Skin & Soft Tissue: Xanthoma
Xanthoma
Basics
- Localized Lipid Deposits in Tissue
- Lipids Undergo Phagocytosis by Tissue Macrophages (“Foam Cells”)
- Often Associated with Hyperlipidemia or Hypercholesterolemia
Types/Presentation
- Plane (Planar) – Soft Yellow Plaques
- Xanthelasma – Plane Xanthoma Over Eyelids
- Most Common Form of Xanthoma Overall
- Xanthelasma – Plane Xanthoma Over Eyelids
- Eruptive – Acute Inflammatory Red-Yellow Papules
- Appear Rapidly in Groups of Small (2-5 mm) Lesions
- Resolve Over 2-3 Weeks
- Tuberous – Firm, Painless, Red-Yellow Nodules
- Develop Over Areas Under Pressure (Knees, Elbows or Heels)
- May Coalesce to Form Large Multilobulated Masses
- Tendinous – Slowly Enlarging Subcutaneous Nodules Over Tendons with Normal Overlying Skin
- Most Common Over the Achilles Tendon & Knuckles
Diagnosis
- Clinical (Based on History of Dyslipidemia and Physical Exam)
- May Require Skin Biopsy
Treatment
- Treat Underlying Pathology
- May Require Surgical Excision if Symptomatic
- Other Options:
- Topical Trichloroacetic Acid (Chemical Peel)
- Electrodessication
- Cryotherapy

Xanthoma 1
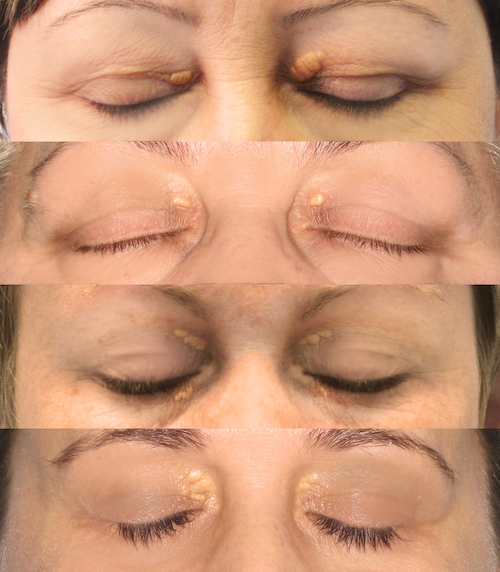
Xanthelasma 2
References
- Min.neel. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-SA-3.0)
- Tymofii O. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-SA-3.0)