Pancreas: Total Pancreatectomy
Total Pancreatectomy
Basics
- Resection of the Entire Pancreas
- Indications:
- Diffuse Chronic Pancreatitis with Small-Normal Ducts
- Malignant Lesions Unable to Undergo Less Extensive Resection
- Trauma
Technique
- Resection:
- Entire Pancreas
- Splenectomy – May Consider Preserving if No Suspicion of Malignancy
- Duodenum – Still Requires Roux-en-Y for Hepaticojejunostomy
- Procedure:
- Mobilize Duodenum, Pancreas & Spleen
- Ligate GDA
- Cholecystectomy & Transect CBD
- Proximal Transection – Prepyloric or Postpyloric
- Distal Transection – Distal to Ligament of Treitz
- Ligate Splenic Artery (First) Then Splenic Vein
- Preserve Left Gastric Artery (Only Remaining Supply to the Stomach)
- Dissect Pancreas Off Portal Vein & SMA
- Reconstruction:
- Hepaticojejunostomy (HJ)
- At Proximal End
- Gastrojejunostomy (GJ)
- ≥ 20-40 cm Distally to Prevent Food Reflux into Biliary/Pancreatic Anastomoses
- Hepaticojejunostomy (HJ)
Islet Cell Autotransplantation
- Contraindications: Diabetic or Pancreatic Malignancy
- Fewer Diabetic Complications & Improved Quality of Life
- Procedure: Islet Cells Isolated in Lab, Infused into Portal Vein & Lodge in Liver
- No Immunosuppression Required
Complications
- Higher Mortality Than Pancreaticoduodenectomy
- Endocrine Insufficiency – Diabetes
- Insulin Independence Possible (29-38%) After Islet Cell Autotransplantation
- Exocrine Insufficiency – Malnutrition
- Requires Chronic Enzyme Supplementation
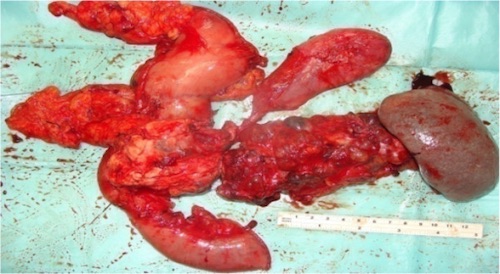
Total Pancreatectomy 1
References
- Al-Jiffry BO, Rayzah F, Khayat SH. A disseminated variant of pancreatic serous cystadenoma causing obstructive jaundice, a very rare entity: a case report and review of the literature. BMC Res Notes. 2014 Oct 22;7:749. (License: CC BY-2.0)