Pediatric Surgery: Thyroglossal Duct Cyst
Thyroglossal Duct Cyst
Basics
- From Abnormal Descent of the Thyroid
- Most Common Congenital Neck Cyst
- Risk for Recurrent Infection (Primary Reason for Excision) & Malignancy
- Ectopic Thyroid Tissue May Present Similarly
Presentation
- Classic Presentation: Midline Mass Between Hyoid & Thyroid
- Moves Up & Down with Swallowing
- Can Communicate with Oral Cavity – May Cause Foul Taste or Infection
- There is Variation
- May Actually Lie Somewhat Lateral to Midline
- May Have a Draining Sinus – More Commonly Associated with Branchial Cleft Cysts
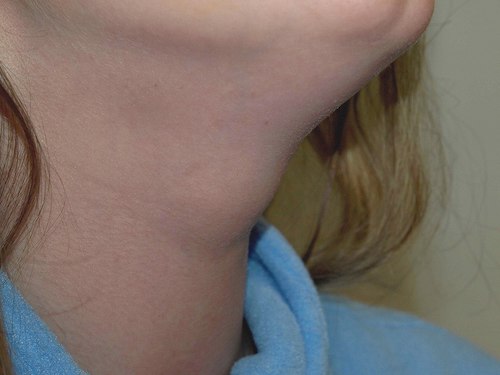
Thyroglossal Duct Cyst 1
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis: US (Some Prefer CT)
- Must Confirm Presence of Normal Thyroid Tissue – May Consider TSH, Thyroid Scan or FNA
Treatment
- Uncomplicated: Sistrunk Procedure
- Infected: Antibiotics
- May Require Aspiration or Incision & Drainage
- Sistrunk Procedure Once Infection Controlled
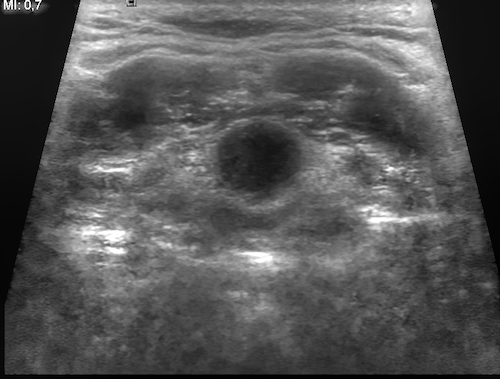
Thyroglossal Duct Cyst on US 2
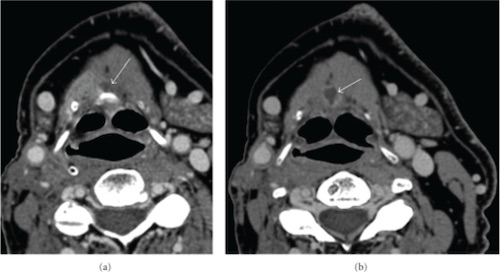
Thyroglossal Duct Cyst on CT 3
Sistrunk Procedure
- Resect Cyst, Tract & Mid-Hyoid
- Positioning: Supine with Neck Extended
- Procedure:
- Transverse Cervical Incision
- Mobilize Cyst Along Its Tract
- Divide Mylohyoid & Hyoglossus Muscle Attachments to the Superior Hyoid
- Divide Hyoid 1 cm from Midline Bilaterally
- Suture Ligate the Proximal Tract
- Remove Specimen En-Bloc
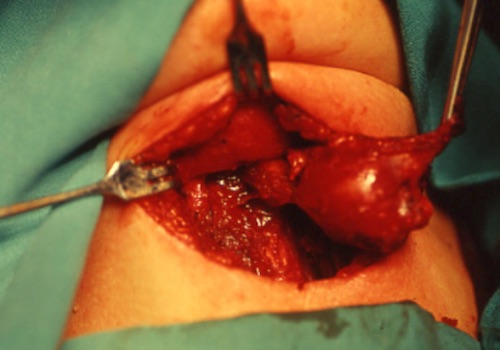
Sistrunk Procedure 4
References
- Peter KD. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-3.0)
- Dilmen N. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-SA-3.0)
- Debnam JM. Imaging of the Head and Neck following Radiation Treatment. Patholog Res Int. 2011;2011:607820. (License: CC BY-3.0)
- Gebbia V, Di Gregorio C, Attard M. Thyroglossal duct cyst carcinoma with concurrent thyroid carcinoma: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2008 Apr 29;2:132. (License: CC BY-2.0)