Cardiothoracic Surgery: Pulmonary Cystic Lesions
Pulmonary Cystic Lesions
Definition
- Definition: Air-Filled, Thin-Walled Cystic Lesions of the Lung
- Cyst in the Lung is a Misnomer – Contains a Collection of Gas (Not Fluid)
Types
- Bleb: Pleural/Subpleural < 1-2 cm
- *Some Now Discourage the Use & Consider Bleb a Subtype of Bullae
- Bulla: Pleural/Subpleural > 1-2 cm
- Pneumatocele: Within the Lung Parenchyma
Causes
- Pneumonia – Most Common
- Trauma/Burns
- Positive-Pressure Ventilation
- Hydrocarbon Inhalation
Presentation
- Most are ASx & Resolve Spontaneously Over Days-Weeks
- PTX – Due to Dissection Through the Pleural Membrane
- Cardiorespiratory Compromise – Due to Compression
- Sepsis – Due to Secondary Infection
Treatment
- General Tx: Directed at the Underlying Process
- Indications for Percutaneous Drainage:
- Cardiorespiratory Compromise Due to Compression
- Secondary Infection
- Indications for Surgery (Deroofing vs Resection):
- Failure of Percutaneous Drainage
- Persistent Air Leak or PTX
- Failure of Lung Expansion Despite Thoracostomy Tube
- Massive Hemoptysis
- Spontaneous Pneumothorax:
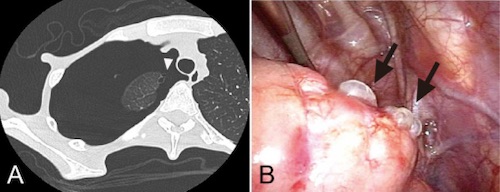
Pulmonary Blebs; (A) CT, (B) VATS 1
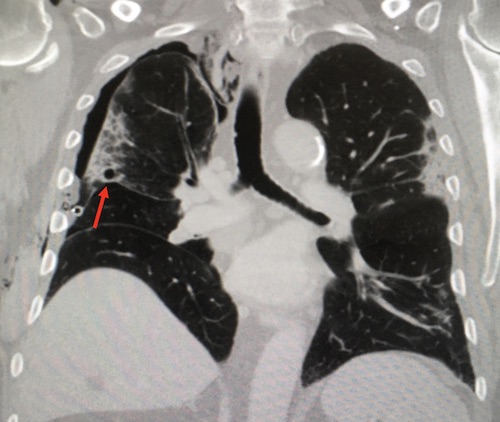
Pulmonary Bleb (Arrow)
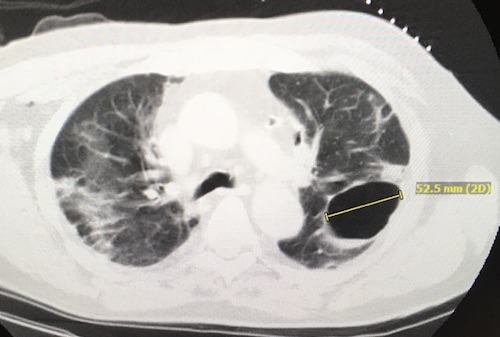
Pneumatocele
References
- Ozawa Y, Ichimura H, Sakai M. Reexpansion pulmonary edema after surgery for spontaneous pneumothorax in a patient with anorexia nervosa. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2016 Mar 3;7:20-3.(License: CC BY-NC-ND-4.0)