Spleen: Developmental Pathology
Accessory Spleen
Definition
- An Additional Segment of Splenic Tissue at an Ectopic Site
- Prevalence: 10-30%
Locations
- Splenic Hilum (75%) – Most Common
- Pancreatic Tail (20%)
- Greater Omentum
- Along the Splenic Artery
- Gastrosplenic Ligament
- Splenocolic Ligament
- Retroperitoneum
- Greater Curve of the Stomach
- Gastrocolic Ligament
- Small Bowel Mesentery
Presentation
- Usually Asymptomatic
- Often Seen as ITP Relapse After Splenectomy
- Risk for Torsion
Evaluation
- First Step in Evaluation After Splenectomy: Peripheral Blood Smear
- *Howell-Jolly Bodies will Be Absent – Only Present in Complete Asplenia
- To Locate: Radiolabeled RBC Scan
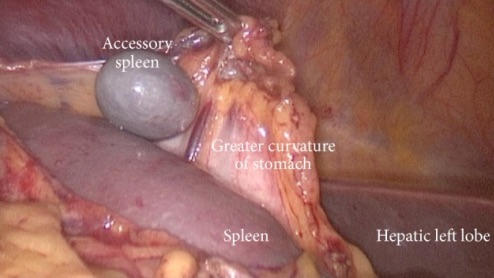
Accessory Spleen 1
Wandering Spleen
Basics
- Also Known as Displaced Spleen, Drifting Spleen or Splenic Ptosis
- Absence or Weakness of Ligaments & Peritoneal Attachments
- Can “Wander” Presenting Ectopically in Lower Abdomen/Pelvis
Presentation
- Presentation: Usually Asymptomatic
- Risk for Torsion
Diagnosis
- Dx: US or CT (Noncontrasted or Whorled Pedicle Indicates Torsion)
Treatment
- Incidental/Not Infarcted: Splenopexy to LUQ
- Infarcted: Splenectomy
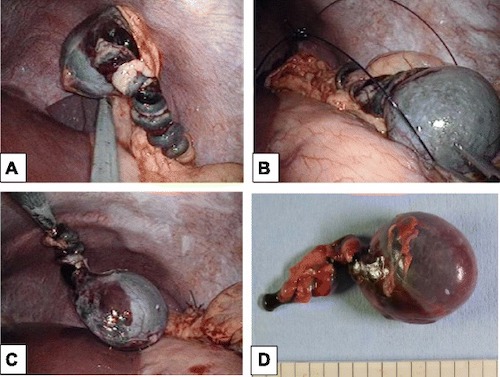
Splenic Torsion 2
References
- Gundogdu K, Altintoprak F, Uzunoğlu MY, Dikicier E, Zengin İ, Yağmurkaya O. Coexisting Situs Inversus Totalis and Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura. Case Rep Surg. 2016;2016:8605673. (License: CC BY-4.0)
- Ozeki M, Asakuma M, Go N, Ogura T, Inoue Y, Shimizu T, Hirokawa F, Yamamoto K, Hayashi M, Narumi Y, Higuchi K, Uchiyama K. Torsion of an accessory spleen: a rare case preoperatively diagnosed and cured by single-port surgery. Surg Case Rep. 2015 Dec;1(1):100. (License: CC BY-4.0)