Vascular: Anatomy & Physiology
Vessel Types
Arteries
- Pumps Blood Away from the Heart to Tissues
- Oxygenation:
- Pulmonary Arteries: Carry Deoxygenated Blood from Heart to Lungs
- Systemic Arteries: Carry Oxygenated Blood from Heart to Body Tissues
- More Muscular than Veins or Lymphatics
- Vasa Vasorum – Network of Small Blood Vessels that Supply the Walls of Larger Blood Vessels
Veins
- Drains Blood from Tissues Back to the Heart
- Types:
- Deep Veins – Deep in the Body, Typically Correlate with Arterial Supply
- Superficial Veins – Superficial, Do Not Correlate with Arterial Supply
- Perforator Veins – Connect Superficial to Deep Veins
- Oxygenation:
- Pulmonary Veins: Carry Oxygenated Blood from Lungs to Heart
- Systemic Veins: Carry Deoxygenated Blood from Body Tissues to Heart
- Less Muscular than Arteries
- Veins Have Valves
- No Valves in Portal Vein, SVC, IVC, or Common Iliacs
Lymphatics
- Thin Walled Vessels that Drain Lymph Through the Lymphatic System
- Components:
- Lymphatic Capillaries: Absorbs Interstitial Fluid & Drains into Afferent Vessels
- Afferent Vessels: Drain Lymph from Tissues to Lymph Nodes
- Efferent Vessels: Drain Lymph from Lymph Nodes to Other Lymph Nodes or Veins
- Very Thin Muscular Layer
- Deep Lymphatics Have Valves
- No Lymphatics in Bone, Muscle, Tendon, Cartilage, Brain or Cornea
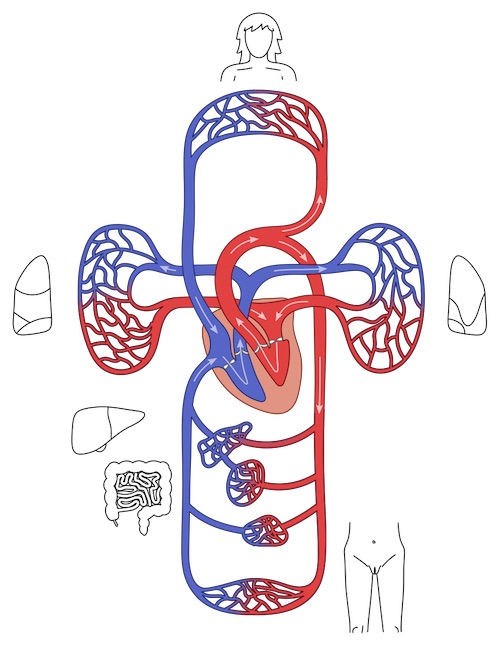
Vascular Circulation (Pulmonary & Systemic) 1
Vessel Structure
Tunica Adventitia
- External Layer
- Composed of Collagen & Elastic Fibers
Tunica Media
- Middle Layer
- Composed of Smooth Muscle, Collagen & Elastic Fibers
- Arteries are Muscular
- Veins & Lymphatics are Much Less Muscular
Tunica Intima
- Internal Layer in Contact with Blood
- Composed of Endothelium
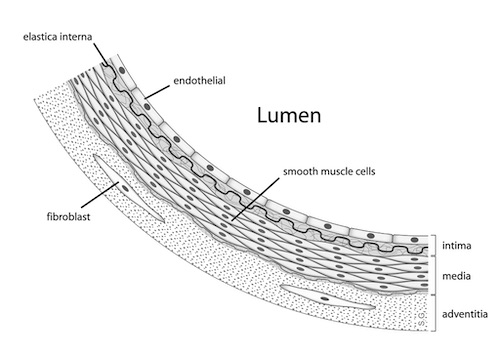
Arterial Wall Layers 2
References
- Kebert T, Umimeto.org. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-SA-4.0)
- Ghesquiere SA. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-SA-2.5)