Spleen: Splenic Cyst
Splenic Cyst
Basics
- Benign but May Secrete Tumor Markers (CA 19-9)
- Presentation: Usually Asymptomatic
- Always Preform Serologic Testing for Echinococcal Ab
Causes
- Trauma
- Parasitic – Hydatid (Echinococcal)
- Congenital
- Manifestation of Polycystic Kidney Disease
Treatment
- Parasitic: Albendazole & Splenectomy
- Non-Parasitic:
- ASx & Small: Conservative
- Sx or Large (> 4-5 cm): Intervention
- Superficial: Marsupialization or Unroofing
- Deep: Partial Splenectomy
- Other Options: Percutaneous Drainage or Total Splenectomy
- *Some Argue for Conservative Management of All Asymptomatic Cysts Regardless of Size
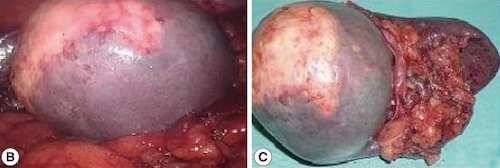
Hydatid Cyst 1
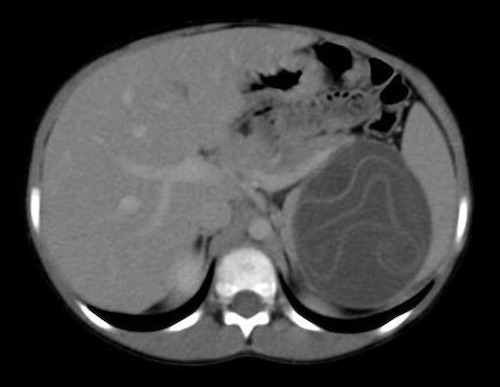
Hydatid Cyst on CT 2
References
- Vezakis A, Dellaportas D, Polymeneas G, Tasoulis MK, Chondrogiannis C, Melemeni A, Polydorou A, Fragulidis GP. Two cases of primary splenic hydatid cyst in Greece. Korean J Parasitol. 2012 Jun;50(2):147-50.(License: CC BY-NC-4.0)
- Limas C, Soultanidis C, Kirmanidis MA, Tsigalou C, Deftereos S. Management of abdomen hydatidosis after rupture of a hydatid splenic cyst: a case report. Cases J. 2009 Sep 2;2:8416. (License: CC BY-3.0)