Pediatric Surgery: Other Head & Neck Pathology
Head & Neck Pathology
Lymphadenopathy
- FNA if Fluctuant
- Excisional Biopsy if No Improvement with Antibiotics (Lymphoma Concern)
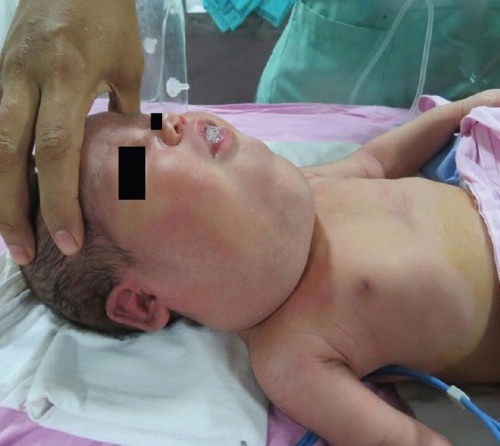
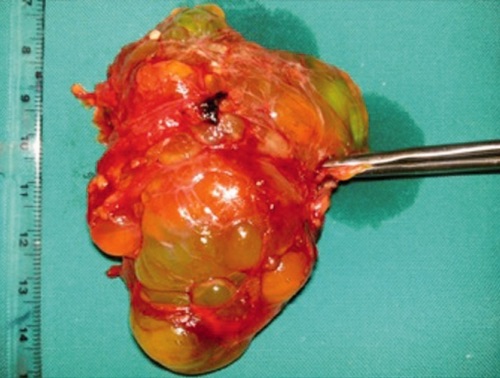
Cystic Hygroma (Lymphangioma)
- Congenital Communication Defects Between Lymphatics & Internal Jugular Vein
- Most Common Locations:
- Posterior Neck (Most Common) – Lateral to SCM
- Axilla (Second Most Common)
- Presentation: Soft Multiloculated Cysts (Often in Clusters)
- Transilluminates
- Nonmalignant
- Associated with Down Syndrome & Turner Syndrome
- Treatment: Resection
Dermoid Cyst
- Lined by Squamous Epithelium with Sebaceous Debris
- Often Difficult to Distinguish from a Branchial Cleft Cyst if on Neck
- Treatment: Excision
Cleft Lip/Palate
Cystic Hygroma 1
Cystic Hygroma 2
References
- Rao KS, Shenoy T. Anesthetic management of a large cystic hygroma in a newborn. Anesth Essays Res. 2015 May-Aug;9(2):270-2. (License: CC BY-NC-SA-3.0)
- Romeo V, Maurea S, Mainenti PP, Camera L, Aprea G, Cozzolino I, Salvatore M. Correlative imaging of cystic lymphangiomas: ultrasound, CT and MRI comparison. Acta Radiol Open. 2015 May 18;4(5):2047981614564911. (License: CC BY-NC-SA-3.0)