Surgical Critical Care: Pulmonary Hygiene (Pulmonary Toilet)
Pulmonary Hygiene (Pulmonary Toilet)
Basics
- Definition: Exercises & Procedures to Help Clear Airway Secretions & Mucous
- Also Referred to as Airway Clearance Techniques (ACT)
- Promotes Adequate Oxygenation & Pulmonary Function
- Often Used for Traumatic Rib Fractures, COPD, Asthma, Pneumonia or Other Pulmonary Pathology
- Decreases Mucociliary Clearance & Cough Increases Risk for Infection & Pulmonary Complication
Basic Methods
- Deep Breathing Exercise
- Can Be Relaxed with Slow Exhalation or Hard Pushes with Rapid Exhalation
- Coughing
- Huffing (Huff Coughing)
- Definition: Taking a Long Inhalation & Holding it, Then Actively Exhaling
- Less Forceful than a Cough but Less Exhausting & May Work Better
- Frequent Orotracheal Suctioning
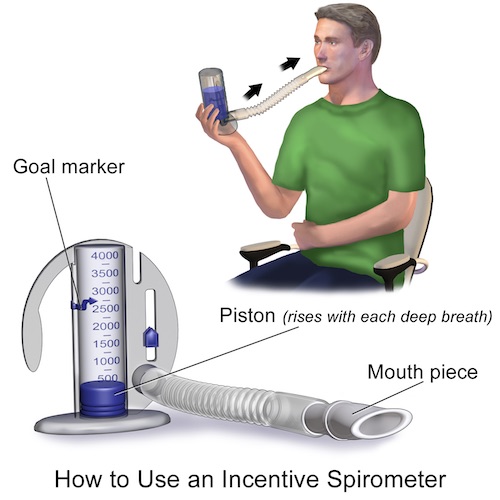
- Incentive Spirometry (IS)
- A Hollow Cylinder with a Flexible Mouthpiece to Incentivize Good Inhalation
- Use:
- Inspire Slowly & Deep (Keeping Indicator Between the Marked Lines to Indicate Appropriate Speed)
- Hold Inspiration for as Long as Able (Watching Piston Rise as High as Able)
- Exhale Slowly
- Generally Recommended Use About 10 Times per Session, 10 Sessions per Hour
- Should Attempt to Cough/Huff After Each Session to Clear Mucous
Chest Physiotherapy (CPT)
- Definition: Physical Therapies to Release & Help Clear Mucous
- Postural Drainage
- Patient is Placed into Various Positions to Promote Mucous Clearance by Gravity
- Chest Percussion/Clapping
- Therapist Lightly Claps a Patient’s Chest & Back
- More Common in Outpatient Setting & Generally Not Used in Practice
- Vest Physiotherapy (High-Frequency Chest Wall Oscillation)
- A Vest Worn by the Patient that Induces Frequent Vibrations
- Helps to Release & Thin Mucous as Well as Helping Clear
Advanced Methods
- Positive Expiratory Pressure (PEP)
- Mask/Mouthpiece Provides Resistance (Positive Pressure) During Expiration but Does Not Affect Inhalation
- Effects:
- Increases Gas Pressure Behind Mucous by Collateral Ventilation & Temporary Increase in Functional Residual Capacity
- Releases Mucous off Airway Walls
- Hold Airways Open & Prevents Collapse
- Use:
- After Multiple Uses/Breaths the Patient Stops to Cough & Clear Mucous
- Sessions Last Around 20 Minutes
- Includes: TheraPEP & Resistex PEP Mask
- Oscillating Positive Expiratory Pressure (OPEP)
- Provides Resistance During Expiration (Similar to PEP)
- Similar Effects as PEP
- Also Creates Vibrations During Expiration
- More Commonly Used than PEP Alone
- Brand Names: Flutter, Acapella, AerobikA & RC-Cornet
- Provides Resistance During Expiration (Similar to PEP)
- Intrapulmonary Percussive Ventilators (IPV)
- Delivers Short Bursts of Air (150-300/Minute) Through a Mouthpiece to Clear Mucous
- Mechanical Insufflation-Exsufflation (CoughAssist)
- Delivers a Gradual Positive Pressure for Large Volume Insufflation
- Then Rapidly Reverses to a Negative Pressure Inducing Exsufflation & Cough
- Bronchoscopy
Incentive Spirometry (IS) 1
References
- Blaus B. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-SA-4.0)