Pancreas: Pancreatic Cystic Neoplasia
Pancreatic Cystic Neoplasia (PCN)
Types
- Serous Cystic Neoplasia (SCN)
- Mostly Benign
- Most Common in Head Mn
- Most Common in Middle-Aged Females
- Mucinous Cystic Neoplasia (MCN)
- Premalignant Mn
- Most Common in Body/Tail
- Almost Exclusively in Elderly Women
- Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasia (IPMN)
- Sub-Types:
- Main Duct (MD-IPMN)
- High Malignancy Risk (> 60%)
- Endoscopy: Gaping “Fish-Mouth” Papilla (Pathognomonic)
- Branch Duct (BD-IPMN)
- Lower Malignancy Risk
- Mixed-Type IPMN
- Involves Main & Branch Ducts
- Main Duct (MD-IPMN)
- WHO Dysplasia Grades
- Low Grade: Adenoma
- Moderate: Borderline
- High Grade: Carcinoma in Situ
- High Incidence of Extrapancreatic Malignancy (10-50%)
- Most Common: Colorectal Adenocarcinoma (#1 in US) & Gastric Adenocarcinoma
- Sub-Types:
- Solid Pseudopapillary Epithelial Neoplasm (SPEN)
- Most Common in Young Women Age < 35 Mn
- Have Malignant Potential
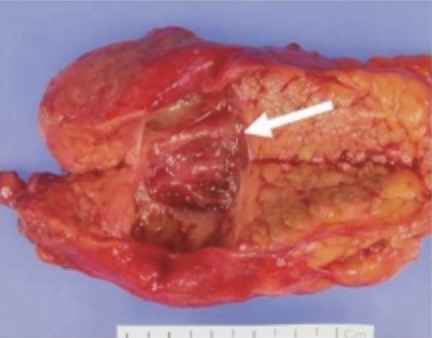
MCN 1
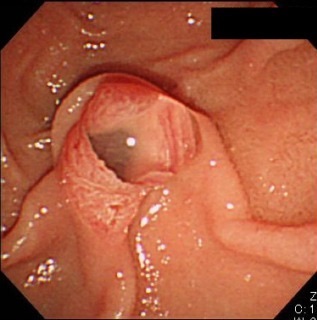
“Fish Mouth” Papilla of MD-IPMN 2
Diagnosis
- First Step: MRCP
- If Highly Suspicious for CA: Resection
- Indications: MCN, MD-IPMN or SPEN
- If Not Highly Suspicious: EUS-FNA
- If Obviously Serous May Consider No EUS/FNA
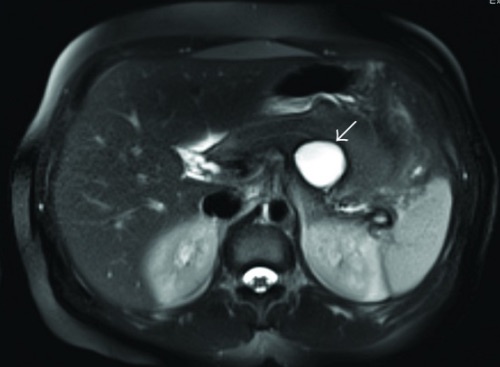
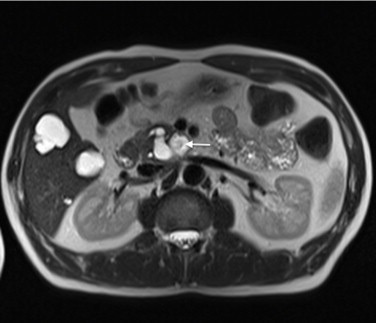
MCN on MRI 3
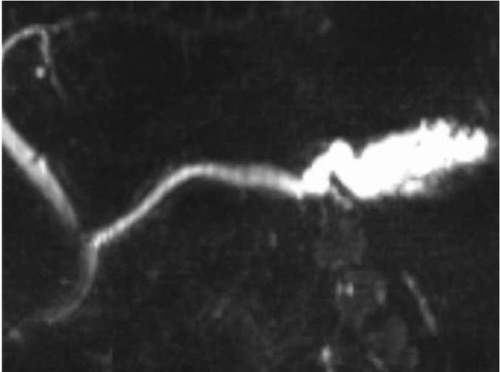
MD-IPMN on MRCP 4
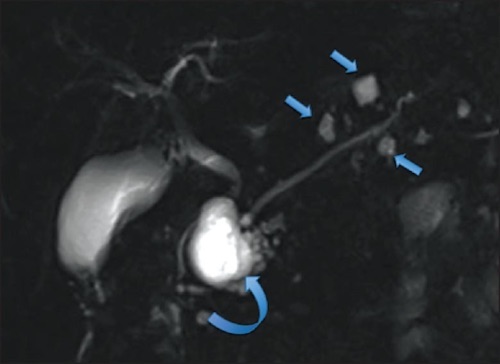
BD-IPMN on MRCP 5
BD-IPMN with Mural Nodule 6
Aspirate Findings
| CEA | Amylase | Cytology | |
| SCN | Low | Low | Cuboidal Cells, Glycogen Positive |
| MCN | High | Low | Columnar Cells, Mucin Positive (Similar to IPMN)
“Ovarian-Type” Stroma |
| IMPN | Variable | High | Columnar Cells, Mucin Positive (Similar to MCN) |
| SPEN | – | – | Branching Papilla with Myxoid Stroma |
Treatment
- SCN: Conservative
- Resection if Sx
- MCN: Resection
- IPMN:
- MD-IPMN: Resection
- BD-IPMN: Surveillance vs. Resection
- Resection Indications: See Fukuoka Guidelines
- If Patient Presents with Multiple Benign-Appearing BD-IMPN & a Single Concerning Cyst: Resect the Concerning Cyst & Monitor the Others
- Mixed-Type IPMN: Resection
- SPEN: Resection
Fukuoka Guidelines – Resection Indications for BD-IPMN
- High Risk:
- Jaundice
- Mural Nodules
- Main Duct > 10 mm
- Worrisome:
- ≥ 3 cm
- Pancreatitis/Sx
- Thickened Wall
- Main Duct > 5 mm
- LN
Mnemonics
Serous vs Mucinous Cystic Neoplasia – Location & Malignancy
- Third Rule of Surgery: Don’t Mess With the Pancreas – “S&M” Written on the Pancreas
- Head (Serous) to Body/Tail (Mucinous)
- Benign (Serous/Side) to Malignant (Mucinous/Main/Mixed)
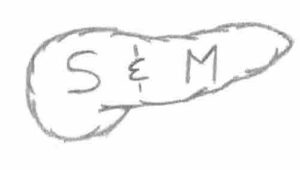
Mucinous Cystic Neoplasia Malignancy
- M-M: Mucinous – Malignant
Most Common Ages at Presentation of Pancreatic Cystic Neoplasia
- “Daughter-Mother-Grandma”
- Daughter – SPEN Most Common in Young Women (SP-Sprouts)
- Mother – MCN Most Common in Middle-Aged Women (M-Mother)
- Grandma – SCN Most Common in Older Women (S-Senile)
References
- Cho HW, Choi JY, Kim MJ, Park MS, Lim JS, Chung YE, Kim KW. Pancreatic tumors: emphasis on CT findings and pathologic classification. Korean J Radiol. 2011 Nov-Dec;12(6):731-9. (License: CC BY-NC-3.0)
- Tanaka M. Current roles of endoscopy in the management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. Dig Endosc. 2015 May;27(4):450-457. (License: CC BY-4.0)
- Lee LS, Clancy T, Kadiyala V, Suleiman S, Conwell DL. Interdisciplinary management of cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2012;2012:513163.(License: CC BY-3.0)
- Takuma K, Kamisawa T, Tabata T, Kurata M, Honda G, Horiguchi S. Main-duct intraductal papillary mucinous adenoma of the pancreas. World J Surg Oncol. 2011 Nov 23;9:153. (License: CC BY-2.0)
- Machado NO, Al Qadhi H, Al Wahibi K. Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm of Pancreas. N Am J Med Sci. 2015 May;7(5):160-75. (License: CC BY-NC-SA-3.0)
- Paiella S, De Pastena M, Esposito A, Salvia R, Morigi C, Bassi C. Selective agenesis of pancreatic isthmus parenchyma with preservation of main pancreatic duct continuity, a very rare entity: Case report. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015;6C:169-71. (License: CC BY-NC-ND-3.0)