Vascular: Peripheral Pseudoaneurysm
Pseudoaneurysm
Basics
- Definition: Blood Collection Between the Tunica Media and Adventitia
- False Aneurysm (Not Enclosed by All 3 Layers)
- Cause:
- Iatrogenic (Peripheral Catheterization) – Most Common Cause
- Infection
- Trauma
- Most Common Site: Femoral Artery
Presentation
- Painful Pulsating Mass
- Associated Hematoma
- Bruit
- Rupture
Diagnosis
- Duplex US – Preferred
Treatment
- Asymptomatic & < 2-3 cm: Observation & Repeat US in 4 Weeks
- Symptomatic or > 2-3 cm: US-Guided Thrombin Injection
- Consider US-Guided Compression if Thrombin Contraindicated
- Compress for 10-20 Minutes to Induce Thrombosis
- Avoid Excessive Pressure – Causes Thrombosis within the Artery
- Disadvantages of Being Very Painful & Time-Consuming
- Consider US-Guided Compression if Thrombin Contraindicated
- Indications for Surgical Repair:
- Rupture
- Rapid Expansion
- Nerve Compression
- Skin Ischemia
- If Infected (Mycotic): Excision
- Most Common in IV Drug Users
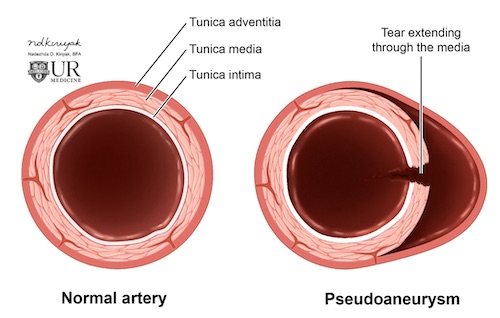
Pseudoaneurysm 1
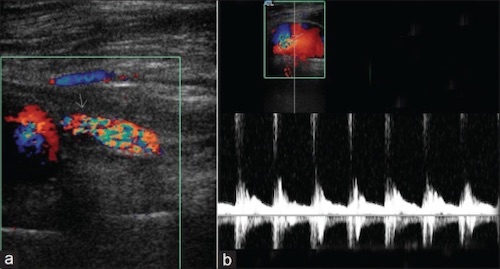
Pseudoaneurysm Doppler; (a) Pseudoaneurysm (Arrow), (b) Arterial Flow Across the Pseudoaneurysm 2
References
- Chengazi, H.U., Bhatt, A.A. Pathology of the carotid space. Insights Imaging 10, 21 (2019). Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-4.0)
- Agarwala SR, Mohrir GS, Dotivala SJ. Posttraumatic pseudoaneurysm of popliteal artery following total knee arthroplasty. Indian J Orthop. 2013 Jan;47(1):101-3. (License: CC BY-NC-SA-3.0)