Endocrine: Parathyroid Anatomy & Physiology
Parathyroid Anatomy
Embryology Mn
- Superior Parathyroids: From Fourth Pharyngeal Pouch
- Along with Lateral Thyroid
- Inferior Parathyroid: From Third Pharyngeal Pouch
- Along with Thymus
Average Size
- Average Size: 3 x 5 x 7 mm
- Average Weight: 30-60 mg
Typical Gland Location
- Superior Parathyroids
- Posterolateral to Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve
- Above Inferior Thyroid Artery
- Inferior Parathyroids
- Anteromedial to Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve
- Below Inferior Thyroid Artery
Abnormal Gland Location
- Missing Gland Locations:
- Most Common Location of a Missed Gland: Normal Position
- Most Common Location of an Ectopic Gland: Thymus
- Most Common Ectopic Sites:
- Superior: Retroesophageal or Paraesophageal Space
- 80% of Superior Parathyroid Glands Will Appear in the Same Position as the Contralateral Gland
- Inferior: Tail of Thymus
- Position is More Variable (Further Travel)
- Superior: Retroesophageal or Paraesophageal Space
- Different Number Occurrence
- Supernumerary (Extra Glands)
- Frequency: 13% (More Common than Infranumerary)
- Most Common Site: Thymus
- Infranumerary (≤ 4 Glands)
- Frequency: 3%
- Supernumerary (Extra Glands)
Blood Supply
- Inferior Thyroid Artery
- Supplies Both Superior & Inferior Parathyroid Glands
- From the Thyrocervical Trunk (Off Subclavian Artery)
- Artery Enters Gland Medially – If Preforming a Partial Resection Should Resect the Lateral Half (Spare the More Perfused Portion)
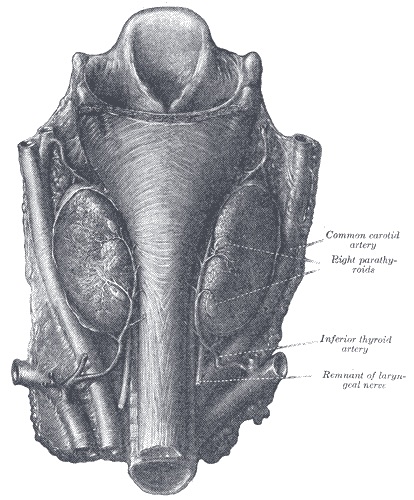
Parathyroid Glands and Inferior Thyroid Artery 1
Parathyroid Gland (Arrow) 2
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
- Secreted by Parathyroid Chief Cells
- Short Half-Life: 2-4 Minutes
- Overall Effects:
- Increased Calcium, Hydrogen (Acidosis) & Chloride
- Decreased Phosphate Mn
- Renal Effects:
- Increase Calcium Absorption (Overall Increased Urinary Calcium)
- Decrease Phosphate Absorption
- Increase Vitamin D Production
- Inhibits Na/H Antiporter > Inhibits Bicarb Reabsorption > Acidosis > High Chloride
- Urine cAMP Increased
- Bone Effects:
- Increase Osteoclast Calcium Secretion Mn
- GI Effects:
- No Direct Effect
- Increased Vitamin D from Kidney Increases GI Absorption of Calcium
Calcium Physiology
- Physiologic Effects:
- Other Factors:
- Vitamin D
- Increases Calcium
- *See Fluids, Electrolytes & Nutrition: Calcium
- Calcitonin
- Decreases Calcium
- *See Endocrine: Thyroid Anatomy & Physiology
- Vitamin D
Mnemonics
Parathyroid Embryology
- P-P: Parathyroids from Pouch (Not Arch or Cleft)
- 4-4: 4 Glands – First Think of the Fourth Pouch (4)
- Superior: Bigger Number (4) – Superior Parathyroids from Fourth Pharyngeal Pouch
- Inferior: Smaller Number (3) – Inferior Parathyroids from Third Pharyngeal Pouch
PTH Effects on Phosphate
- PTH – “Phosphate Trashing Hormone”
Bone Cells Affected by PTH/Calcitonin
- C-C: Calcium Alters by Changes in Osteo-Clasts (Not Osteoblasts)
- For Both PTH and Calcitonin
References
- Gray H. Anatomy of the Human Body (1918). Public Domain.
- Haggstrom M. Wikimedia Commons. (License: Public Domain)