Small Intestine: Anatomy & Physiology
Anatomy
Structure
- Duodenum
- 1st Portion (Bulb)
- 2nd Portion (Descending)
- Contains Ampulla of Vater
- 3rd Portion (Transverse)
- Transition of 3rd/4th Portion: Aorta/SMA
- 4th Portion (Ascending)
- Ends at the Duodenojejunal Flexure
- Jejunum
- 100 cm
- Long Vasa Recta
- Ileum
- 150 cm
- Short Vasa Recta
Layers
- Mucosa
- Submucosa
- Strength Layer
- Muscularis
- Serosa
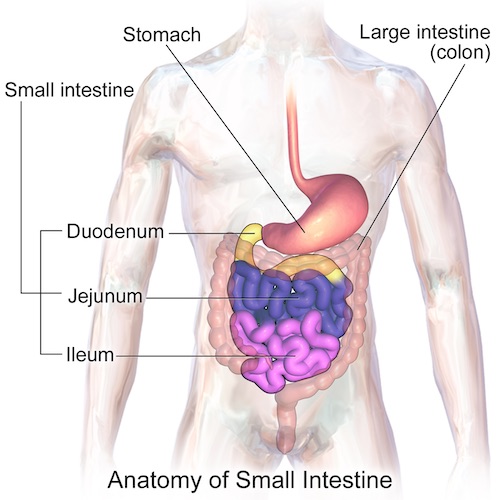
Small Intestine Structure 1
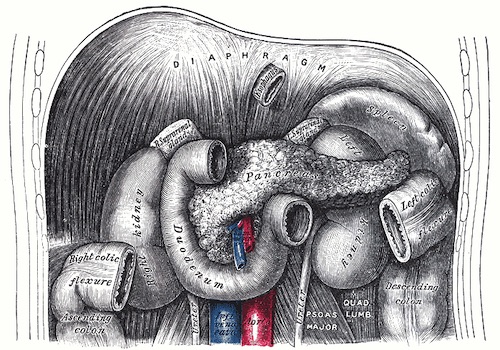
Duodenum Structure 2
Vascular Supply
- Duodenum: Anterior & Posterior Pancreaticoduodenal Arteries
- Superior off GDA
- Inferior off SMA
- Jejunum & Ileum: SMA
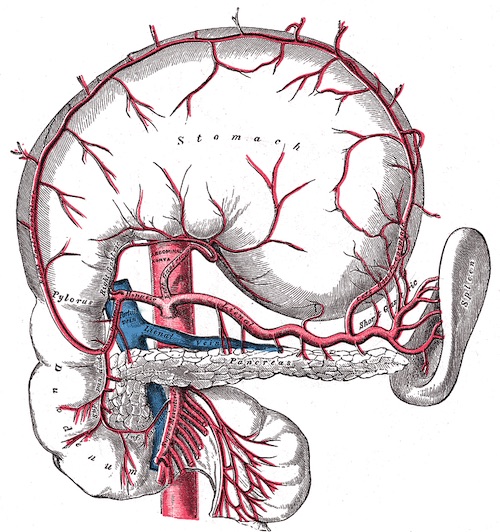
Duodenum Blood Supply 2
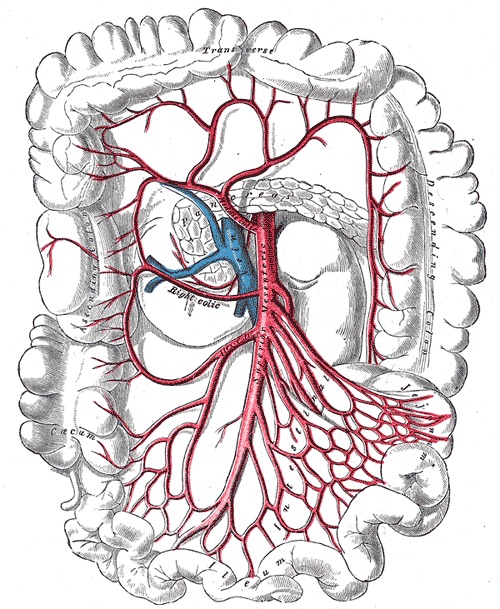
Jejunum/Ileum Blood Supply 2
Other
- Plicae Circulares (Valvulae Conniventes)
- Crescentic Mucous Membrane Folds
- Ligament of Treitz (Suspensory Muscle of the Duodenum)
- Connects to the Third & Fourth Portions of the Duodenum
- Occasionally the Beginning of the Jejunum Also
- Arises from the Right Crus of the Diaphragm
- Connects to the Third & Fourth Portions of the Duodenum
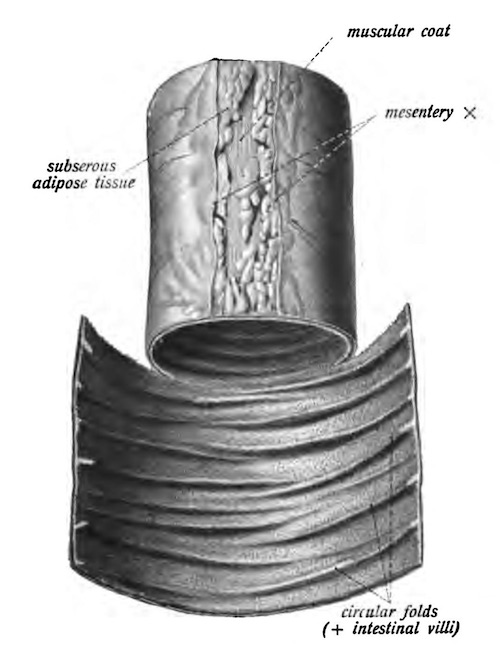
Plicae Circulares 3
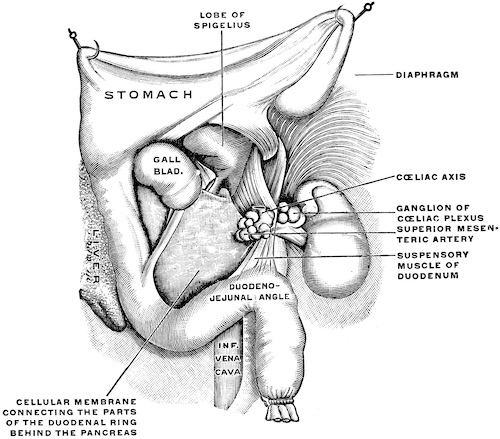
Ligament of Treitz 2
Physiology
Migrating Motor Complex (MMC)
- Functions:
- “Housekeeping” Electromechanical Activity During Fasting
- Sweeps Residual Undigested Material Through GI Tract
- Peristalsis Originates in Stomach and Propagates Through Small Intestine
- “Housekeeping” Electromechanical Activity During Fasting
- Phases:
- I: Rest
- 45-60 Minutes
- II: Acceleration
- 30 Minutes
- Progressively Increasing Frequency
- III: Peristalsis
- 5-15 Minutes
- Rapid Strong Evenly Spaced Contractions
- When Motilin Acts
- IV: Deceleration
- I: Rest
Sites of Absorption
- Small Intestine: Water & Nutrients
- Duodenum:
- Minerals (Iron, Calcium, etc)
- Jejunum:
- Most Absorption (Protein, 90% H2O & 95% NaCl)
- Ileum:
- Non-Conjugated Bile Acids (Passive)
- Terminal Ileum:
- Conjugated Bile Acids (Active)
- B12 & Folate
- Duodenum:
- Large Intestine: Water
Cell Types
- Primary Cell Types:
- Absorptive Enterocytes
- Goblet Cells
- Secrete: Mucus
- Paneth Cells
- Secrete: Enzymes
- Provide Mucosal Defense
- Enteroendocrine Cells
- Secrete: Hormones
- Other Cells
- Interstitial Cells of Cajal
- Regulate Peristalsis
- GIST Precursors
- Enterochromaffin Cells
- APUD (Amine Precursor Uptake & Decarboxylase) Cells
- High Uptake of 5-HTP & DOPA
- Carcinoid Precursors
- APUD (Amine Precursor Uptake & Decarboxylase) Cells
- Brunner’s Glands
- Secrete: Alkaline Solution
- Interstitial Cells of Cajal
- Immune Cells
- Peyer’s Patches
- Lymphoid Tissue
- Increased in Ileum
- M Cells
- Antigen Presenting Cells
- IgA
- Released into Gut
- Also in Mother’s Milk
- Peyer’s Patches
GI Hormones
- *See General Abdomen: GI Hormones
- Duodenum
- I Cells – CCK
- S Cells – Secretin
- Motilin
- Terminal Ileum
- Peptide YY
GI Microflora
Abdominal X-Ray (AXR)
- Gas Composed of:
- Normal: 80% Swallowed Air
- Obstructed Gut: 70% Nitrogen, 10% Oxygen, 8% CO2
References
- Blaus B. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-3.0)
- Gray H. Anatomy of the Human Body (1918). Public Domain.
- Sobotta J. Atlas and Textbook of Human Anatomy (1906). Public Domain.