PTEN Hamartoma Tumor Syndrome (PHTS)
Jackson Phillip Bauer, MD
The Operative Review of Surgery. 2023; 1:129-133.
Table of Contents
Pathophysiology and Presentation
Genetic Mutation
- Mutation in the Phosphatase Tensin Homologue (PTEN) Gene 1
- Tumor Suppressor Gene
- Autosomal Dominant Inheritance 1
Associated Malignancy 1
- Breast Cancer (85%)
- Thyroid Cancer (35%)
- Predominantly Follicular, Rarely Papillary, Never Medullary 2
- Renal Cell Cancer (34%)
- Predominantly Papillary 2
- Endometrial Cancer (28%)
- Colorectal Cancer (9%)
- Melanoma (6%)
Benign Tumors 1
- Gastrointestinal Polyps
- Lipomas
- Acral Keratosis
- Mucosal Papillomas
- Fibromas
- Benign Breast, Thyroid, and Uterine Lesions
Neurodevelopmental Associations 1
- Macrocephaly (Large Head Size) – 94%
- Dolichocephaly (Head Longer than Wide)
- Autism
- Intellectual Disability
- Developmental Delays
Variations
Spectrum of Disorders
- PHTS Presents with a Spectrum of Disorders (Previously Believed to Be Completely Separate Conditions) 1
- Cowden Syndrome
- Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba Syndrome (BRRS)
- Proteus-Like Syndrome/SOLAMEN Syndrome
- Traditionally Cowden Syndrome was Diagnosed in Adults and BRRS Diagnosed in Pediatrics 1
- Cowden Characteristics Generally Do Not Appear Later 1
- Major Criteria:
- Breast Cancer
- Endometrial Cancer (Epithelial)
- Thyroid Cancer (Follicular)
- Gastrointestinal Hamartomas
- Lhermitte-Duclos Disease (Adult)
- Macrocephaly
- Macular Pigmentation of the Glans Penis
- Multiple Mucocutaneous Lesions (Trichilemmomas, Acral Keratoses, Mucocutaneous Neuromas, Oral Papillomas)
- Minor Criteria:
- Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Colon Cancer
- Esophageal Glycogenic Acanthosis
- Lipomas
- Mental Retardation
- Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Testicular Lipomatosis
- Thyroid Cancer (Papillary of Follicular Variant of Papillary)
- Thyroid Structural Lesions
- Vascular Anomalies
- Macrocephaly
- Hamartomatous Intestinal Polyposis
- Lipomas
- Vascular Malformations/Hemangiomas
- Pigmented Penile Macules
- Developmental Delay
- Intellectual Disability
- Typical Proteus Syndrome (PS) Itself is No Longer Considered to Be Due to a germline PTEN Mutation 5,6
- Proteus-Like Syndrome is Undefined but Describes Individuals with Clinical Features of Proteus Syndrome with a PTEN Mutation that Do Not Meet the Diagnosis of PS
- Proteus Syndrome (PS) Characteristics: 7
- Distorting and Progressive Overgrowth of the Skeletal Architecture
- Cerebriform Connective Tissue Nevi
- Linear Verrucous Epidermal Nevus
- Lipomatous Overgrowth
- Vascular Malformations
- Overgrowth of Other Tissues (Spleen, Liver, and Thymus)
- Dysmorphic Facial Features
- Some Recommend the Term SOLAMEN Syndrome to Describe the Phenotypic Features of PS but with a PTEN Mutation 8
- Segmental Overgrowth, Lipomatosis, Arteriovenous Malformation, and Epidermal Nevus (SOLAMEN)
Diagnosis and Management
Diagnosis
- Clinical Diagnosis of Cowden: 4
- Individual with Either:
- Three Major Criteria, One Must Include Macrocephaly, Lhermitte-Duclos Disease, or GI Hamartomas
- Two Major and Three Minor Criteria
- Family with an Individual Meeting Criteria or a PTEN Mutation
- Any Two Major Criteria
- One Major and Two Minor Criteria
- Three Minor Criteria
- Individual with Either:
- Clinical Diagnosis of Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba Syndrome is Poorly Established
- Diagnosis Confirmed by Genetic Testing
Screening/Surveillance 9-11
- Physical Exam at Diagnosis
- Include Dermatologic, Neurological, and Cognitive Exams
- Thyroid US Annually, Starting at Age 18
- Consider Baseline Ultrasound at Age 15
- Breast MRI or Mammography Annually, Starting at Age 30
- Transvaginal Ultrasound Annually, Starting at Age 30-35
- Also Consider Endometrial Biopsy
- Utility of Endometrial Cancer Surveillance is Debated
- Colonoscopy Every 5 Years, Starting at Age 35
- Renal US Every 2 Years, Starting at Age 40
Mnemonics
Cowden Syndrome Associations 12
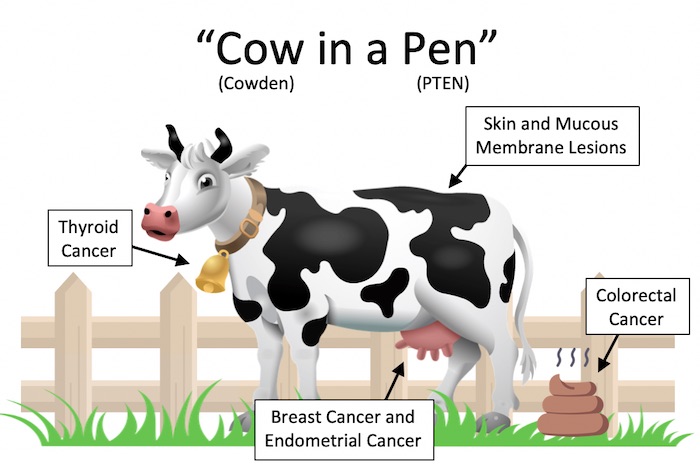
References
- Eng C, Malhotra S, Mester J. PTEN Hamartoma Tumor Syndrome. National Organization for Rare Disorders. 2018.
- Yehia L, Eng C. PTENHamartoma Tumor Syndrome. 2001 Nov 29 [updated 2021 Feb 11]. In: Adam MP, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Bean LJH, Gripp KW, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews
- Pilarski R, Burt R, Kohlman W, Pho L, Shannon KM, Swisher E. Cowden syndrome and the PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome: systematic review and revised diagnostic criteria. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013 Nov 6;105(21):1607-16.
- Gorlin RJ, Cohen MM Jr, Condon LM, Burke BA. Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1992;44:307–14
- Biesecker LG, Rosenberg MJ, Vacha S, Turner JT, Cohen MM. PTEN mutations and proteus syndrome. Lancet. 2001 Dec 15;358(9298):2079-80.
- Cohen MM Jr, Turner JT, Biesecker LG. Proteus syndrome: misdiagnosis with PTEN mutations. Am J Med Genet A. 2003 Nov 1;122A(4):323-4.
- Biesecker LG, Sapp JC. Proteus Syndrome. 2012 Aug 9 [updated 2019 Jan 10]. In: Adam MP, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Bean LJH, Gripp KW, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews
- Caux F, Plauchu H, Chibon F, Faivre L, Fain O, Vabres P, Bonnet F, Selma ZB, Laroche L, Gérard M, Longy M. Segmental overgrowth, lipomatosis, arteriovenous malformation and epidermal nevus (SOLAMEN) syndrome is related to mosaic PTEN nullizygosity. Eur J Hum Genet. 2007 Jul;15(7):767-73.
- Syngal S, Brand RE, Church JM, Giardiello FM, Hampel HL, Burt RW; American College of Gastroenterology. ACG clinical guideline: Genetic testing and management of hereditary gastrointestinal cancer syndromes. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015 Feb;110(2):223-62; quiz 263.
- Tischkowitz M, Colas C, Pouwels S, Hoogerbrugge N; PHTS Guideline Development Group; European Reference Network GENTURIS. Cancer Surveillance Guideline for individuals with PTEN hamartoma tumour syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet. 2020 Oct;28(10):1387-1393.
- Smerdel MP, Skytte AB, Jelsig AM, Ebbehøj E, Stochholm K. Revised Danish guidelines for the cancer surveillance of patients with Cowden Syndrome. Eur J Med Genet. 2020 May;63(5):103873.
- Bauer JP. Cow in a Pen. PTEN Hamartoma Tumor Syndrome. The Operative Review of Surgery. 2023.