Trauma: Trauma in Pediatrics
Pediatrics
Normal Vital Signs
Modified GCS in Peds < Age 5
| Score | Motor (6) | Verbal (5) | Eyes (4) |
| 1 | None | None | None |
| 2 | Decerebrate | Moans to Pain* | Open to Pain |
| 3 | Decorticate | Cries to Pain* | Open to Speech |
| 4 | Withdraws to Pain | Irritable Cries* | Spontaneous |
| 5 | Withdraws to Touch* | Coos & Babbles* | |
| 6 | Spontaneous/Purposeful* |
- * = Different
General Considerations
- Unintentional Injury is the #1 Cause of Death in Peds
- Relative Neuron Plasticity
- Focal Injury Produces Less Severe Deficit
- Higher Risk for Diffuse Injury
- Rib Fractures Uncommon in Peds
Resuscitation
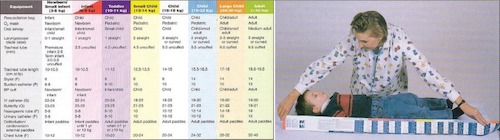
- Broselow Tape
- Tape Laid at the Side of the Bed to Estimate Height & Weight
- Used to Estimate Equipment Sizes & Drug Dosing
- For Children ≤ 12 Years
- Obesity will Confound
- Shock
- Best Indicator of Shock in Peds: Tachycardia
- Hypotension is a Late Finding, Will Compensate Well and Decompensate Rapidly
- BP Poor Indicator of Hemodynamic Stability
- High Risk of Hypothermia (High Body Surface Area)
- Fluids
- Bolus: 20 cc/kg
- Maintenance: 4-2-1 Rule
- Goal UOP: 2-4 cc/kg/hr
- Intubation
Broselow Tape 1
Imaging in Pediatrics
Malignancy Risk
- Risk is Inversely Proportional to Age
- Risk of Developing a Fatal Malignancy:
- After Abdominal CT: 0.18%
- After Head CT: 0.07%
- 3x Increased Risk of Leukemia & Brain Tumors
Head CT – Indications (PECARN Guidelines)
- Younger than 2 Years Old:
- High Risk of TBI (4.4%): CT Head Recommended
- Altered Mental Status
- GCS < 15
- Palpable Skull Fracture
- Intermediate Risk of TBI (0.9%): CT Head vs Observation
- Loss of Consciousness > 5 Seconds
- Non-Frontal Scalp Hematoma
- Not Acting Normally
- Severe Mechanism
- Low Risk of TBI (< 0.02%)
- High Risk of TBI (4.4%): CT Head Recommended
- At Least 2 Years Old:
- High Risk of TBI (4.3%): CT Head Recommended
- Altered Mental Status
- GCS < 15
- Signs of Basilar Skull Fracture
- Intermediate Risk of TBI (0.9%): CT Head vs Observation
- Any Loss of Consciousness
- History of Vomiting
- Severe Headache
- Severe Mechanism
- Low Risk of TBI (< 0.05%)
- High Risk of TBI (4.3%): CT Head Recommended
- Severe Mechanism:
- Fall > 3 Feet (< 2 Years) or > 5 Feet (≥ 2 Years)
- MVC with Ejection, Rollover or Fatality
- Bike/Ped vs Vehicle without Helmet
- Struck by a High-Impact Object
Neck CT Indications
- Follows NEXUS Criteria Similar to Adults
Chest CT Indications
- If Otherwise Indicated for Penetrating Thoracic Trauma
- Abnormal CXR (Widened Mediastinum, etc.)
Abdominal CT Indications
- If Otherwise Indicated for Penetrating Abdominal Trauma
- Symptoms:
- Abdominal Pain
- Vomiting
- Physical Exam:
- GCS < 14
- Abdominal Tenderness
- Evidence of Abdominal Wall Trauma – Seat Belt Sign, Handlebar Sign or Ecchymosis
- Decreased Breath Sounds
- Positive FAST Exam
- Labs:
- AST > 200 U/L
- ALT > 100-125 U/L
- Elevated Lipase/Amylase
- Hematuria with 0.5 RBC/hpf on Urinalysis
References
- Greene N, Bhananker S, Ramaiah R. Vascular access, fluid resuscitation, and blood transfusion in pediatric trauma. Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci. 2012 Sep;2(3):135-42. (License: CC BY-NC-SA-3.0)