Symptom
- Fatigue
- Weight Loss
- Anorexia
- Abdominal Pain
- Nausea & Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Courvoisier Sign – Painless Palpable Gallbladder with Jaundice
- Indicates Malignancy (Pancreas/Gallbladder)
- *Historical Sign with Limited Utility and Many Exceptions
- Trousseau’s Sign – Unexplained Superficial Migratory Thrombophlebitis
Diagnosis
- Initial Imaging: CT (85% Sensitive)
- If CT Positive:
- If Resectable: Surgery
- No Bx Needed – High False Negative
- If Appears Borderline/Unresectable/Mets: EUS-Guided Bx
- To Guide Chemotherapy
- Vascular Invasion Unclear: EUS
- If Resectable: Surgery
- If CT Negative but High Suspicion: ERCP (90% Sensitive)
- Tumor Marker: CA 19-9
Unresectable Definition
- Invades Celiac Axis > 50%
- Invades SMA > 50%
- Contact with the Most Proximal SMA or SMV Branches
- Invasion of SMV or Portal Vein if Unable to Reconstruct
- Lymph Nodes Beyond the Field of Resection (Such as Celiac or SMA Nodal Systems)
- Mets
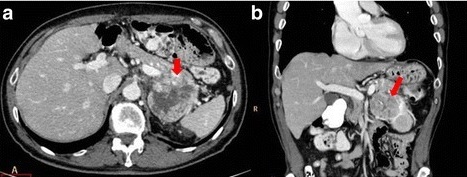
Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma of the Tail 1
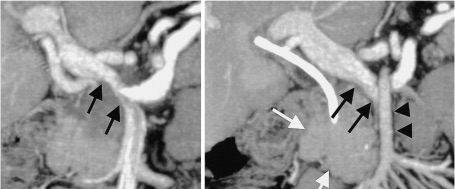
Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Encasing the Portal Vein & SMA 2
TNM Staging – AJCC 8
- TNM
| T | N | M | |
| I | 1a ≤ 0.5 cm 1b > 0.5 cm 1c ≥ 1.0 cm | 1-3 LN | Mets |
| II | > 2.0 cm | ≥ 4 LN | |
| III | > 4.0 cm | ||
| IV | Invades Celiac Axis, SMA or Common Hepatic Artery |
- Stage
| T | N | M | ||
| I | A | T1 | N0 | M0 |
| B | T2 | N0 | M0 | |
| II | A | T3 | N0 | M0 |
| B | T1-3 | N1 | M0 | |
| III | T4 | Any N | M0 | |
| Any T | N2 | M0 | ||
| IV | Any T | Any N | M1 | |
Treatment
- Resectable: Resection & Adjuvant Chemotherapy
- Resection:
- Head/Uncinate: Pancreaticoduodenectomy
- Body/Tail: Distal Pancreatectomy
- Entire Gland: Total Pancreatectomy (Significant Morbidity)
- Considerations:
- Staging Laparoscopy to Confirm Resectability
- Preoperative Biliary Drainage – Debated & May Actually Have Worse Outcomes
- Adjuvant Therapy for All
- Chemotherapy – Gemcitabine or FOLFIRINOX
- Consider Adjuvant XRT Also
- Resection:
- Borderline-Resectable: Neoadjuvant Chemo-XRT (Attempt Downstaging)
- First Need Tissue Diagnosis if Undergoing Neoadjuvant Therapy
- Unresectable: Palliation
- Pain: Opioids & Early Celiac Plexus Neurolysis
- Jaundice: ERCP & Stent
- Surgical Bypass If Unable or Found to Be Unresectable at Time of Surgery
- Gastric Outlet Obstruction: Endoscopic Stent (Preferred Over Surgical Bypass)
References
- Granata V, Fusco R, Catalano O, Setola SV, de Lutio di Castelguidone E, Piccirillo M, Palaia R, Grassi R, Granata F, Izzo F, Petrillo A. Multidetector computer tomography in the pancreatic adenocarcinoma assessment: an update. Infect Agent Cancer. 2016 Nov 15;11:57. (License: CC BY-4.0)
- Maher MM, Kalra MK, Sahani DV, Perumpillichira JJ, Rizzo S, Saini S, Mueller PR. Techniques, clinical applications and limitations of 3D reconstruction in CT of the abdomen. Korean J Radiol. 2004 Jan-Mar;5(1):55-67. (License: CC BY-NC-3.0)