Stomach: Adenocarcinoma
Gastric Polyps
Location
- Most Common Site: Antrum
- Fundus
- Cause: Long Term PPI Use
- No Malignant Potential
Types
- Non-Malignant
- Inflammatory Polyp
- Hamartomatous Polyp
- Premalignant
- Hyperplastic Polyp
- Most Common (70-90%)
- Seen in Chronic Atrophic Gastritis
- Low CA Risk
- Adenomatous Polyp
- Highest CA Risk
- Hyperplastic Polyp
Treatment
- < 2 cm or Not Sessile: EGD Polypectomy
- Can Observe Small Polyps (< 0.5 cm) in Setting of Chronic Inflammation
- > 2 cm & Sessile: Surgical Resection
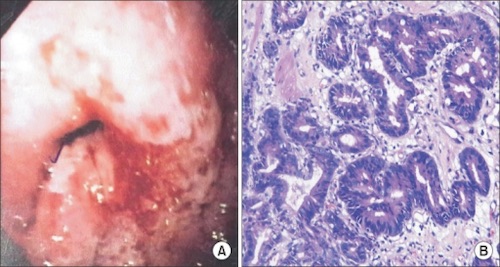
Gastric Adenocarcinoma 1
Gastric Adenocarcinoma
Risk Factors
- H pylori (Most Common)
- Smoked Meats, Pickled Foods & High Salt
- Tobacco
- Blood Type A
- Chronic Gastritis & Pernicious Anemia
- Epstein-Barr Virus
Genetic Syndromes
- Hereditary Diffuse Gastric Cancer
- Lynch Syndrome (Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colon Cancer)
- Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP)
- MUT Y Homolog (MUTYH)-Associated Polyposis (MAP)
- Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome
- Li-Fraumeni Syndrome
- *See Colorectal Cancer & Polyposis Syndromes
Presentation
- Sx: Pain, Nausea, Vomiting, Dyspepsia & Anorexia
- Complications:
- GI Bleed
- Gastric Outlet Obstruction – Cancer is the Most Common Cause
Lauren Classification
- Intestinal Type (Well-Differentiated)
- Histology: Cells Adhere to Each Other & Arrange with Tubule/Gland Formation
- Most Common in High-Risk Populations (Elderly Japanese Male)
- Strongly Associated with H. pylori
- Better Prognosis
- Diffuse Type (Poorly-Differentiated)
- Histology: Lack of Adhesion with Diffuse Lymphatic Invasion
- No Tubule/Gland Formation
- Most Common in Low-Risk Populations (Women & Young)
- More Common in Patients with an Inherited Syndrome
- Worse Prognosis
- Linitis Plastica
- An Aggressive Form with Extensive Submucosal Spread
- Histology: Lack of Adhesion with Diffuse Lymphatic Invasion
Special Metastases
- Sister Mary Joseph Nodule: Met to Umbilicus; Suggests Carcinomatosis
- Krukenberg Tumor: Met to Ovary
- Virchow’s Nodes: Met to Supraclavicular Nodes
- Irish Node: Met to Left Axilla
5-Year Survival
- Stage I: 88-93.6%
- Stage II: 68-81.8%
- Stage III: 17.9-54%
- Stage IV: 4-5%
- Median Survival 3-6 Months
- Up to 1/3 of Patients in the West Stage IV at Diagnosis
Diagnosis
- Dx: Upper Endoscopy
- Biopsy for Tissue Diagnosis
- Endoscopic US – Best Test for T Staging
- Consider CT or PET-CT to Evaluate Distant Metastases
- Diagnostic Laparoscopy Indications:
- Stage ≥ T1b Prior to Gastrectomy or Perioperative Chemoradiation
- Prior to Preoperative Chemotherapy
- Presence of GE-Junction Tumor or Tumor Involving the Entire Stomach
- Lymphadenopathy ≥ 1 cm
TNM Staging – AJCC 8
- TNM
| T | N | M | |
| 1 | 1a: Mucosa/Muscularis Mucosae
1b: Submucosa |
1-2 LN | Mets |
| 2 | Muscularis Propria | 3-6 LN | |
| 3 | Subserosa | 3a: 7-15 LN
3b: ≥ 16 LN |
|
| 4 | 4a: Serosa
4b: Adjacent Structures |
- “Early”: T1, Regardless of N
- Stage
| T | N | M | ||
| I | A | T1 | N0 | M0 |
| B | T1 | N1 | M0 | |
| T2 | N0 | M0 | ||
| II | A | T1 | N2 | M0 |
| T2 | N1 | M0 | ||
| T3 | N0 | M0 | ||
| B | T1 | N3a | M0 | |
| T2 | N2 | M0 | ||
| T4a | N0 | M0 | ||
| III | A | T2 | N3a | M0 |
| T3 | N2 | M0 | ||
| T4a | N1-2 | M0 | ||
| T4b | N0 | M0 | ||
| B | T1-2 | N3b | M0 | |
| T3-4a | N3a | M0 | ||
| T4b | N1 | M0 | ||
| C | T4b | N3a | M0 | |
| T3-4b | N3b | M0 | ||
| IV | Any T | Any N | M1 | |
Gastric Adenocarcinoma – Treatment
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection
- Requirements:
- ≤ 2.0 cm without Ulceration
- Well-Moderate Differentiation
- T1
- No Vascular or Lymphatic Invasion
- If Margins Positive: Surgical Resection
- May Consider Repeat Endoscopic Resection if Only the Lateral Margins are Positive
Surgical Resection
- Start with Diagnostic Laparoscopy to Evaluate Resectability
- Can Skip if T1a
- Unresectable:
- Periaortic or Mediastinal LN
- Distant Metastases
- Peritoneal Involvement
- Invasion of Vascular Structures (Not Splenic)
- Resection:
- Approach:
- Proximal Tumor: Total Gastrectomy
- Reconstruction: Roux-en-Y
- *Proximal Gastrectomy with Pyloroplasty Has High Risk of Alkaline Reflux Esophagitis
- Distal Tumor: Distal Gastrectomy
- Reconstruction: Roux-en-Y or Billroth II (Avoids Outlet Obstruction if Recurs)
- Proximal Tumor: Total Gastrectomy
- Margins: 4-6 cm
- Residual Disease Mn
- R0 – No Residual Disease
- R1 – Microscopic Residual Disease
- R2 – Gross Residual Disease
- Approach:
- Lymphadenectomy:
- Extent: Mn
- D1 – Perigastric Nodes (Stations 1-6)
- D2 – Celiac Axis (Stations 1-11)
- Possible Include 12a
- Generally Recommended (Debated)
- D3 – Celiac & Para-Aortic (Stations 1-16)
- No Survival Benefit
- LN Requirements: ≥ 15 LN for Accurate Staging
- Extent: Mn
Chemotherapy
- Best Regimen Not Established
- Indications:
- Neoadjuvant: ≥ T2 or N1
- Adjuvant: ≥ T3 or N1
Palliative Treatment
- Pain: Multimodal Analgesia & Consider XRT
- Obstruction:
- Proximal: Stent
- Distal: Venting Gastrostomy, Gastrojejunostomy or Gastrectomy
- Bleeding: Endoscopy, Angioembolization or XRT
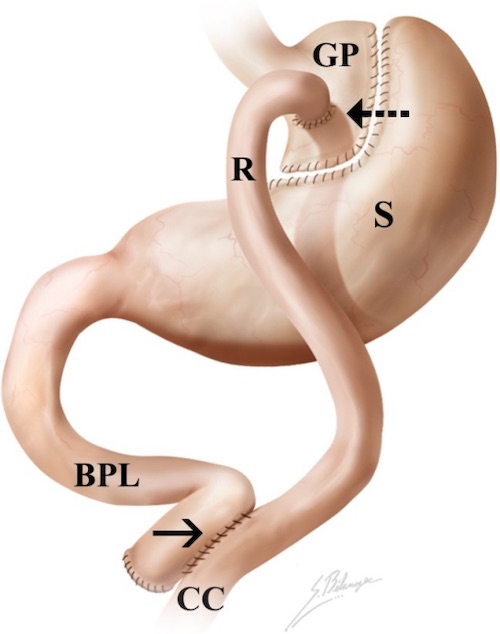
Roux-en-Y 2
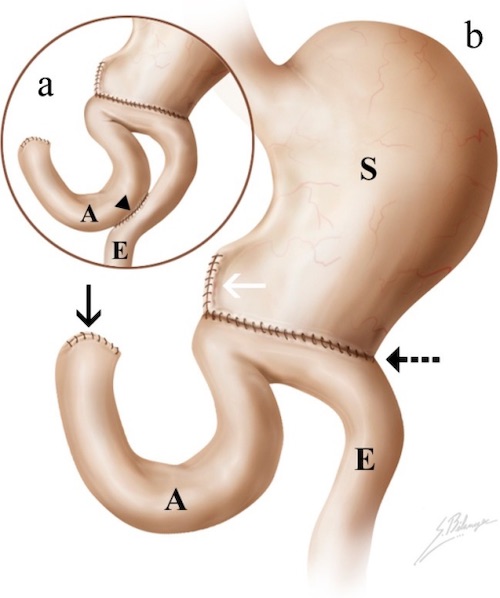
Billroth 2 2
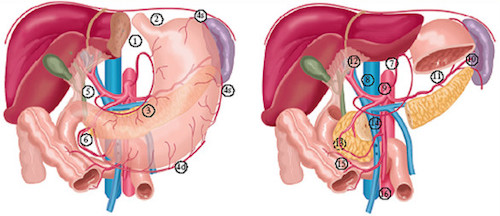
Lymph Node Stations 3
Mnemonics
Extent of Dissection
- R-Residual
- D-noDes
References
- Roshni S, Anoop T, Preethi T, Shubanshu G, Lijeesh A. Gastric adenocarcinoma with prostatic metastasis. J Gastric Cancer. 2014 Jun;14(2):135-7. (License: CC BY-NC-3.0)
- Terrone DG, Lepanto L, Billiard JS, Olivié D, Murphy-Lavallée J, Vandenbroucke F, Tang A. A primer to common major gastrointestinal post-surgical anatomy on CT-a pictorial review. Insights Imaging. 2011 Dec;2(6):631-638. (License: CC BY-2.0)
- Dikken JL, van Sandick JW, Maurits Swellengrebel HA, Lind PA, Putter H, Jansen EP, Boot H, van Grieken NC, van de Velde CJ, Verheij M, Cats A. Neo-adjuvant chemotherapy followed by surgery and chemotherapy or by surgery and chemoradiotherapy for patients with resectable gastric cancer (CRITICS). BMC Cancer. 2011 Aug 2;11:329. (License: CC BY-2.0)