Biliary Tract: Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction (SOD)
Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction (SOD)
Causes
- Stenosis – Narrowing from Gallstone, Pancreatitis, Trauma, Malignancy or Infection
- Dyskinesia – Functional Disturbance
- Most Commonly Found After Cholecystectomy Due to Unmasking of Pre-Existing SOD
Types
- I: Pain, Abnormal LFT & Dilated CBD
- II: Pain, Abnormal LFT or Dilated CBD
- III: Pain, Normal LFT & CBD
Diagnosis
- Tests:
- Gold Standard: Sphincter of Oddi Manometry (SOM)
- Nardi Test (Morphine & Neostigmine Cause Pain)
- HIDA (Hepatobiliary Scintigraphy)
- Work-Up:
- Type I – Likely Underlying Obstruction
- Proceed with ERCP
- Type II – SOD Suspected
- Proceed with SOM Before Tx
- Type III – SOD vs Functional Bowel Disease
- Avoid Invasive Testing; Proceed with Medical Tx
- Type I – Likely Underlying Obstruction
Treatment
- Type I/II: ERCP & Endoscopic Sphincterotomy
- If Fails or in a Gastric Bypass Patient: Surgery (Transduodenal Sphincteroplasty)
- Type III: Medical Tx (CCB/Ursodeoxycholic Acid)
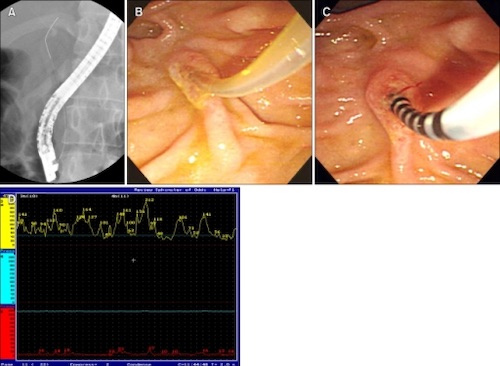
Sphincter of Oddi Manometry 1
References
- Cheon YK. How to interpret a functional or motility test – sphincter of oddi manometry. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2012 Apr;18(2):211-7. (License: CC BY-NC-3.0)