Surgical Technology: Drains
Drains
Jackson-Pratt (JP) Drain
- Silicone Tube with Perforations
- *Specifically Refers to the Tube, Not the Bulb
- Fluid Actively Drained Through the Perforation to a Negative Pressure Device
- Plastic Bulb Drain Most Common
Blake Drain
- Round Silicone Tube with Channels
- Fluid Actively Drained Through Channels to a Negative Pressure Device
- Plastic Bulb Drain Most Common
Penrose Drain
- Soft Flexible Rubber Tube
- Allows Passive Drainage of Fluid
Other Types of Drains Discussed Elsewhere
- Nasogastric/Orogastric Tube
- Foley Catheter
- T-Tube
- Chest Tube
- Percutaneous/Pigtail Drains

Jackson-Pratt (JP) Drain

Blake Drain

Penrose Drain
Active Suction Devices
Bulb Suction (Grenade)
- Plastic Bulb – Grenade-Shaped
- Bulb Should Be Compressed with the Side-In (Much Better Suction)
- Side-In: 87.4 cmH2O
- Bottom-Up: 17.7 cmH2O
- Negative Pressure with Filling:
- 25 cc: 72.6 cmH2O
- 50 cc: 41.3 cmH2O
- 75 cc: 37.0 cmH2O
- 100 cc: 35.6 cmH2O
Hemovac
- Flat Spring-Loaded Container
Davol Drain
- Suction Device with a Rubber Bulb on Top to Provide Suction
- Least Commonly Used in Modern Practice
Other Suction Devices
- Wall Suction
- Chest Tube Atrium – Collects Fluid but Suction is Provided by Wall Suction
- Wound Vacuum System
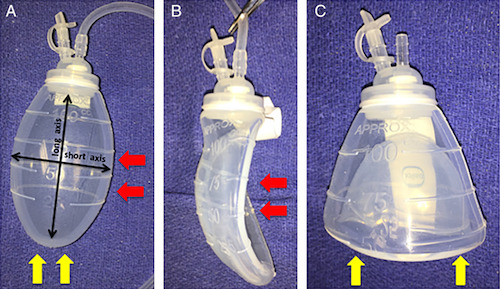
Bulb Suction
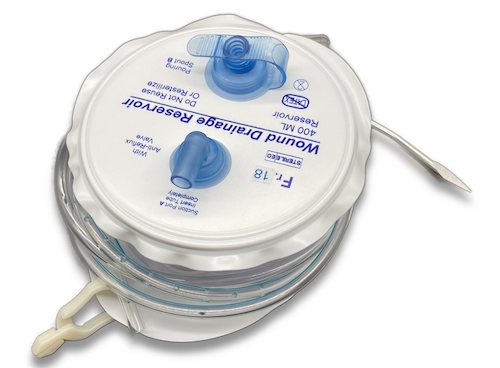
Hemovac
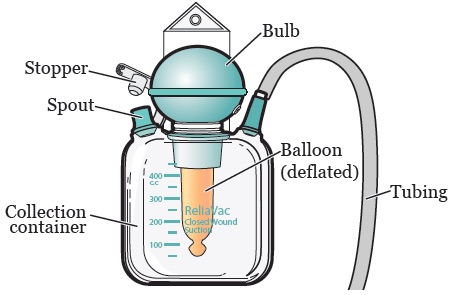
Davol Drain