Trauma: Trauma in Pregnancy
Pregnancy
General Considerations
- Always Mother Before Baby
- Most Common Cause of Death: Intimate Partner Violence
- Blunt Trauma
- Fetal Injury After Blunt Trauma is Rare (< 1%)
- Most Common Cause of Fetal Death in Blunt Trauma: Maternal Death
- Penetrating Trauma
- High Fetal Death Rate – GSW 71% & Stabs 42%
- Gravid Uterus Provides Protection for Mother with Decreased Mortality
Fetal Maturity
- Fundal Height (Umbilicus = 20 cm = 20 Weeks)
- Signs of Maturity:
- Lecithin:Sphingomyelin (LS) Ratio > 2:1
- Phosphatidylcholine in Amniotic Fluid
Radiology
- Do Not Delay or Withhold if Indicated
- No Increased Risk of Fetal Defects/Loss if < 5 Rad
- Fetus Exposed to About 30% of Maternal Radiation Dose
- Approximate Fetal Dose:
- CXR: < 0.001 Rad
- Abdominal XR: 0.1 Rad
- Head CT: < 0.05 Rad
- Chest CT: < 0.1 Rad
- Abdominal CT: 2.6 Rad
- Timing:
- Most Vulnerable During Organogenesis (Weeks 2-8)
- Generally Safe Past 20 Weeks
- FAST US
- Any Amount of Free Fluid is Considered Positive
- Physiologic Free Fluid is Small (7-21 cc) & Not Large Enough to Be Seen on FAST
Managements
- Cardiotrophic Fetal Monitoring for ≥ 6 Hours if Over 20 Weeks Gestation
- Give Supplemental O2 in All Pregnant Patients Regardless of SaO2
- Physiologic Respiratory Alkalosis with Concern for Hypoxia
- Give Rh Immunoglobulin to All Rh-Negative Patients
- Give within 72 Hours of Injury
- Should Also Be Given within 72 Hours of Delivery
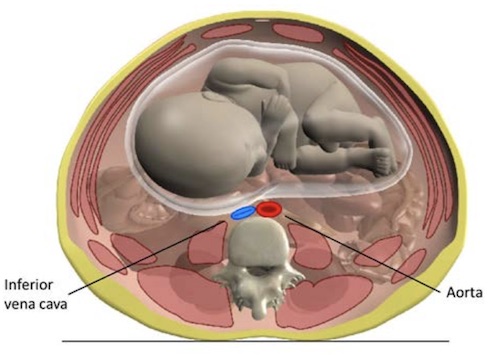
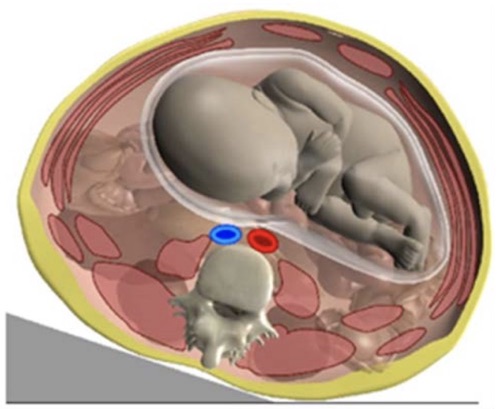
- Aortocaval Compression Syndrome (Supine Hypotensive Syndrome)
- Gravid Uterus Compresses Aorta & IVC When Laying Supine
- Presentation: Maternal Hypotension
- Tx: Roll to Left Side (Improves Venous Return)
- If Unable to Adequately Expose Injury Due to Enlarged Uterus: Cesarean Section
Aortocaval Compression Syndrome 1
Left Lateral Tilt – Relieves Compression Off IVC 1
Specific Trauma
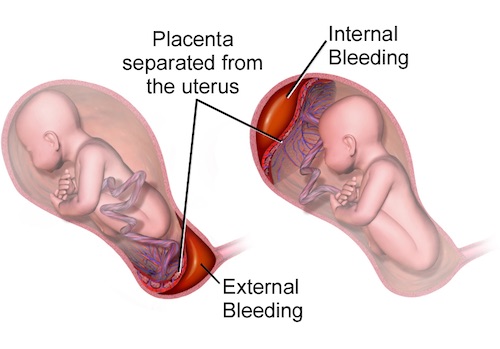
- Placental Abruption
- Separation of Placenta from Uterus
- Causes:
- Uteroplacental Ischemia from Shock – Most Common
- Mechanical Force
- Presentation: Abdominal Pain, Vaginal Bleeding, Shock or DIC
- Kleihauer-Betke Test: Detects Occult Placental Hemorrhage
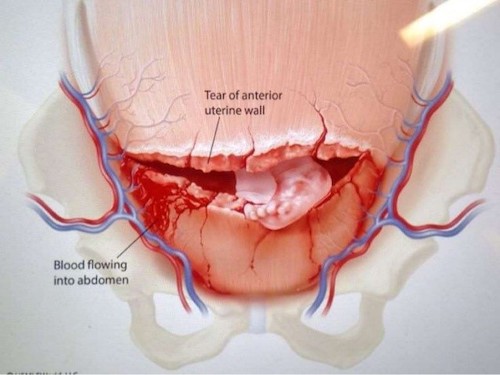
- Uterine Rupture
- Most Common Site: Posterior Fundus
- Most Common Risk Factor: Previous C-Section
Placental Abruption 2
Uterine Rupture 3
Perimortem Cesarean Section
- Definition: C-Section Delivery After Maternal Death
- Baby Must Be > 24 Weeks
- Arrest Timing:
- Best if < 4 Minutes of Arrest
- Contraindicated > 20 Minutes
References
- Queensland Clinical Guidelines. Trauma in pregnancy clinical guideline education presentation E19.31-1-V2-R24. Queensland Health. 2019. (License: CC BY-NC-ND-4.0)
- Blaus B. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-3.0)
- Khcnrc01. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-SA-4.0)