Trauma: Tube Thoracostomy (Chest Tube)
Tube Thoracostomy (Chest Tube)
Tube Selection
- PTX: 8-14 French
- Tension PTX: 24-28 French; After Needle Decompression
- HTX: 24-28 French
- *Older Teaching to Use the Largest Possible (36-40 French) Falling Out of Favor, In General Clotted Blood Will Not Drain No Matter How Big
- Use Smaller Sizes in Peds
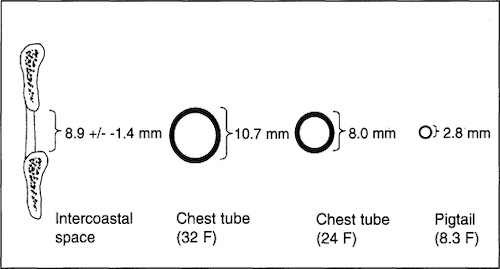
Chest Tube Sizes Compared to Average Intercostal Space (Mid-Axillary 5th Space) 1
Standard Technique
- Prepare:
- Supine, Arm Extended & Skin Prep
- Inject Local Anesthetic All the Way Down to the Pleura
- Incision:
- Target 4th/5th Intercostal Space at Anterior Axillary or Mid-Axillary Line
- For PTX May Consider 2nd Intercostal Space at the Midclavicular Line
- Make 2-3 cm Incision Over the Inferior Rib
- Using Curved Clamp Bluntly Dissect & Tunnel Immediately Above the Rib
- Never Go Below the Rib (Risk Damage to Neurovascular Bundle)
- Penetrate Pleura & Spread the Penetration Site
- Target 4th/5th Intercostal Space at Anterior Axillary or Mid-Axillary Line
- Insertion:
- Insert Finger to Confirm Position & Bluntly Dissect Any Surrounding Adhesions
- Insert the Chest Tube Using a Clamp & Direct into Position
- PTX: Anterior/Superior
- HTX: Posterior
- Suture Anchor the Tube to the Skin
- CXR to Confirm Placement & Lung Expansion
Other Techniques
- Seldinger Technique
- US-Guided
- IR-Guided
Thoracic Irrigation
- May Consider Irrigation with 1 L Warmed Saline Immediately Upon Placement
- For Hemothorax Only (Not Pneumothorax)
- Some Data Suggests Decreased Rates of Retained Hemothorax & Secondary Interventions
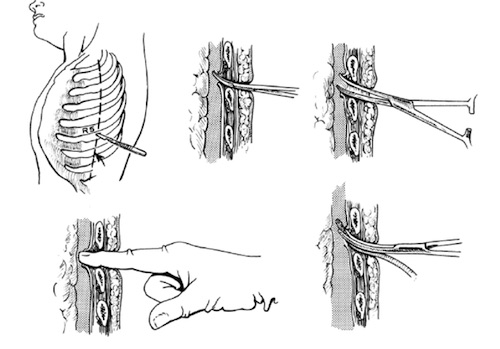
Chest Tube Placement 2
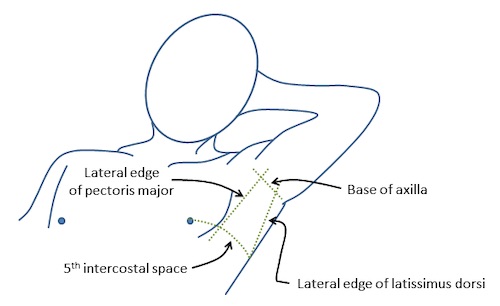
Triangle of Safety 3
Drainage System
- Classic “Three Bottle” System
- Bottle #1 (Collecting Bottle): Collects Fluid from the Patient
- Bottle #2 (Water Seal): Allows Air to Escape but Prevents External Air Entry Back into the Chest
- “Bubbling” Indicates an Air Leak
- Bottle #3 (Suction Control): Adjustable Manometer Set to Specific Depths to Set a Controlled Suction Pressure
- Most Often Set to 20 cm H2O
- “Four Bottle” System
- Adds an Additional Venting Bottle Connected to the Collecting Bottle
- Fourth Bottle is Vented to the Air & Not Connected to Suction
- Acts as an Additional Water Seal to Prevent Pneumothorax in the Event of Unexpected Suction Failure
- Modern Collecting Systems (Atrium, Pleur-Evac)
- Entire System is Combined in a Single Piece of Equipment
- Collecting Chamber Acts as Bottle #1
- Water Seal Acts as Bottle #2
- Suction Control Can be “Wet Suction” or “Dry Suction”
- Wet Suction: Acts as a Traditional Bottle #3 Using Fluid
- Dry Suction: Controls Suction Using a Pressure Control Valve
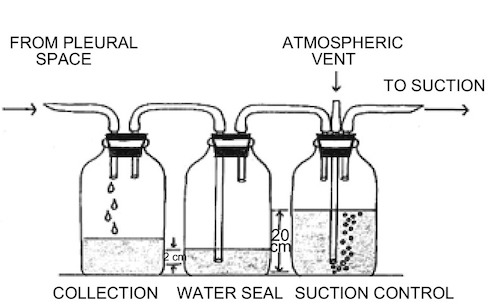
Classic “Three Bottle” System 4
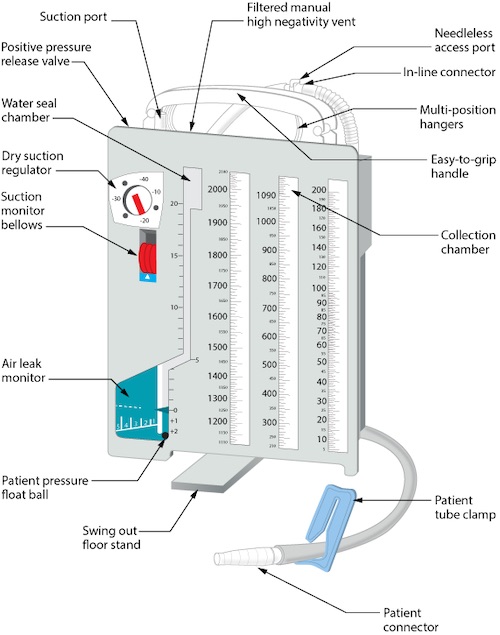
Modern Collecting System 5
Removal
- Use an Occlusive Dressing to Prevent Inspiration of Air Back into the Pleural Cavity
- Ex: Xeroform or Vaseline-Soaked Gauze
- Remove Chest Tube on Expiration, After A Complete Full Inspiration
- Increases Intrathoracic Pressure to Decrease the Risk of Recurrent Pneumothorax Upon Pull
- *Exact Timing is Debated and Some Prefer Pulling with an Inspiratory Hold
- Repeat Chest Radiograph After Chest Tube Removal (Post-Pull CXR)
- Often Done at 4 Hours or 24 Hours
- *No Evidence that Post-Pull CXR is Necessary – Some Prefer Repeat Imaging Based Solely on Symptoms
References
- Gammie JS, Banks MC, Fuhrman CR, Pham SM, Griffith BP, Keenan RJ, Luketich JD. The pigtail catheter for pleural drainage: a less invasive alternative to tube thoracostomy. JSLS. 1999 Jan-Mar;3(1):57-61. (License: CC BY-NC-ND-3.0)
- Mohammed HM. Chest tube care in critically ill patient: A comprehensive review. Egyptian Journal of Chest Diseases and Tuberculosis. 2015. 64(4):849-855. (License: CC BY-NC-ND-4.0)
- Hill J. Taming the SRU. (License: CC BY-NC-SA-3.0)
- Shi H, Mei L, Che G. [The current concepts of closed chest drainage in lobectomy of lung cancer]. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2010 Nov;13(11):999-1003. (License: CC BY-4.0)
- British Columbia Institute of Technology (BCIT). Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-SA-4.0)